Navigation & Management
Sections:
Resources:
Overview:
- In this demonstration, I will briefly go over the Control Center configuration sections to get a better understanding of a Sophos Firewall's configuration parameters
- Navigating the control center on a Sophos Firewall is important for several reasons, as it serves as the central hub for managing and monitoring network security
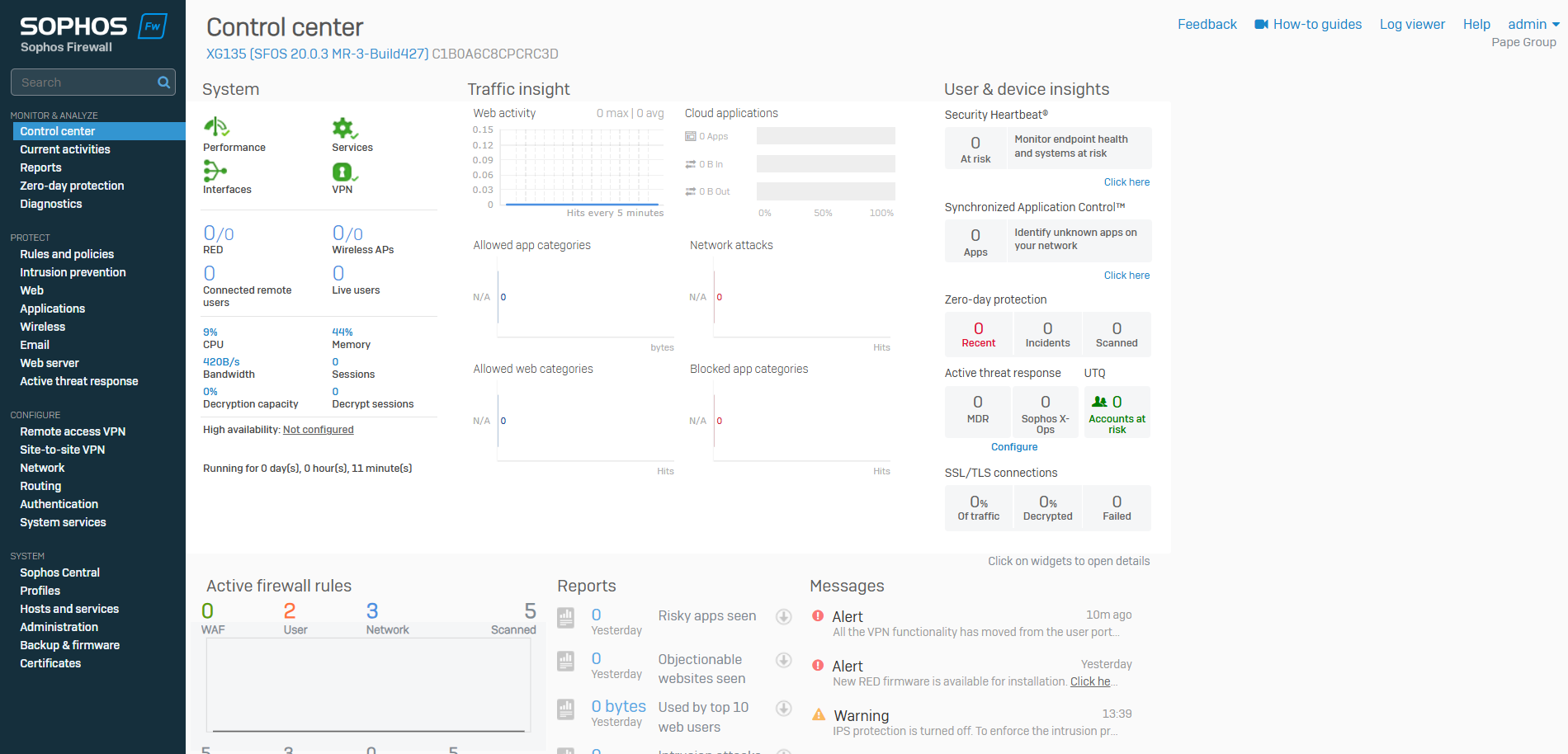
Control Center Overview
Overview
- The Sophos Firewall Control Center is the central management interface that provides an overview of the firewall's status, system health, and key security metrics
- It is the dashboard where you can monitor, configure, and manage various features of your Sophos Firewall
- The Control Center simplifies the management of your Firewall by consolidating key information into a single, easy to navigate interface
System Section
Overview
- The System section in the Sophos Firewall control center is used for configuring a range of system parameters, including controlling how the firewall categorizes applications, and managing system settings

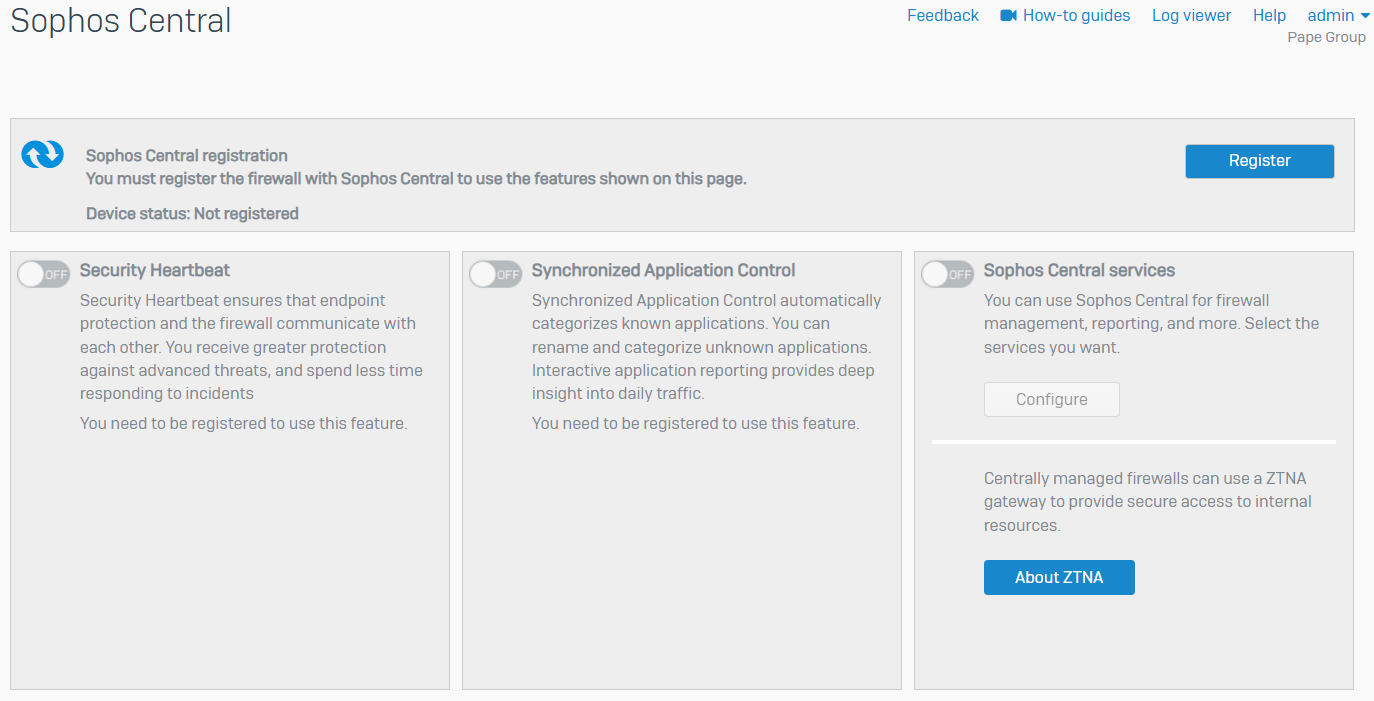
Sophos Central
Overview
- Reference - Registering with Sophos Central
- You can set up a new Sophos Firewall with Sophos Central and manage it centrally
- You can register existing Sophos Firewall devices with Sophos Central and manage the devices centrally
- You can also use Security Heartbeat to enable endpoint devices on your network to share health information
- Synchronized Application Control lets you detect and manage applications in your network
Sophos Central
- Reference - Sophos Central
- You can set up a new Sophos Firewall and claim it in Sophos Central, then activate and synchronize your subscriptions
Profiles
Overview
- Profiles allow you to control users' internet access and administrators' access to the firewall
- You can define schedules, access time, and quotas for surfing and data transfer
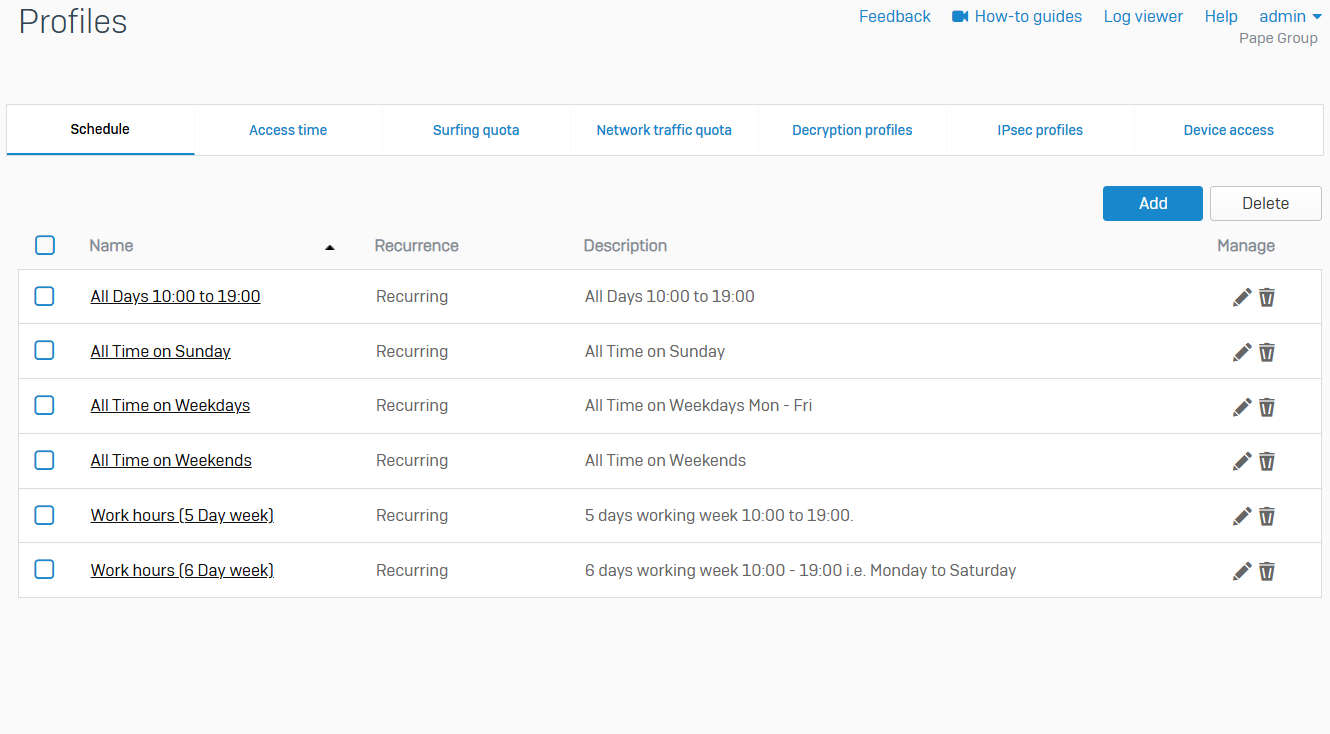
Schedule
- Reference - Schedule
- Schedules specify the duration for which rules and policies are in effect
- You can create recurring and one time schedules, or use the default schedules
- Schedules can be applied to the following
- Firewall Rules
- Web Policies
- Application Policies
- Traffic Shaping Policies
- Access Time Policies
- Rogue Access Point Scan
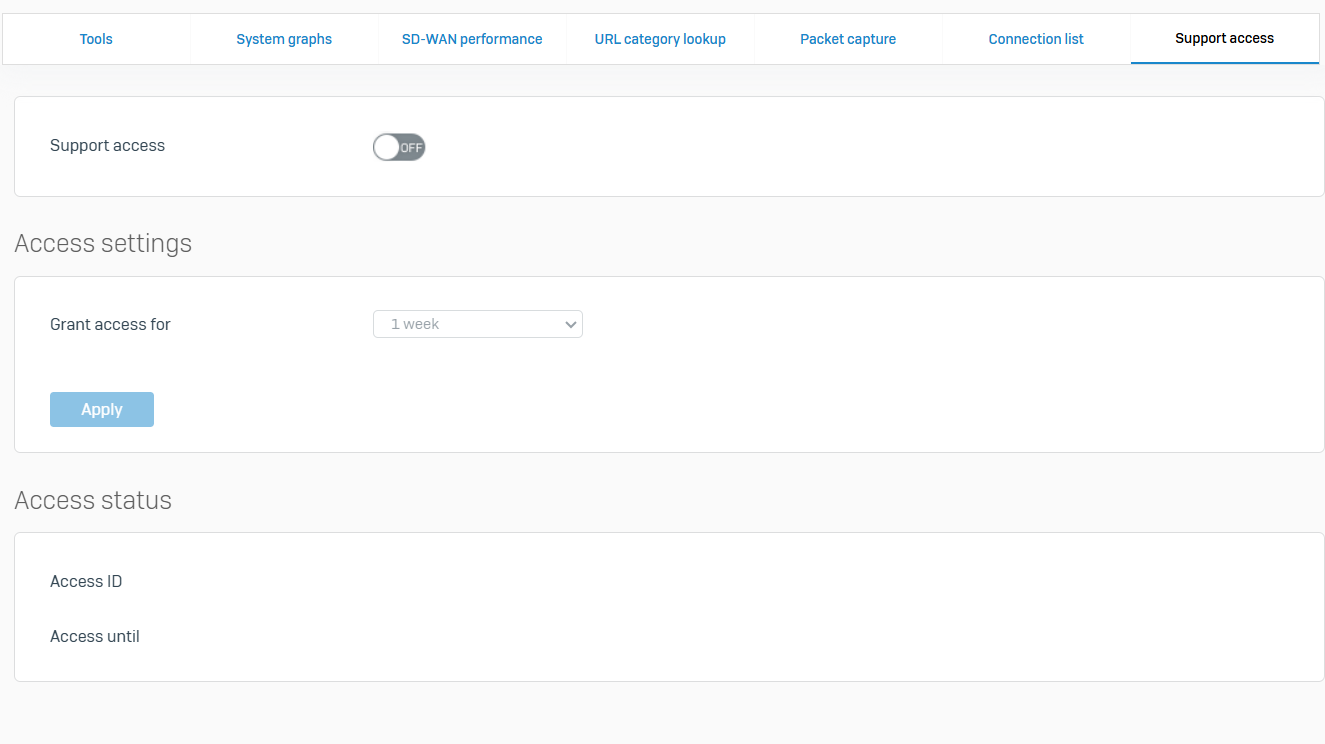
Access Time
- Reference - Access Time
- You can control internet access time for users, groups, and guest users
- You can allow or deny internet access based on a scheduled period
- You can create your own access time policies or use the default policies
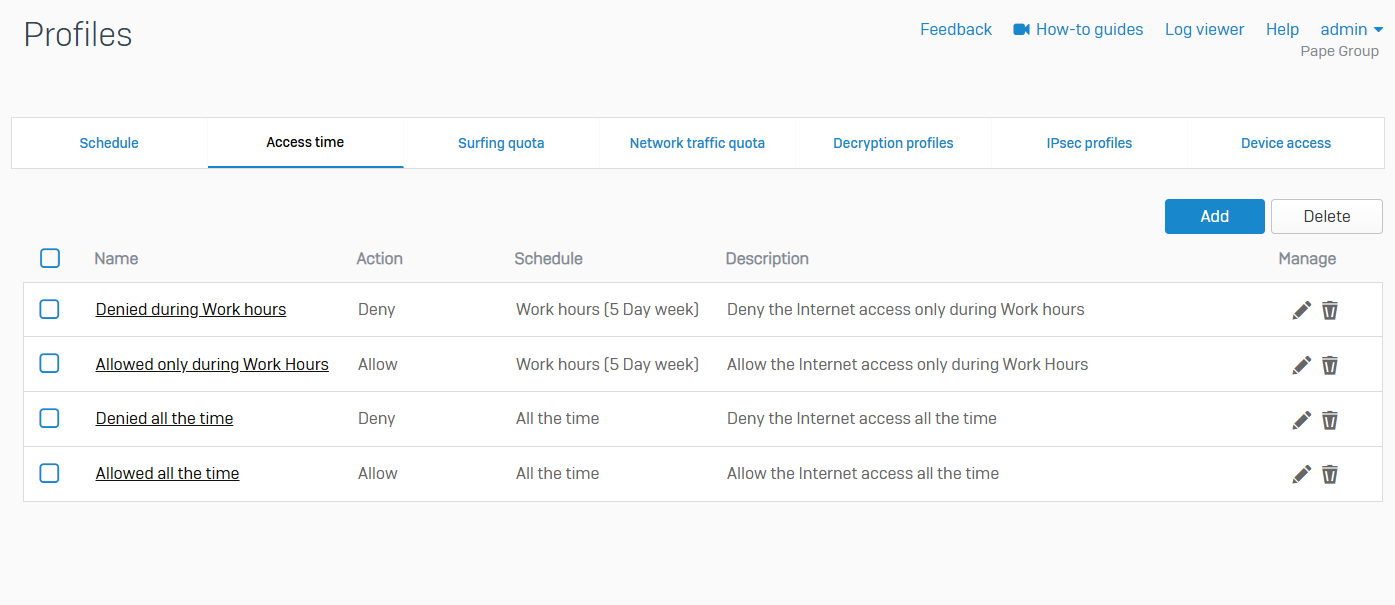
Surfing Quotas
- Reference - Surfing Quotas
- Surfing Quotas allow you to allocate internet access time to your users
- Quotas allow access on a repeat or one time basis
- You can add quotas and specify the access time allowed or use the default quotas
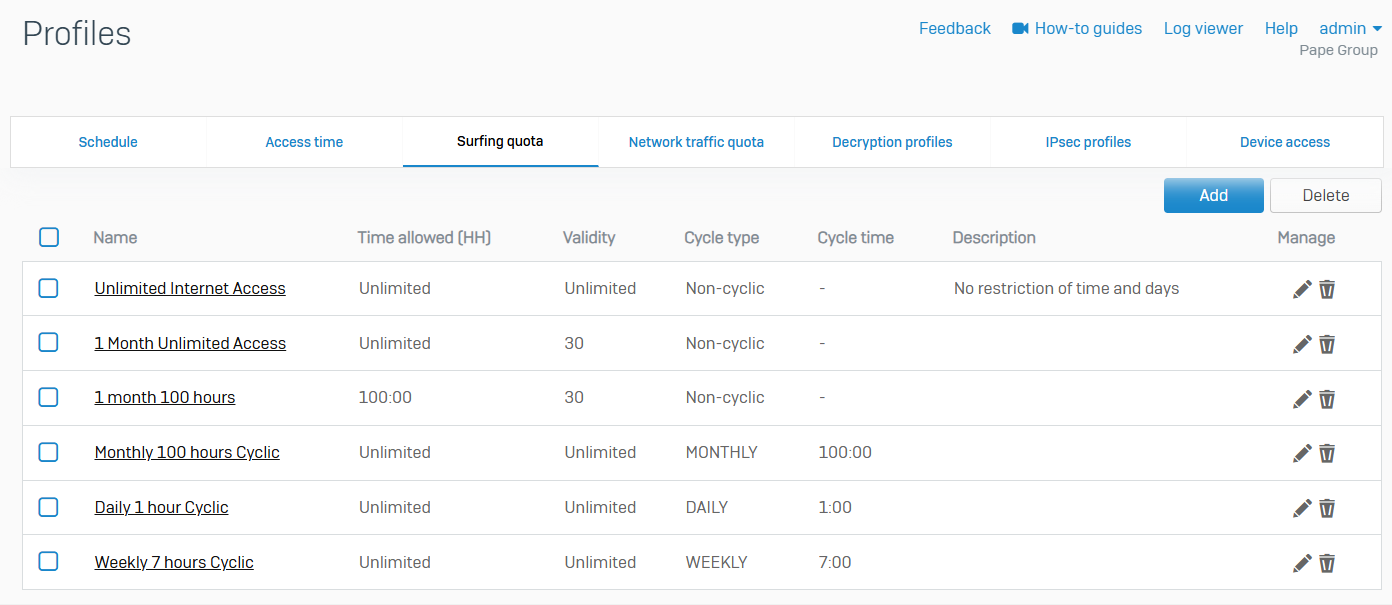
Network Traffic Quotas
- Reference - Network Traffic Quotas
- Use network traffic quota policies to control data transfer by users and groups
- You can restrict data transfer based on total data transfer or individual traffic (upload and download). Quotas can be cyclic (repeating) and non-cyclic (non-repeating). Specify the amount of network traffic allowed
- You can create your own network traffic quota policies or use the default policies
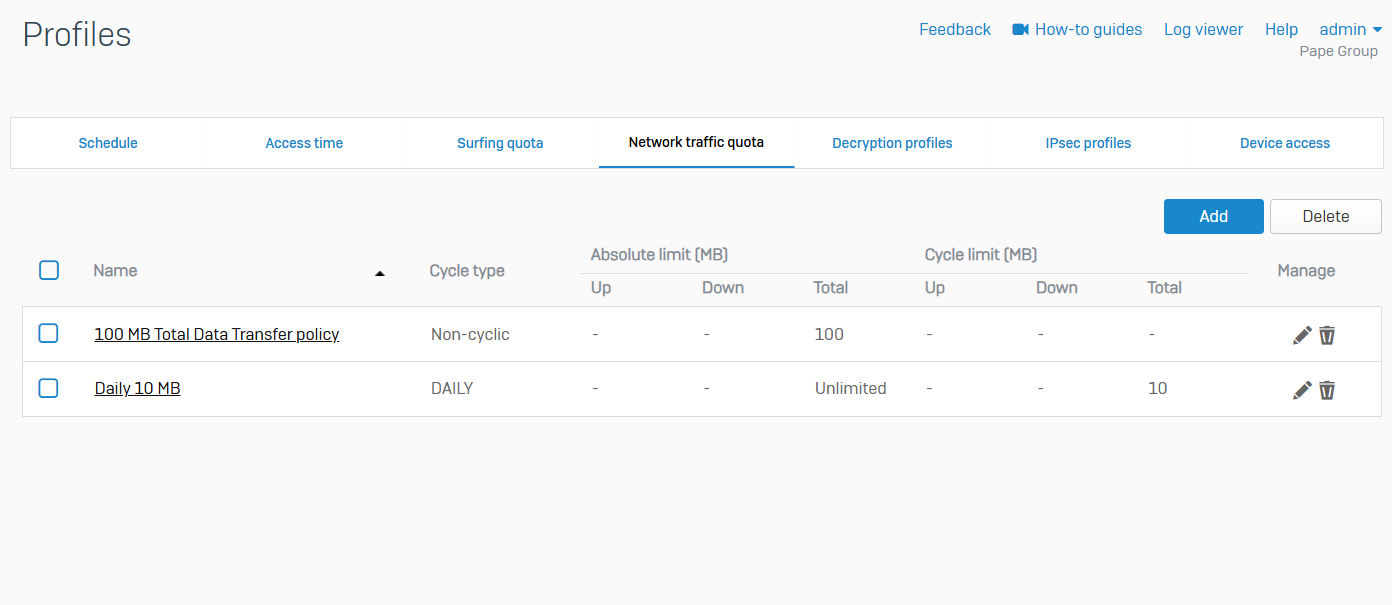
Decryption Profiles
- Reference - Decryption Profiles
- Decryption profiles enable you to enforce decryption settings on SSL/TLS connections
- You can specify the re-signing certificate authorities to sign SSL/TLS server certificates after Sophos Firewall intercepts, decrypts, and inspects secure traffic. You can also specify the action for traffic that can't be decrypted due to issues such as insecure protocol versions, unrecognized cipher suites, SSL compression, or connections that exceed the firewall's decryption capabilities
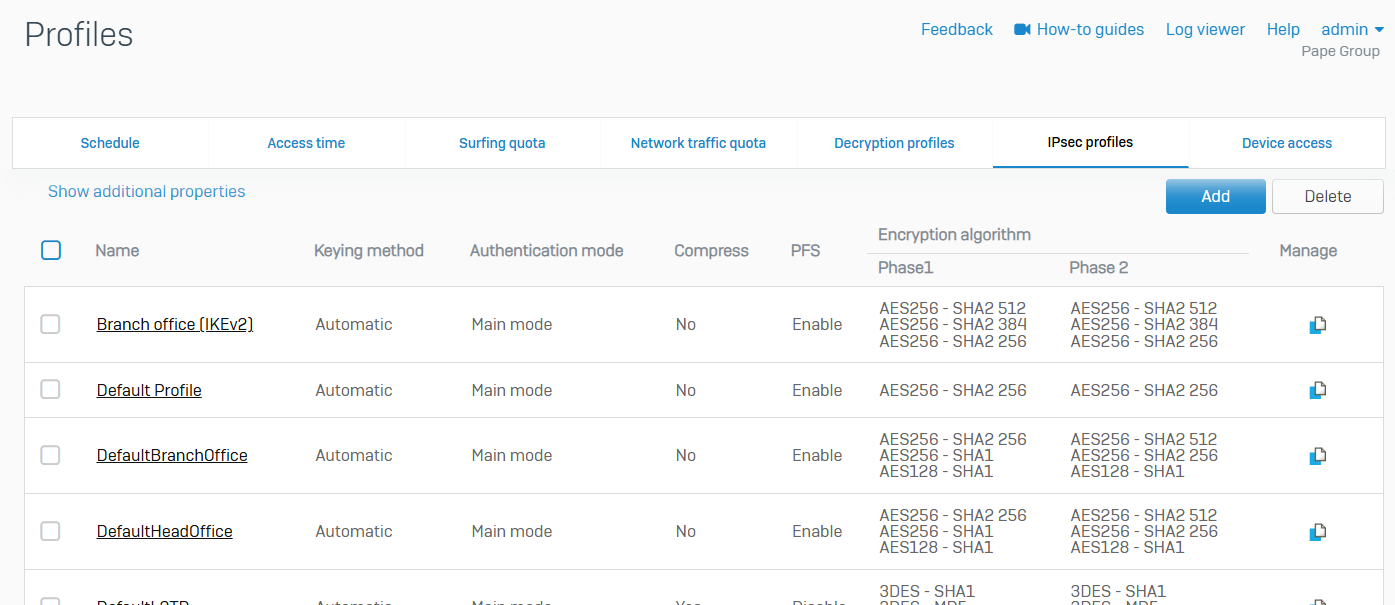
IPsec Profiles
- Reference - IPsec Profiles
- With IPsec profiles, you specify the phase 1 and phase 2 IKE (Internet Key Exchange) parameters for establishing IPsec and L2TP tunnels between two firewalls
- The default profiles support some common scenarios. You can also configure custom profiles
- You can create IPsec tunnels between two Sophos Firewall devices or between a Sophos Firewall and a third party firewall
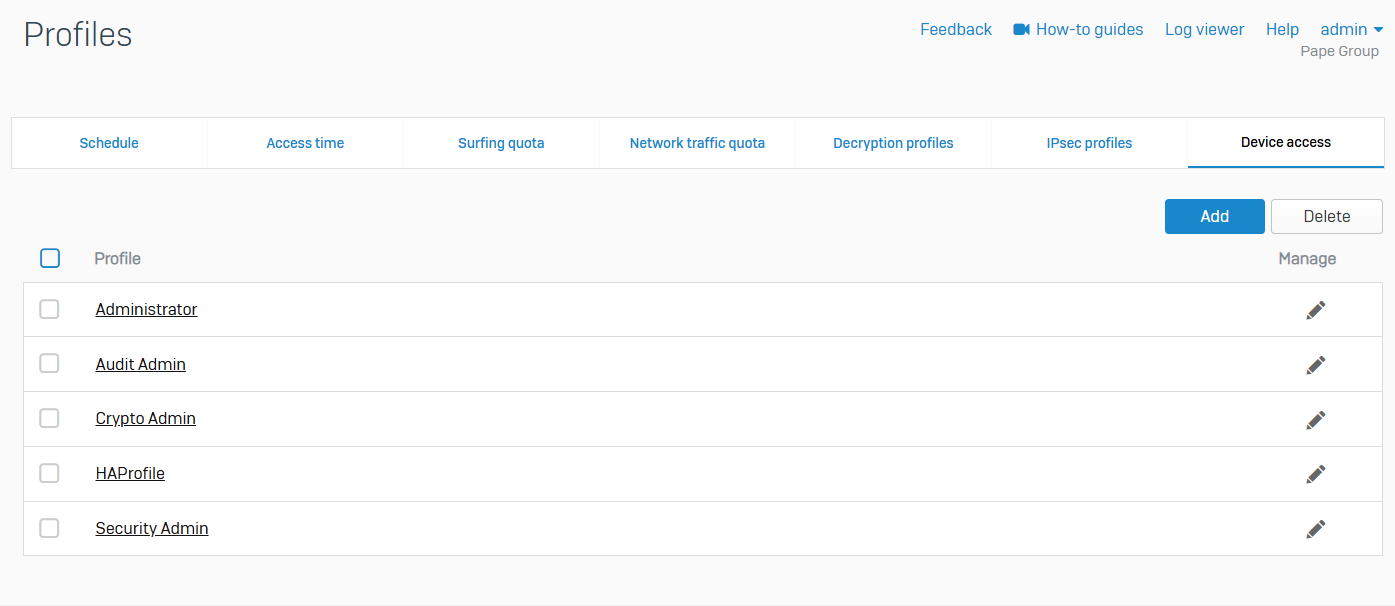
Device Access
- Reference - Device Access
- You can create role-based access to the firewall for administrators
- The default set of profiles specifies privileges for a super administrator and for some common administrator roles. The default administration user account (admin) uses the Administrator profile
- You can create custom profiles and specify their access to the web admin console on a granular basis
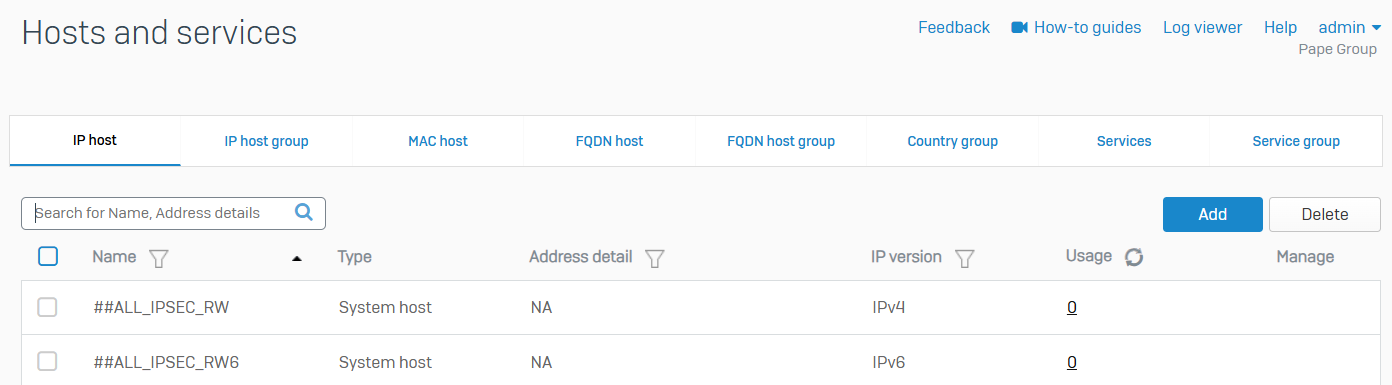
Hosts & Services
Overview
- You can define and manage system hosts and services
- The following host types are available
- IP host
- MAC host
- FQDN host
- Country group
- Sophos Firewall includes common services by default, such as DHCP and DNS
- You can also add, edit, and delete custom services
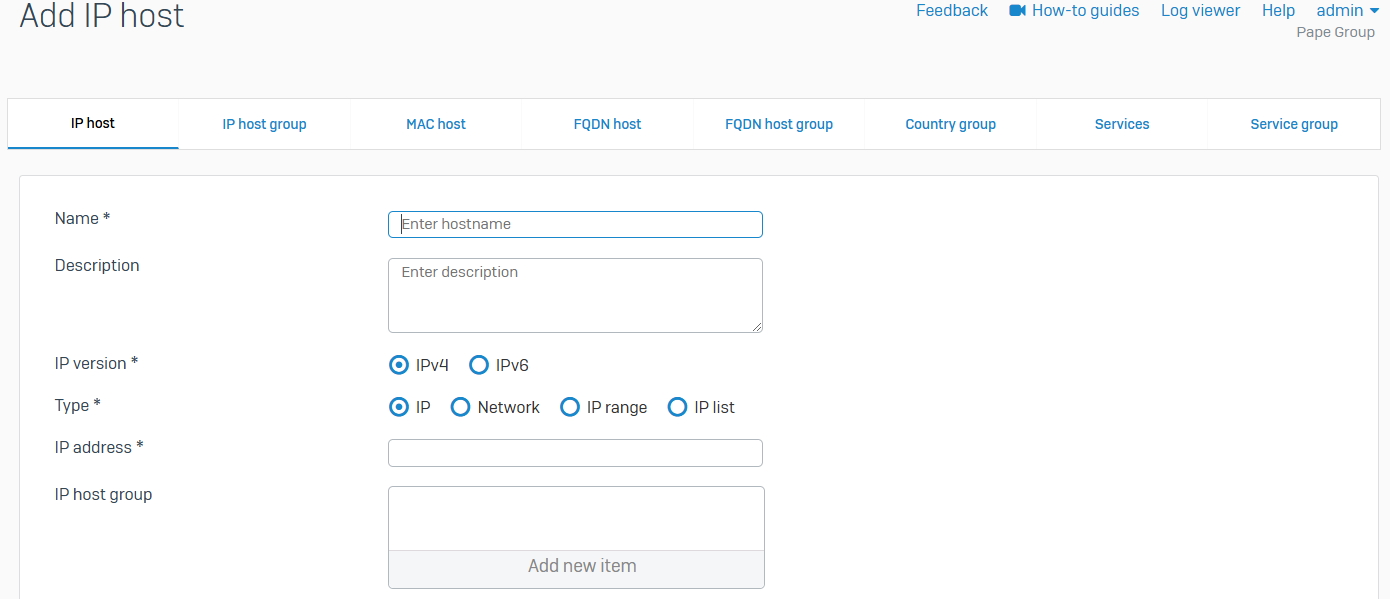
IP host
- Reference - IP host
- You can see the default and custom IP hosts. Default hosts include internet hosts and system hosts, such as dynamic hosts and interface hosts
- You can add, edit, or delete hosts. You can add IP addresses to an IP host group
- You can create IP hosts using an IP address, IP address range or list, and a network. You can specify these hosts in rules and policies
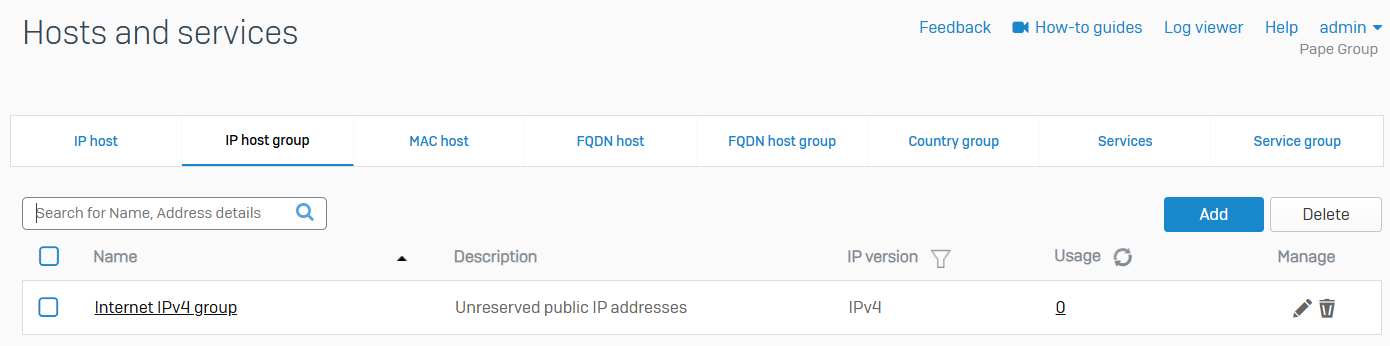
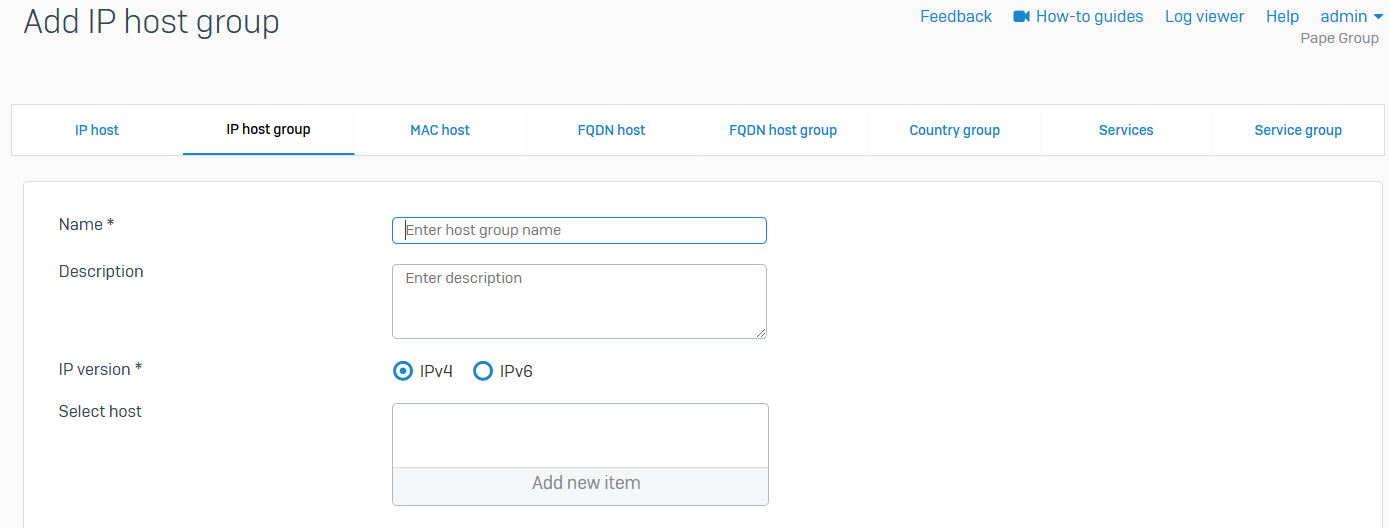
IP host group
- Reference - IP host group
- You can see the IP host groups. You can add, edit, and delete host groups
- You can add the custom IP hosts and default IP hosts, including interface hosts, the cellular WAN host, and internet hosts, to host groups. Internet hosts are the IP ranges reserved for use as public IP addresses
- You can't add the system hosts for remote access VPN connections to a host group
- You can specify IP host groups in rules and policies, such as firewall rules and SD-WAN routes
- Sophos Firewall shows a default IPv4 host group with all the default internet IPv4 hosts
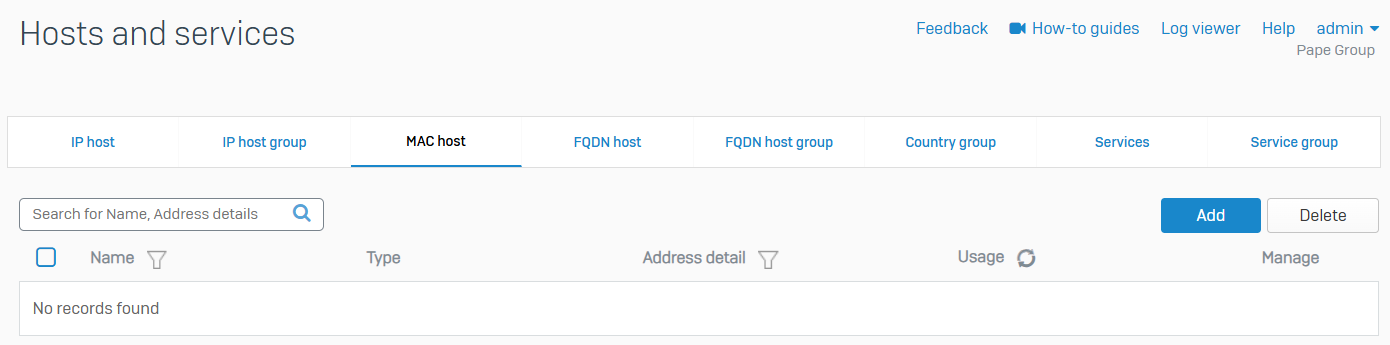
MAC host
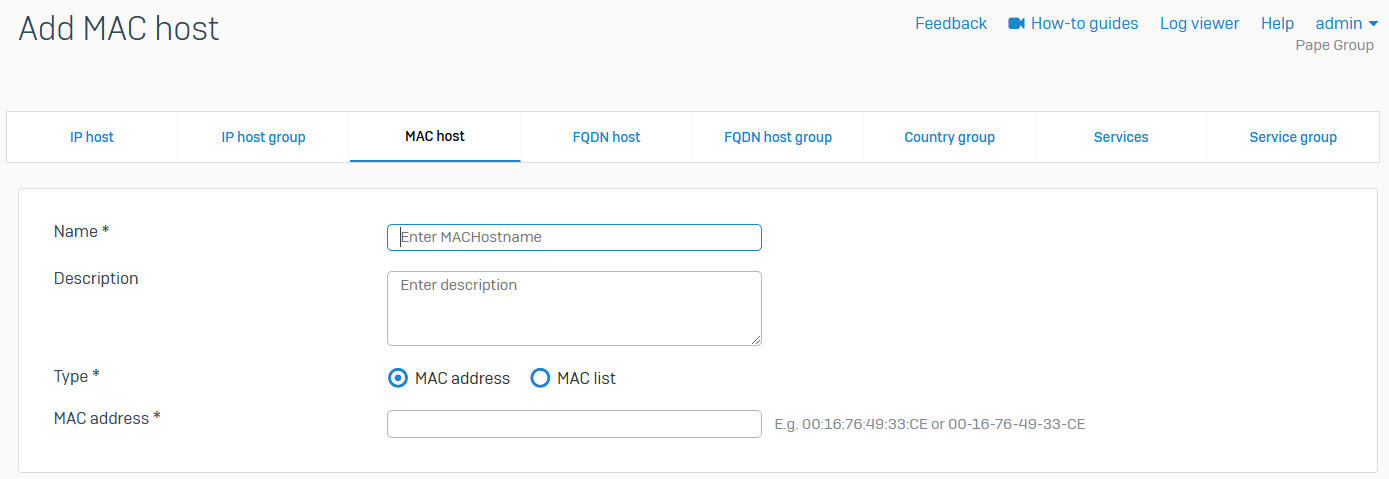
- Reference - MAC host
- You can assign a hostname to one or more MAC addresses
- You can create a MAC host with a single MAC address or multiple MAC addresses
- MAC list supports a maximum of 1000 MAC addresses
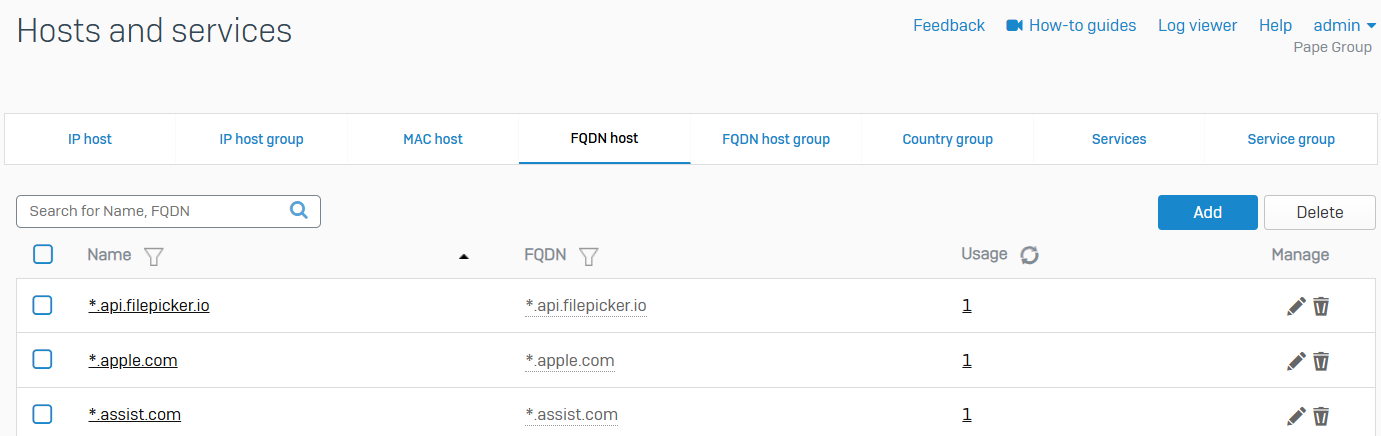
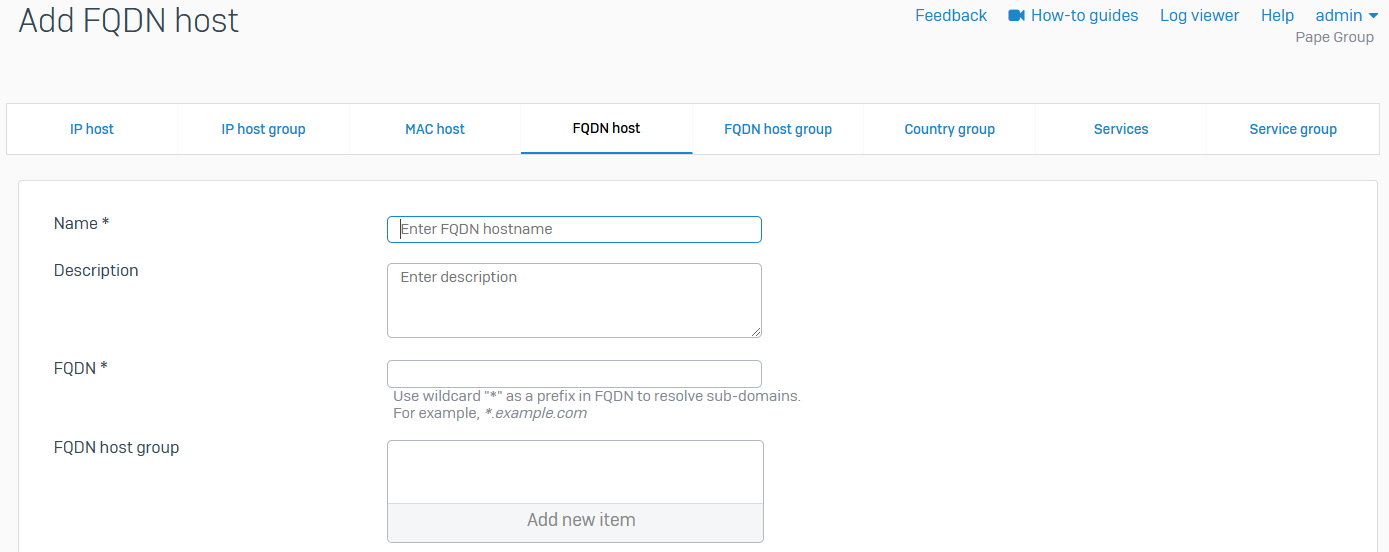
FQDN host
- Reference - FQDN host
- You can configure fully qualified domain name (FQDN) hosts on a Sophos Firewall. You can use FQDN hosts when you configure rules, policies, and settings, such as firewall rules, SD-WAN policy routes, and VPN settings
- You can have FQDNs with and without wildcards
- FQDN hosts make managing hosts and IP addresses easier as FQDN hosts can resolve to multiple IP addresses
- FQDN hosts can be configured for the following objects
- Mail servers
- Proxy servers
- DNS hosts
- External Authentication servers
- Remote Access VPN endpoints
- Syslog servers
- Web servers
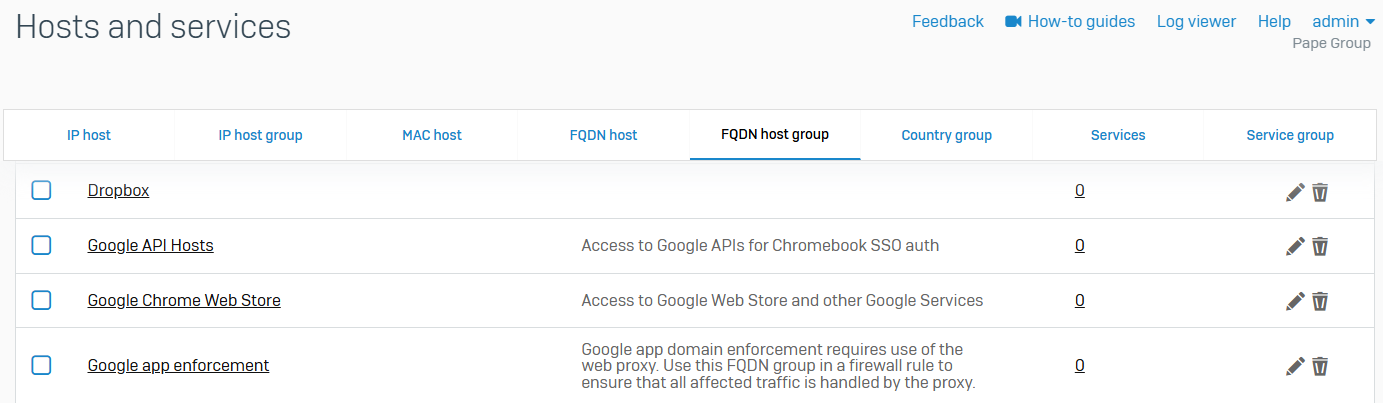
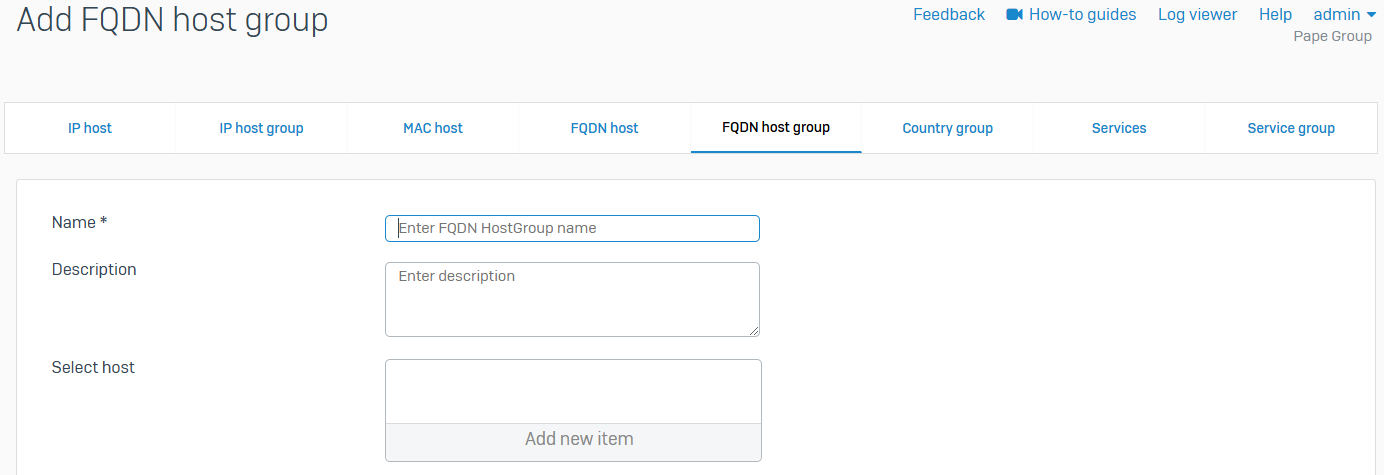
FQDN host group
- Reference - FQDN host group
- You can add individual FQDN hosts to one or more host groups
- You can use FQDN host groups when you configure rules and policies, such as firewall rules, and SD-WAN policy routes
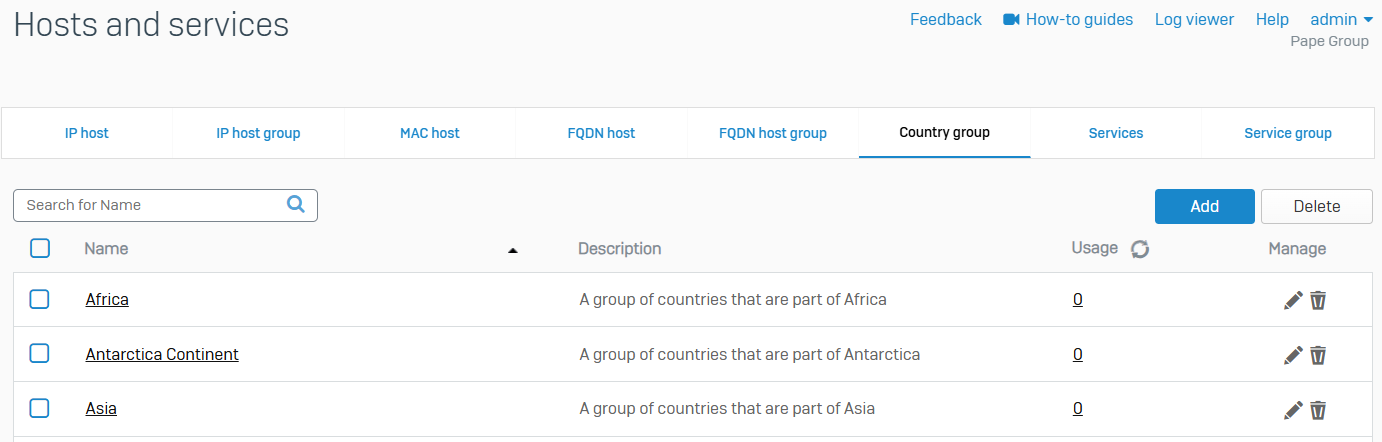
Country group
- Reference - Country group
- Countries and regions are grouped based on their continent into default country groups
- You can allow or block traffic based on the source and destination countries, regions, or their groups in firewall rules. You can also route and translate traffic based on these
- You can add, edit, and delete country and region groups
- Regions that haven't been recognized as countries either currently or in the recent past may not be part of the default country groups. You can manually add these to default and custom groups
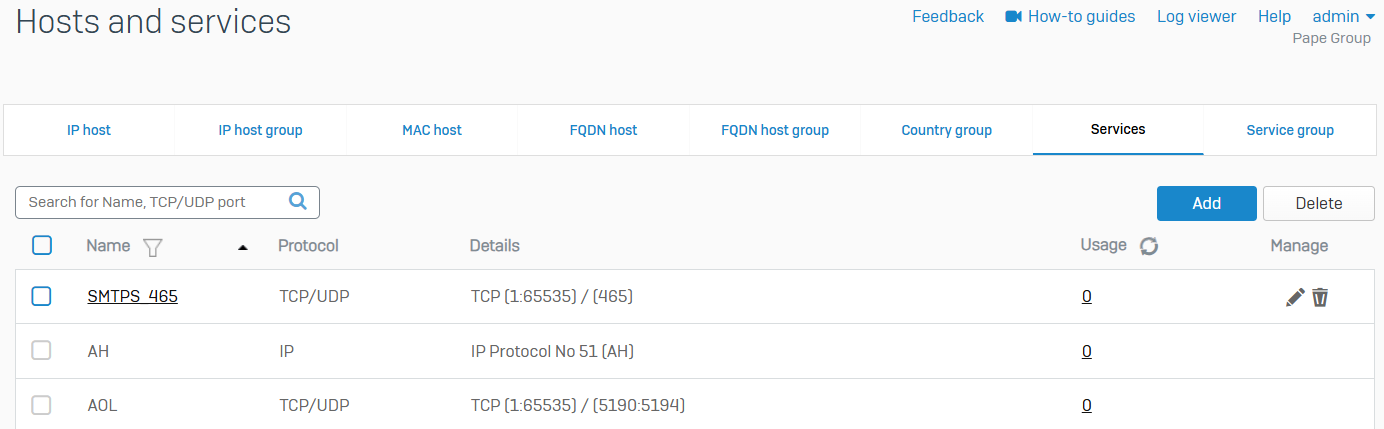
Services
- Reference - Services
- Shows a list of all default and custom services
- Services define specific types of network traffic. They show information about protocols such as TCP, ICMP, or UDP, and protocol-related options such as port numbers
- Use services to determine the types of traffic allowed or denied by Sophos Firewall
- You can add custom services, and edit or delete existing services
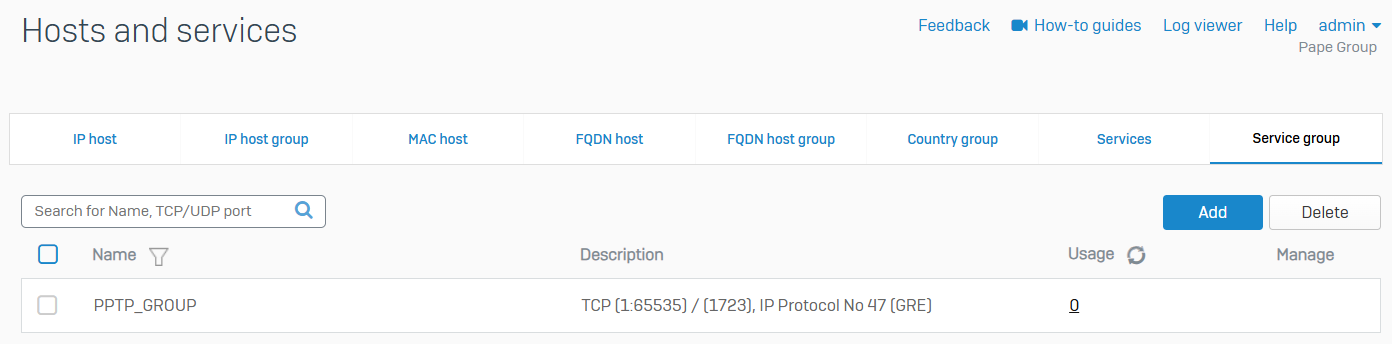
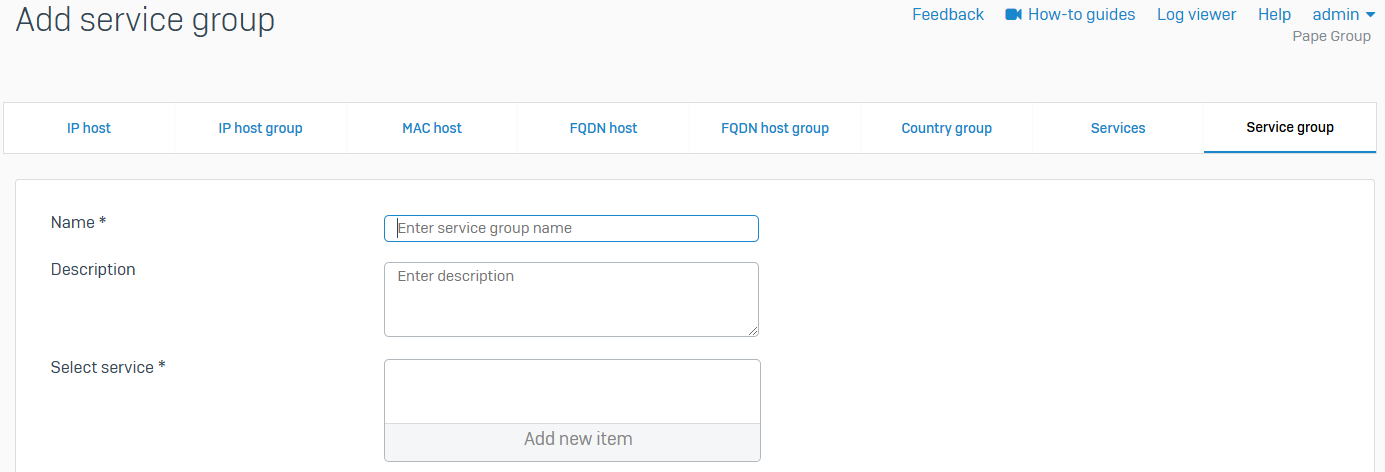
Service group
- Reference - Service group
- Shows a list of all default and custom service groups
- You can combine custom and default services in the same group
- Create groups of services and then add a firewall rule to allow or block access for all the services in the group. A service group can be a member of multiple service groups
- You can also add a new group, edit an existing group, add services to an existing group, or delete a group
Administration
Overview
- Manage device licenses and time, administrator access, centralized updates, network bandwidth and device monitoring, SNMP, and user notifications
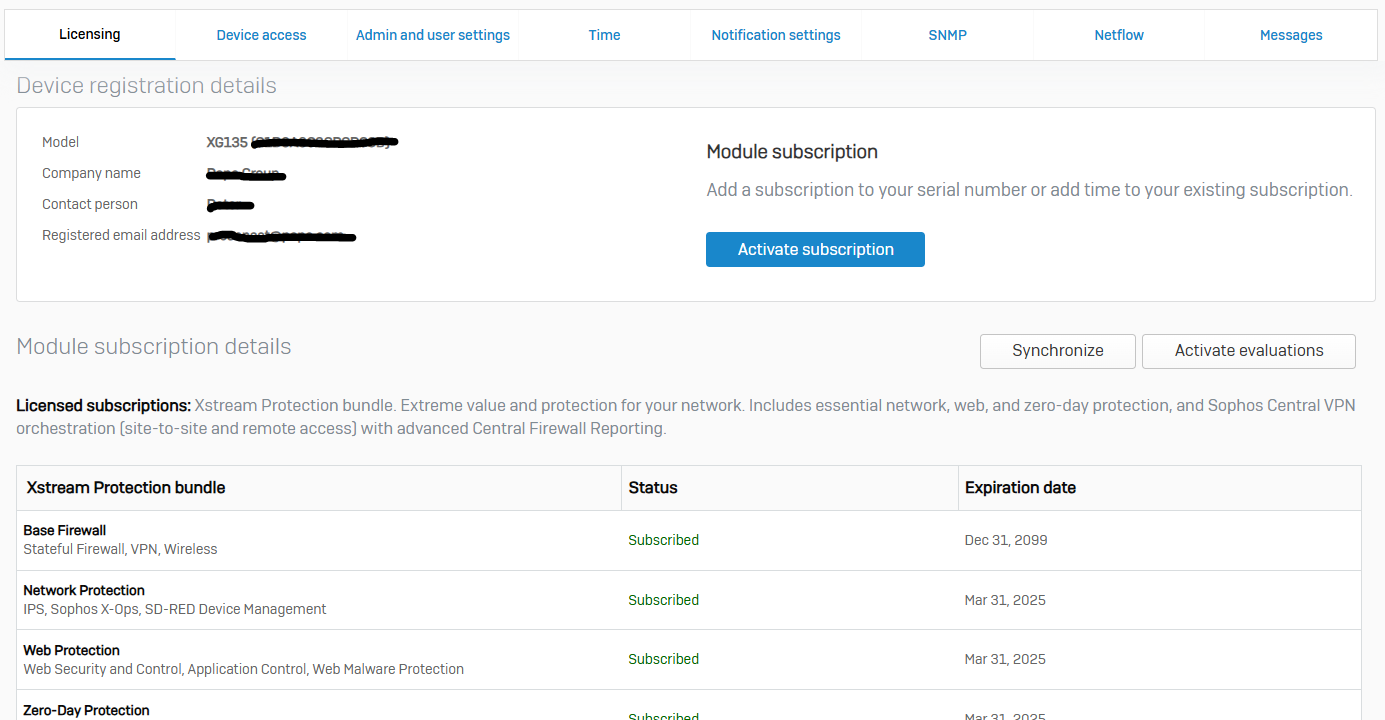
Licensing
- Reference - Licensing
- You can activate your evaluations and subscriptions. You can also synchronize your licenses
- If Sophos Firewall is connected to the Internet, the firewall synchronizes with the Sophos Licensing Portal every 24 hours, and licenses are updated automatically
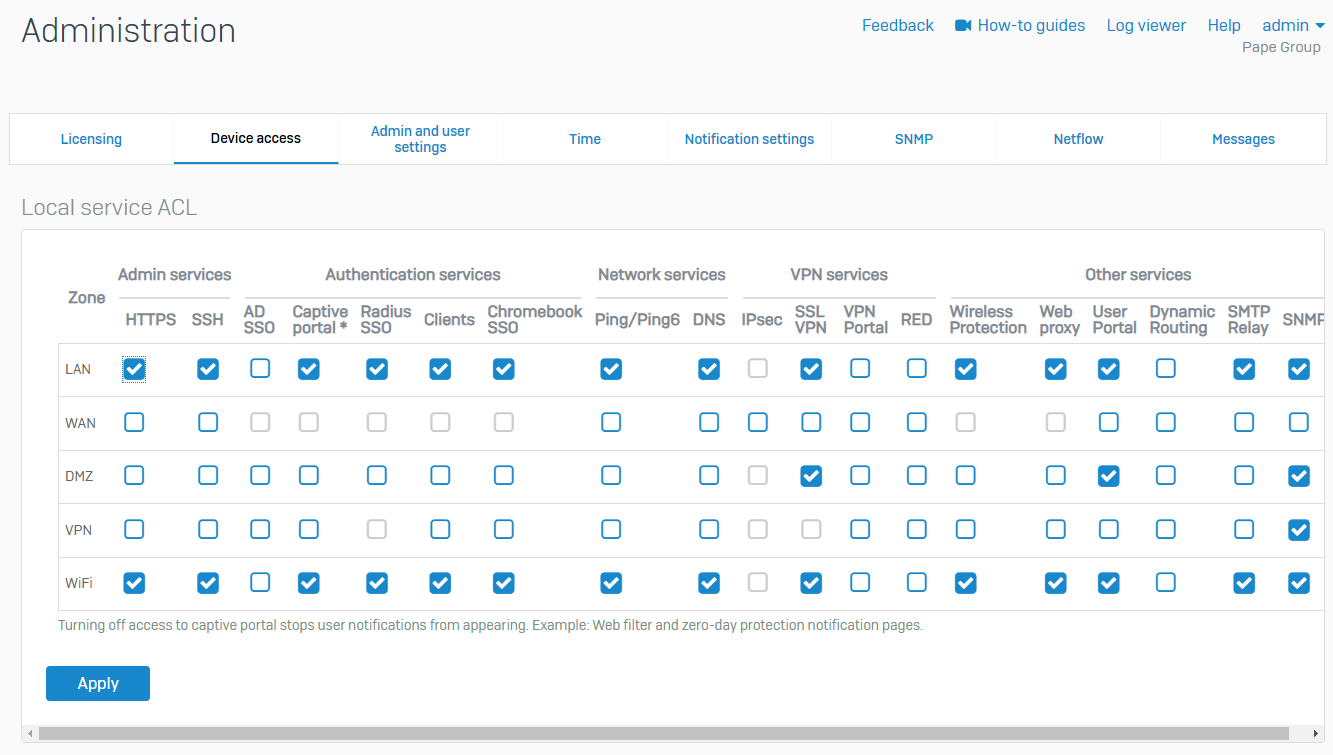
Device Access
- Reference - Device Access
- You can control access to the management services of Sophos Firewall from custom and default zones using the local service ACL (Access Control List)
- Local services are management services specific to the internal functioning of Sophos Firewall, such as web admin and CLI consoles, and authentication services. You can allow or block access to local services from 'Administration >> Device Access'
- Default admin password settings and MFA for the default admin are configurable options to increase security posture
Admin & User Settings
- Reference - Admin & User Settings
- Change the admin port settings and sign-in parameters. Customize the sign-in parameters to restrict local and remote user access based on time duration
- Hostname assignment of firewall is configurable from this page
- From this page, you can configure port and certificate settings for the web admin console and user portal for client VPN
- By default, the admin console HTTPS port is '4444' to access the GUI Control Center whereas the user portal is set to '443'
- You can set sign-in security for administrators via the Login security section in addition to setting administrator and user password complexity settings
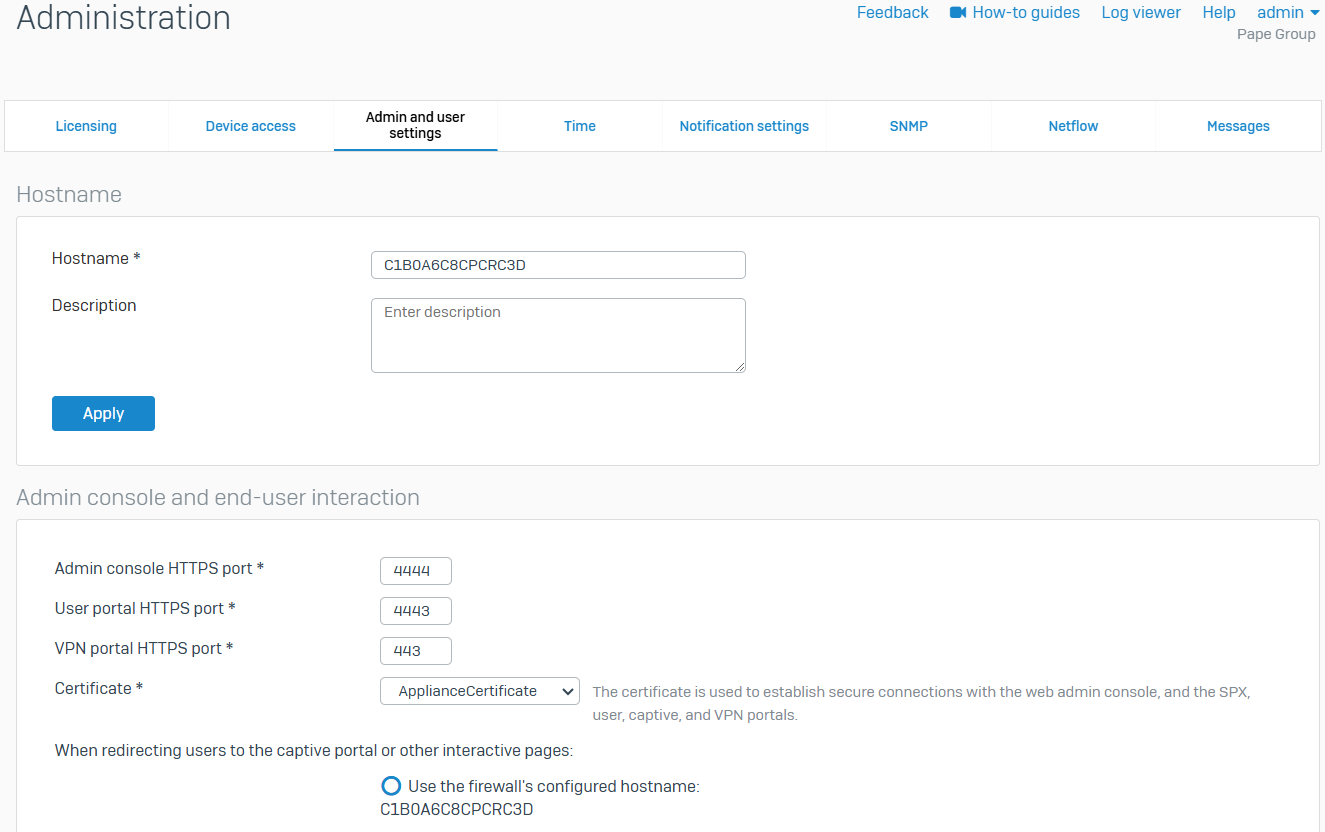
Time
- Reference - Time
- Synchronize the clock on the firewall with predefined or custom Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers. Alternatively, set it to the local time zone or change the time and data manually
- When you change NTP time servers, all IPsec connections will reconnect
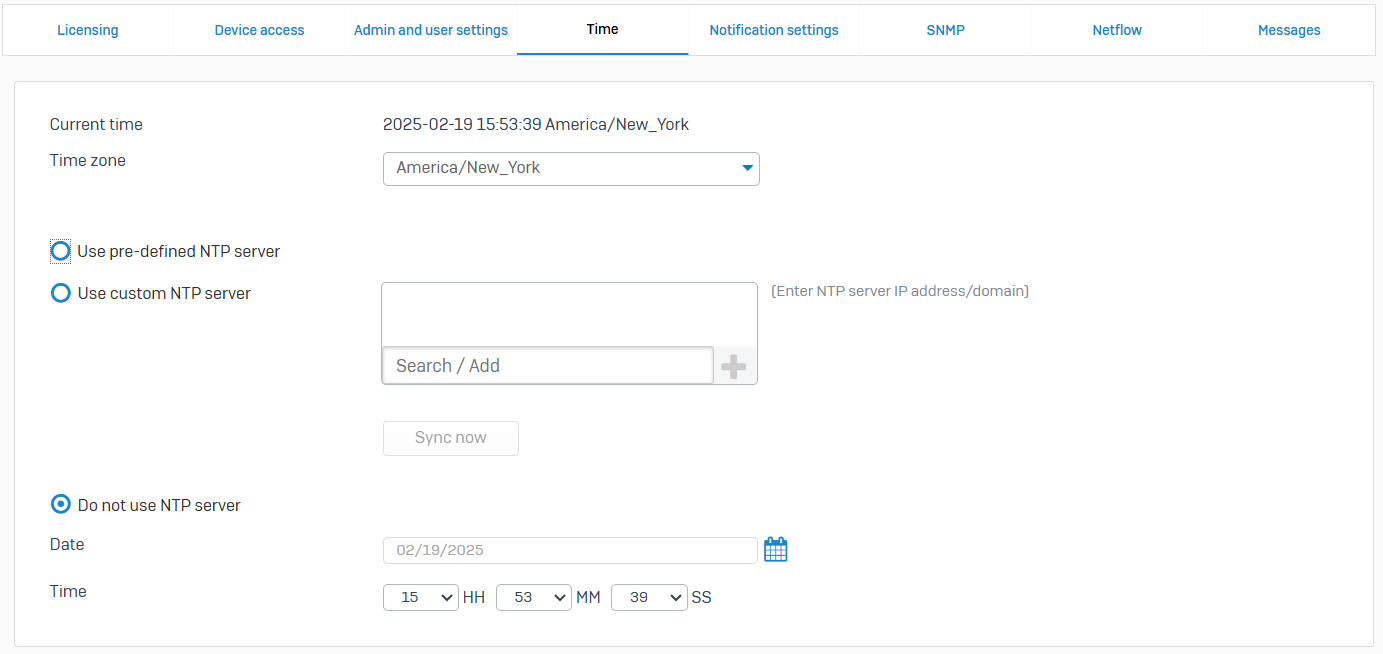
Notification Settings
- Reference - Notification Settings
- Configure a mail server and email settings to send and receive alert emails
- You can configure email notifications for system generated events and reports
- You can use either the built-in mail server or an external mail server
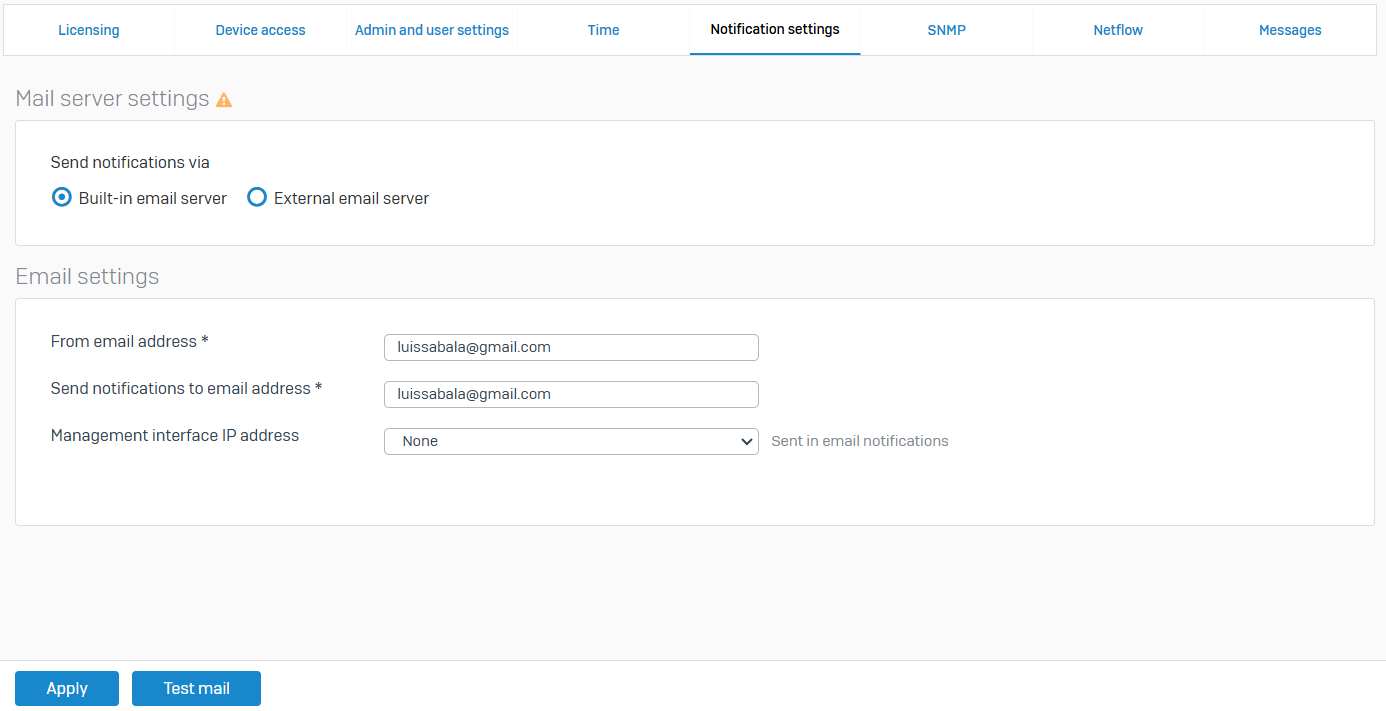
SNMP
- Reference - SNMP
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) gives access to Sophos Firewall information, for example, the status of the firewall, service availability, CPU, memory, and disk usage. Sophos Firewall supports SNMPv3, SNMPv1, and SNMPv2c protocols
- You can configure Sophos Firewall as an SNMP agent. It sends traps (alerts) of system generated events to SNMP managers within its community and to specified SNMPv3 users
Netflow
- Reference - Netflow
- Netflow is a network protocol that enables you to monitor bandwidth usage and traffic flow. If you add a Netflow server to Sophos Firewall, it sends the Netflow records of source, destination, and traffic volume to the Netflow server. The records help you identify the protocols, policies, interfaces, and users consuming high bandwidth. You can use data analysis tools, such as Open Source Data Analyzer and PRTG to generate reports from the Netflow records
- You can add, update, or delete Netflow servers
Messages
- Reference - Messages
- Use messages to notify users and issue administrative alerts. You can send messages of up to 256 characters to one or more users
- You can send notification messages for the following events
- Authentication
- SMTP
- Administration
- SMS customization
Backup & Firmware
Overview
- You can manage the firmware versions, hotfixes, and pattern updates
- You can also perform backup & restore, and import-export of configurations
Backup & Restore
- Reference - Backup & Restore
- You can take encrypted backups and restore the configurations
- Backups contain the entire configuration on Sophos Firewall and are encrypted. You can save backups on Sophos Firewall, use FTP to save them on a server, or email the backup. You can set up an automatic backup schedule, or take a backup manually
- You must enter a password to encrypt the backup. To restore the backup, you must reenter the password and the secure storage master key
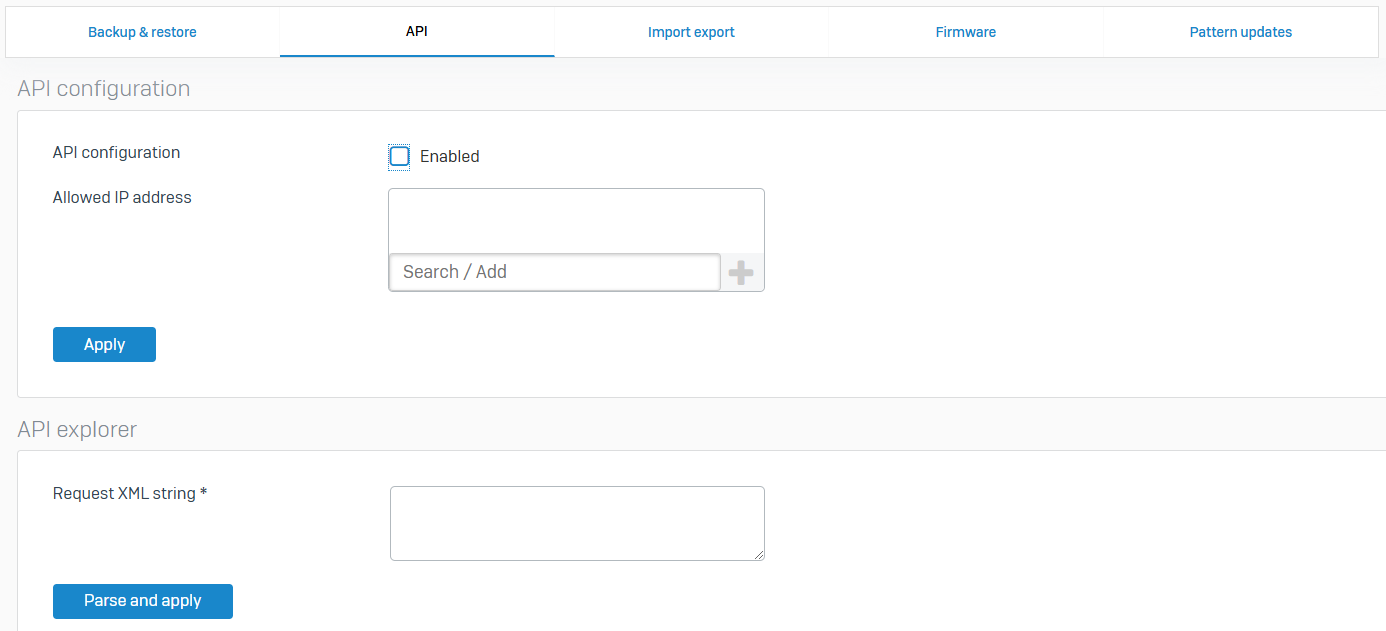
API
- Reference - API
- You can add, update, or delete the firewall configuration using the API
- The firewall's API allows you to manage your firewall configuration programmatically. Rather than sign in to your firewall's web admin console and manually add, update, or remove configurations, you can use the API to code to automate these tasks
- You can use it to apply the same configuration to multiple firewalls. The API client can be a browser or an API application such as Postman or CLI
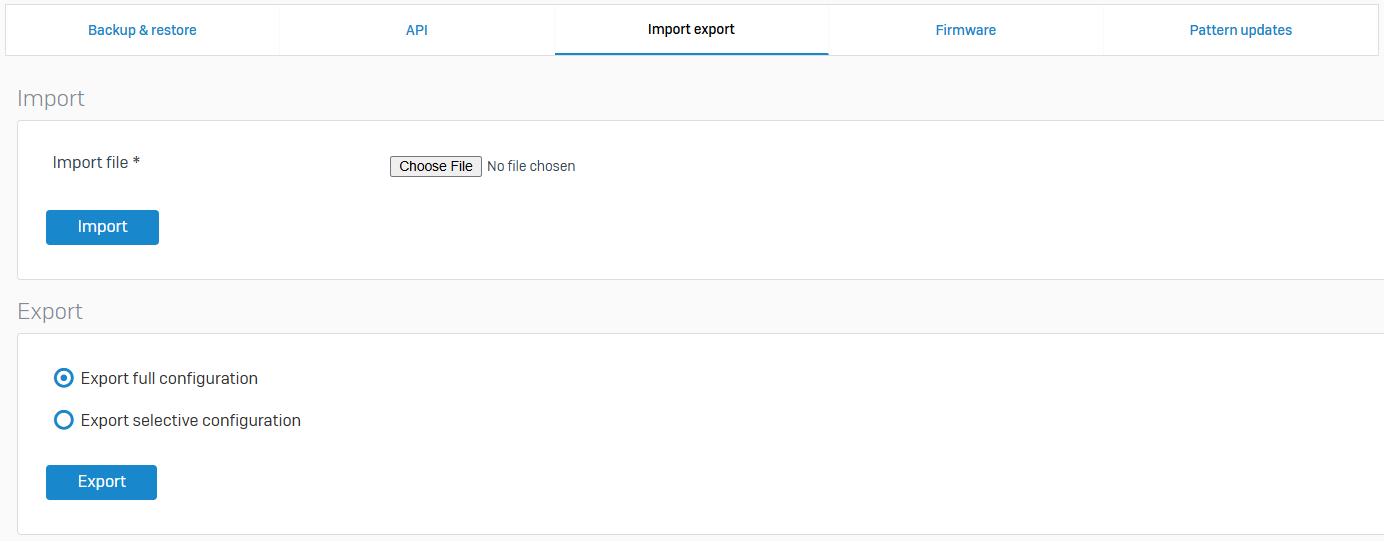
Import Export
- Reference - Import Export
- You can import and export the full or partial configuration of Sophos Firewall
- You can only import and export configurations between compatible devices. The configuration file is a .xml file. You can update the configuration offline and then import it
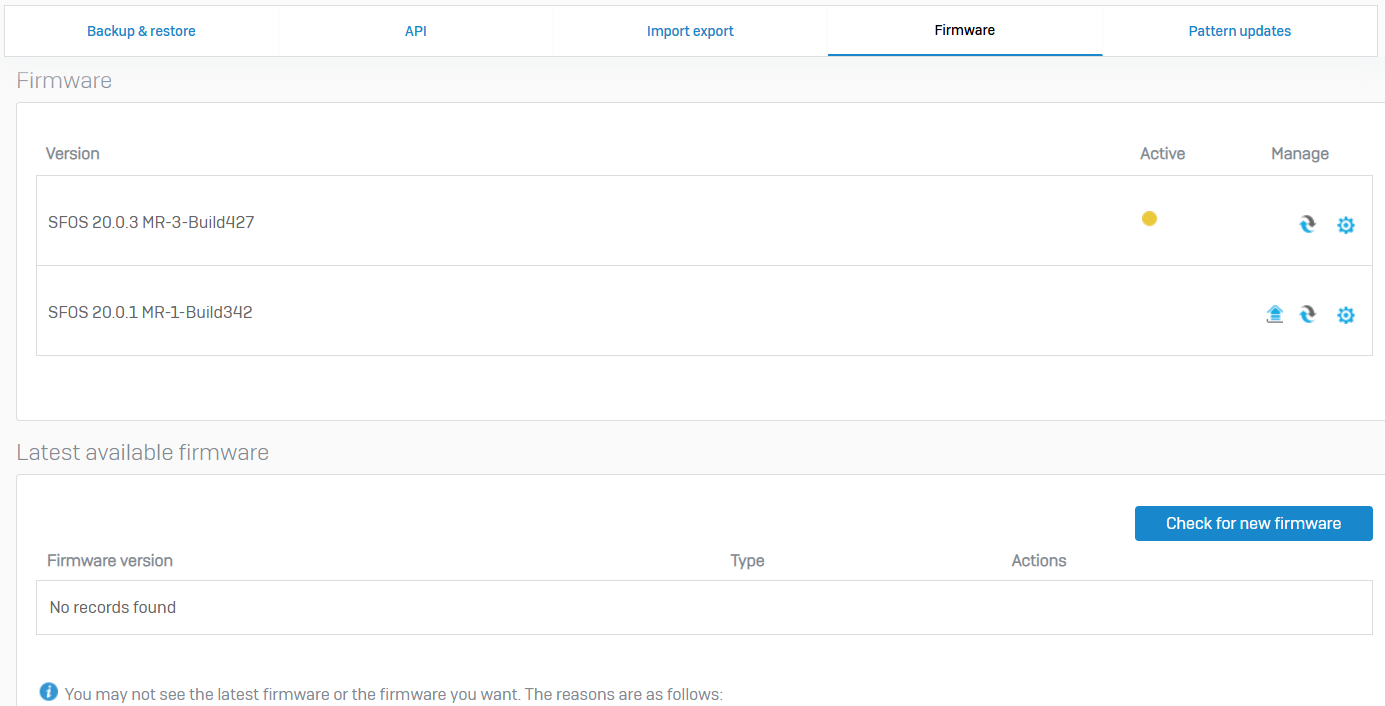
Firmware
- Reference - Firmware
- You can manage firmware versions, install hotfixes, and change the default language
- You can upgrade to a later firmware version, downgrade to an earlier version, or roll back to the previous version
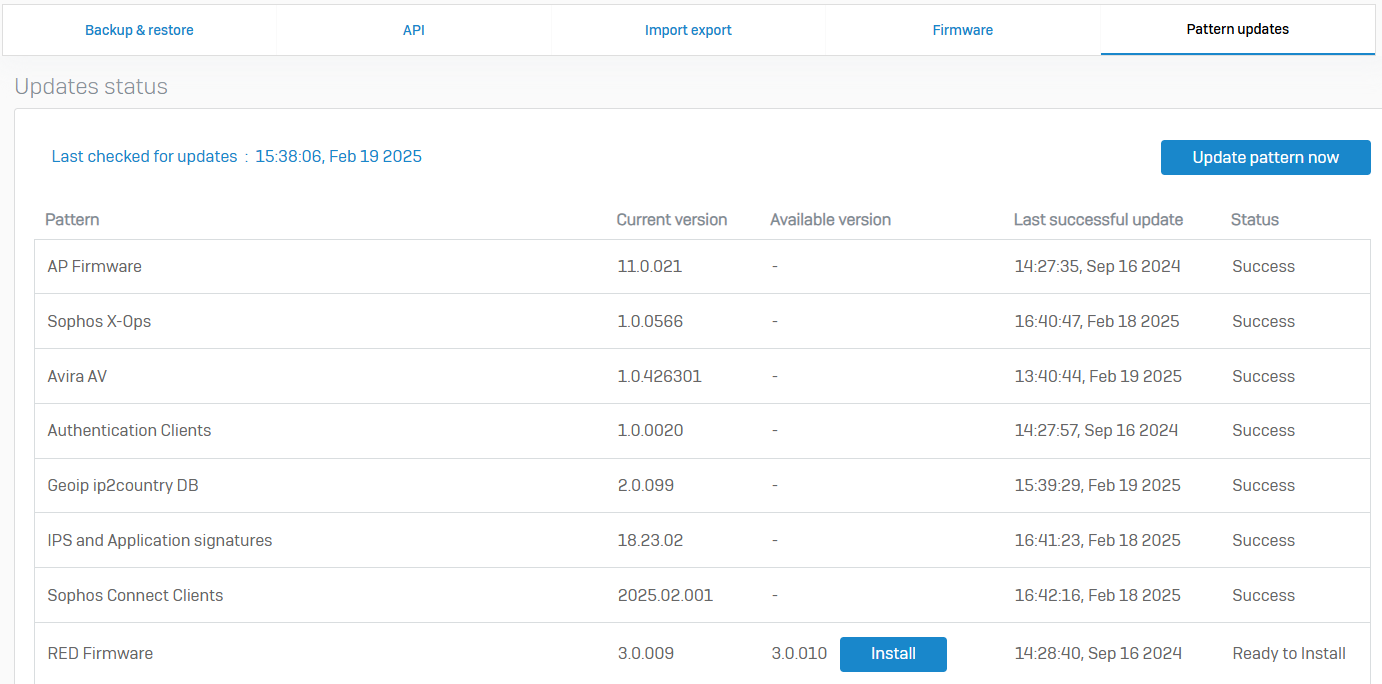
Pattern Updates
- Reference - Pattern Updates
- You can update pattern definitions for components, such as signatures, engines, clients, and devices
- Sophos Firewall updates patterns automatically by default. You need to update patterns for access points and RED appliances manually. Firmware updates for these devices are available as pattern updates
Certificates
Overview
- You can add certificates and generate a locally signed certificate or certificate signing request (CSR)
- You can also add certificate authorities (CA) and certificate revocation lists (CRL)
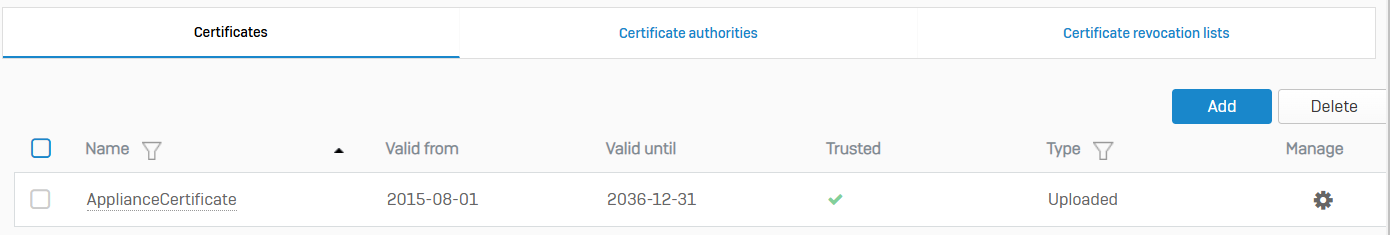
Certificates
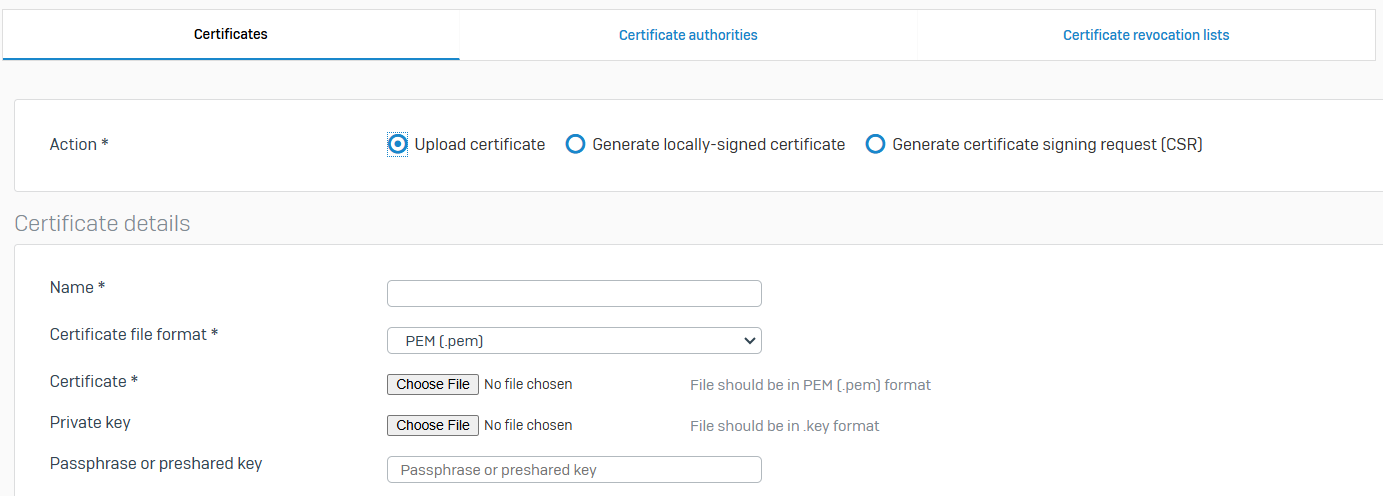
- Reference - Certificates
- You can upload an external certificate, generate a locally-signed certificate, and generate a certificate signing request (CSR)
- Sophos Firewall provides a built-in certificate (ApplianceCertificate) that's selected by default for services, such as the web admin console, user portal, and captive portal
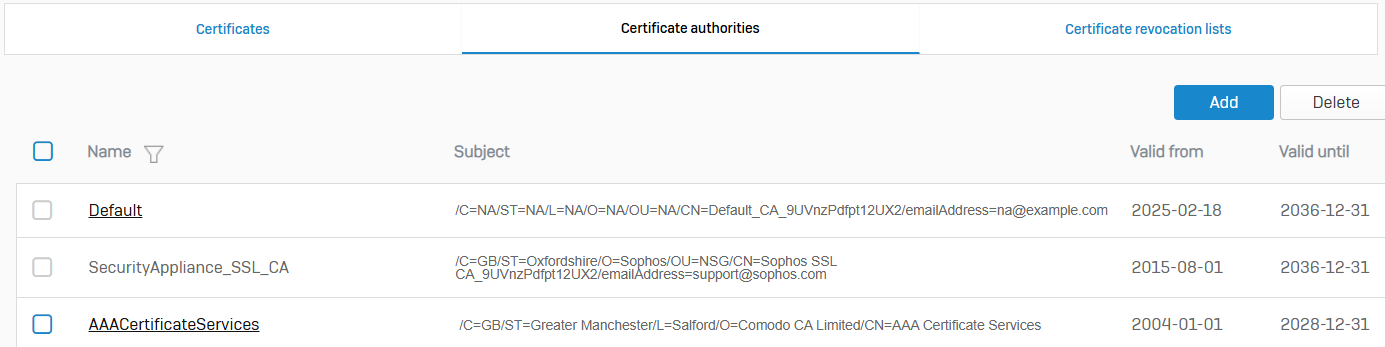
Certificate Authorities
- Reference - Certificate Authorities
- You can add, download, update, and regenerate Certificate Authorities (CAs)
- CAs are trusted entities that issue digital certificates to verify the ownership of a user, host, or organization. Ownership is verified through a public key, the owner's information, and a private key
Certificate Revocation Lists
- Reference - Certificate Revocation Lists
- Certificates are revoked, for example, when the private key or CA has been compromised or the certificate is no longer valid for the original purpose. CAs maintain a list of revoked certificates
- You can only revoke locally-signed certificates in the firewall. The firewall automatically updates the default certification revocation list (CRL) with the revoked certificate details
Configure Section
Overview
- The Configure section in the Sophos Firewall control center is a critical area where network administrators set up, modify, and manage the key network settings and VPN policies for the firewall

Remote Access VPN
Overview
- Reference - Sophos Connect Client
- You can configure remote access IPsec and SSL VPNs to establish connections using the Sophos Connect client
- You can also configure clientless SSL VPN, L2TP, and PPTP VPNs
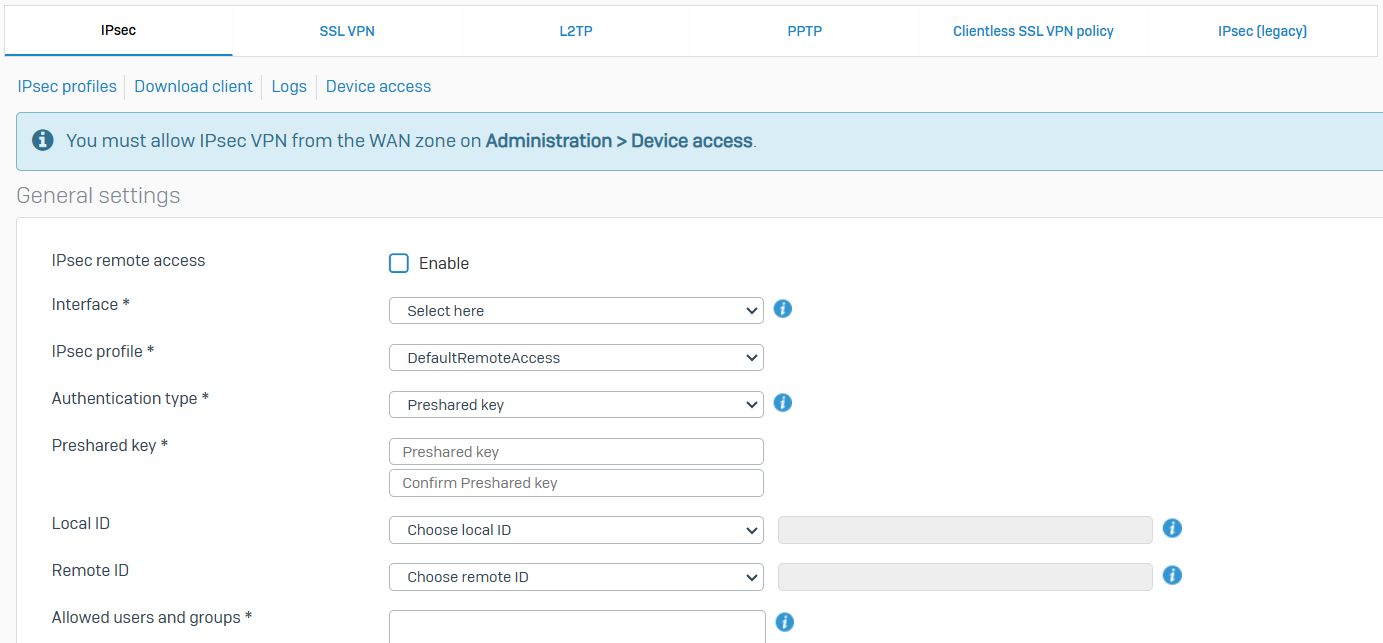
IPsec
- Reference - IPsec
- You can establish remote access IPsec VPN connections using the Sophos Connect client
- To specify the phase 1 and phase 2 IKE (Internet Key Exchange) parameters for establishing IPsec tunnels between two firewalls, go to 'Remote access VPN > IPsec' and click IPsec profiles
- To download the Sophos Connect client, click Download client
- To see the logs, click Logs
- To export the configuration after specifying the settings, scroll down and click Export connection
- To reset the settings, scroll down and click Reset
- Add a firewall rule to allow traffic between the Sophos Connect clients and Sophos Firewall. For higher levels of security, configure individual rules for inbound and outbound traffic
SSL VPN
- Reference - SSL VPN
- You can enable remote users to connect to the network securely over the Internet using remote access SSL VPN connections
- Users can establish IPv4 and IPv6 SSL VPN connections. These connections use OpenVPN. Remote access requires digital certificates and a username and password
- Users can download the Sophos Connect client from the user portal
- If you share the provisioning (.pro) file, users can double click the file, which automatically imports the configuration into the client. Alternatively, they can download the .ovpn configuration file from the user portal and import it into the Sophos Connect client. Sophos Connect client then establishes the connection
- Add firewall rules allowing traffic between the LAN and VPN zones. The rule allows Sophos Connect clients to access the configured LAN networks
- The SSL VPN global settings apply to all remote access SSL VPN policies. These settings are part of the .ovpn configuration file imported to the SSL VPN client
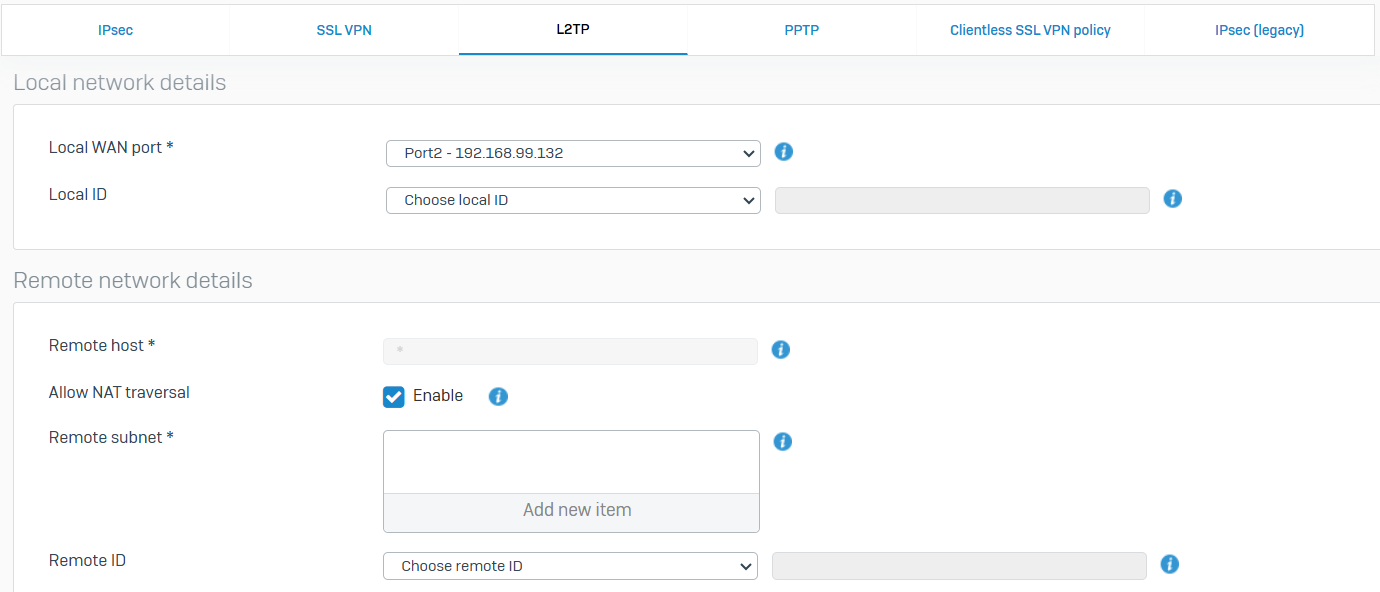
L2TP
- Reference - L2TP
- The Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) enables you to provide connections to your network through private tunnels over the Internet. The firewall supports L2TP defined in RFC 3931
- You can specify the global settings for L2TP remote access connections. These settings apply to all L2TP policies. You can specify the IP addresses to assign to L2TP users and the DNS servers to use for these connections
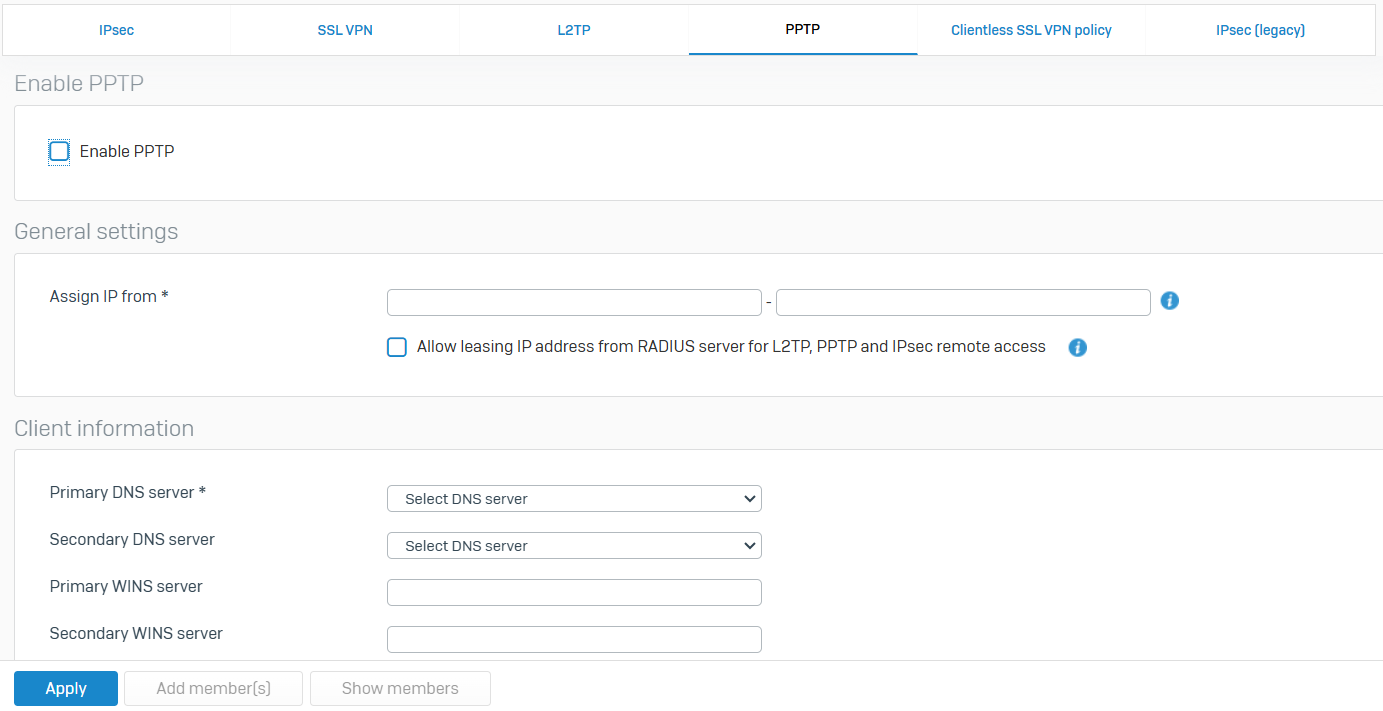
PPTP
- Reference - PPTP
- Using the Point-to-point Tunneling protocol (PPTP), you can provide connections to your network through private tunnels over the Internet
- The protocol itself does not describe encryption or authentication features. However, the firewall supports several authentication options including PAP, CHAP, and MS-CHAPv2. The firewall supports PPTP as described in RFC 2637
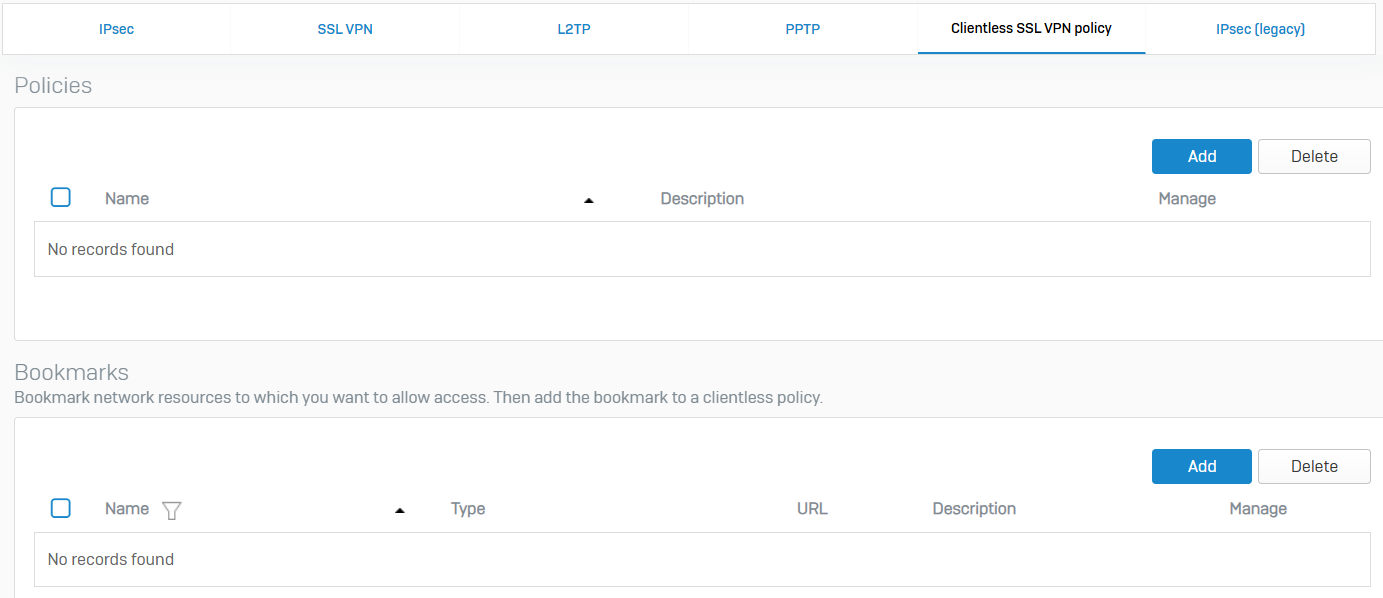
Clientless SSL VPN Policy
- Reference - Clientless SSL VPN Policy
- You can allow users to access endpoints, servers, terminals, and file servers using a browser. Users don't need to install VPN clients
- Clientless SSL VPN policies allow you to limit users and their access to specific resources and services
- With Bookmarks, you can create bookmarks to specify the protocol, such as RDP, SSH, and FTPS, the destination server, and the security settings to access the server
- You assign the bookmarks to clientless SSL VPN policies, specifying users (policy members) who can access the resources through the bookmarks
Site-to-site VPN
Overview
- You can configure policy-based (host-to-host and site-to-site) IPsec VPNs, route-based IPsec VPNs, and SSL VPNs
- You can also create RED tunnels between the main office and the branch offices
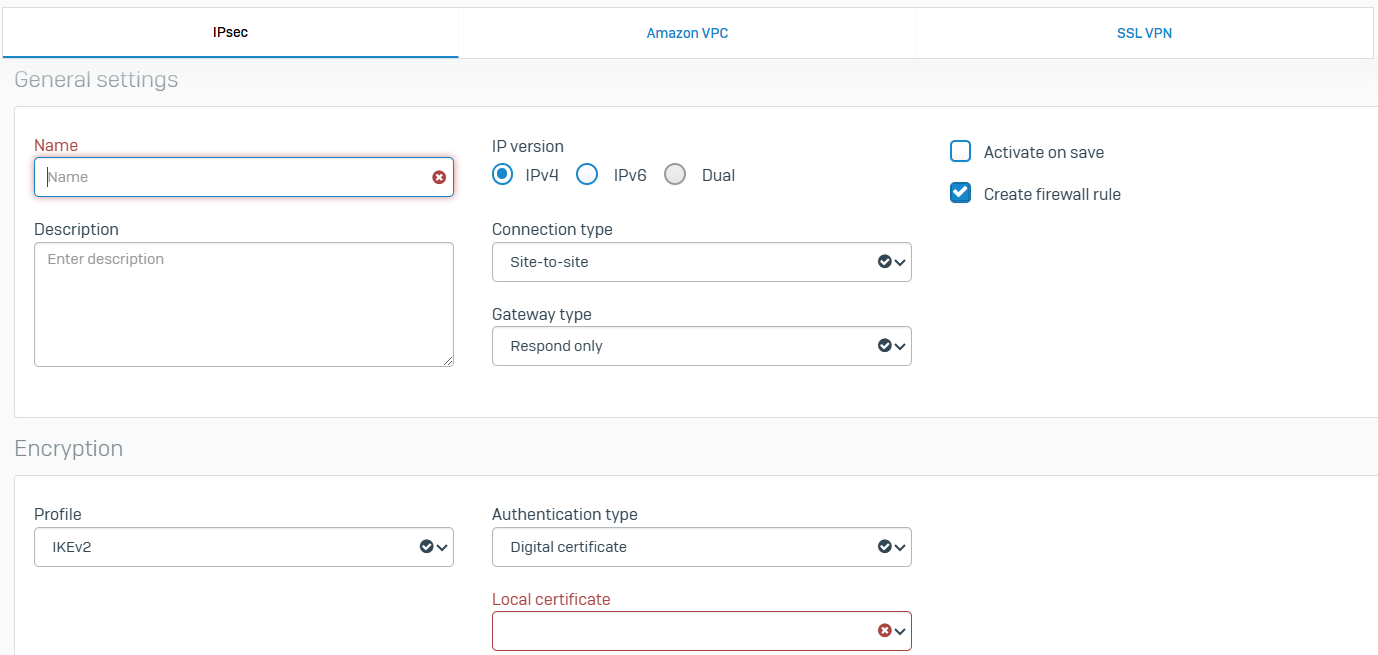
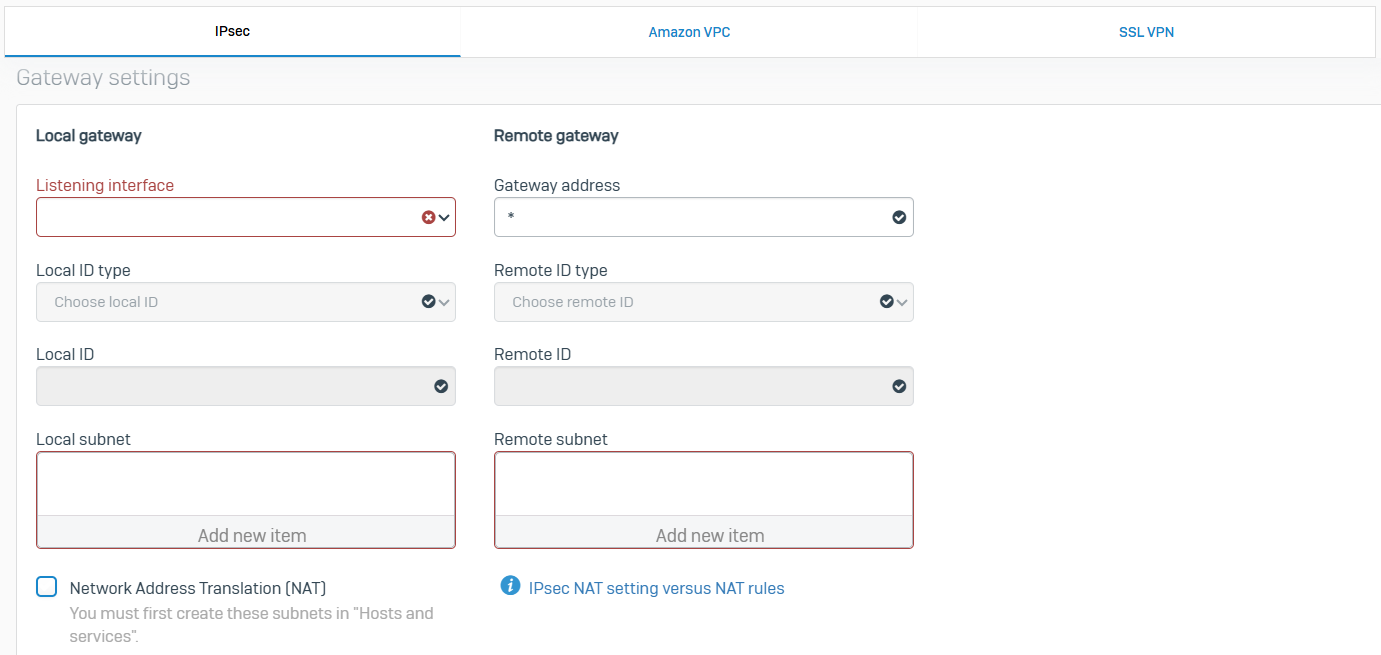
IPsec
- Reference - IPsec
- You can configure IPsec VPN connections to allow cryptographically secure communications over the public network between two Sophos Firewall devices or between Sophos Firewall and third-party firewalls
- You can configure Route-based or Policy-based VPNs
- Policy-based VPNs are IPsec connections that encrypt and encapsulate traffic flowing through the listening interface if the traffic matches the specified local and remote subnets and the corresponding firewall rule
- Route-based VPNs are IPsec connections that encrypt and encapsulate all traffic going through the XFRM interface
- With site-to-site IPsec, you can also manage IPsec connections using failover groups
- With IPsec profiles, they specify the encryption and authentication algorithms and key exchange mechanisms for policy-based and route-based IPsec connections. With IPsec profiles, you define the phase 1 and phase 2 security parameters, and assign a profile to IPsec connections
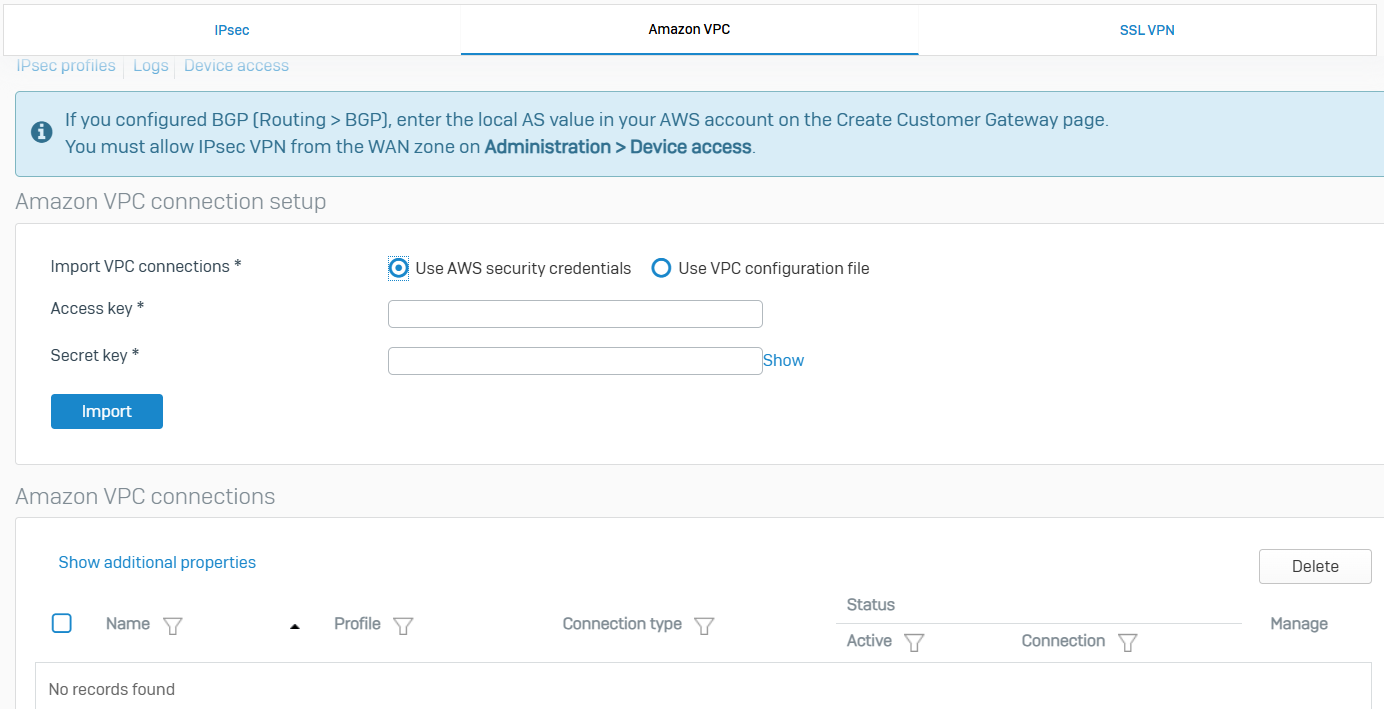
Amazon VPC
- Reference - Amazon VPC
- Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a cloud computing service that allows you to create virtual networks for your Amazon Web Service (AWS) resources
- You can connect Amazon VPC to Sophos Firewall by importing the connection information using your Amazon security credentials or a VPC configuration file
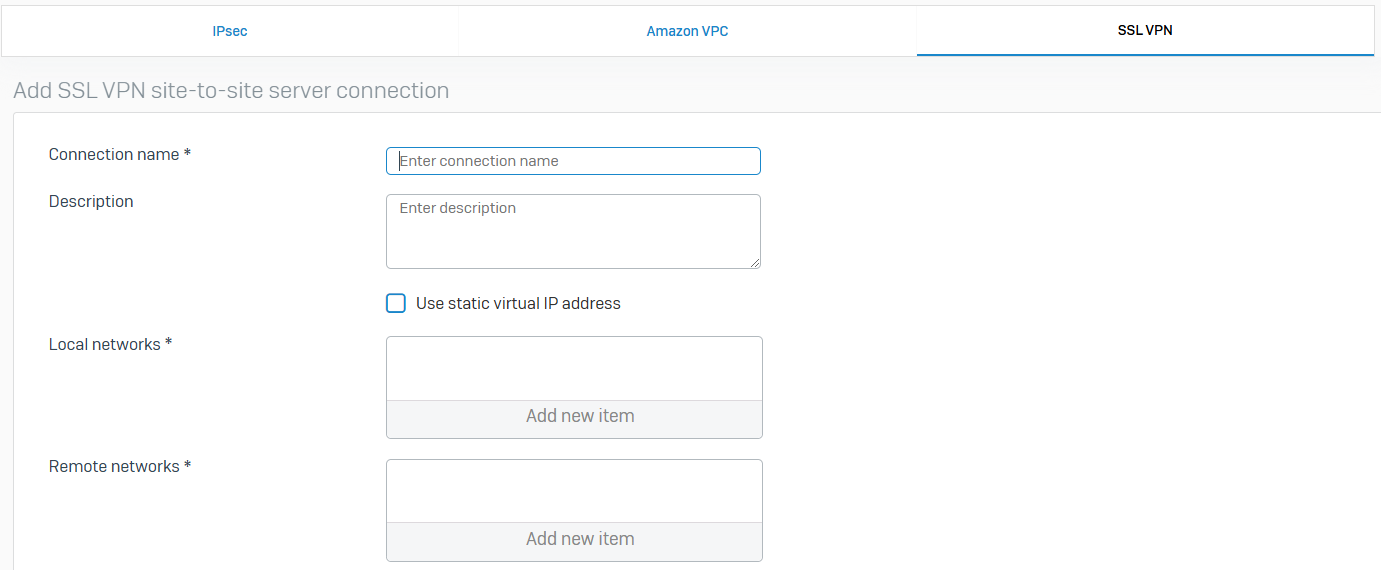
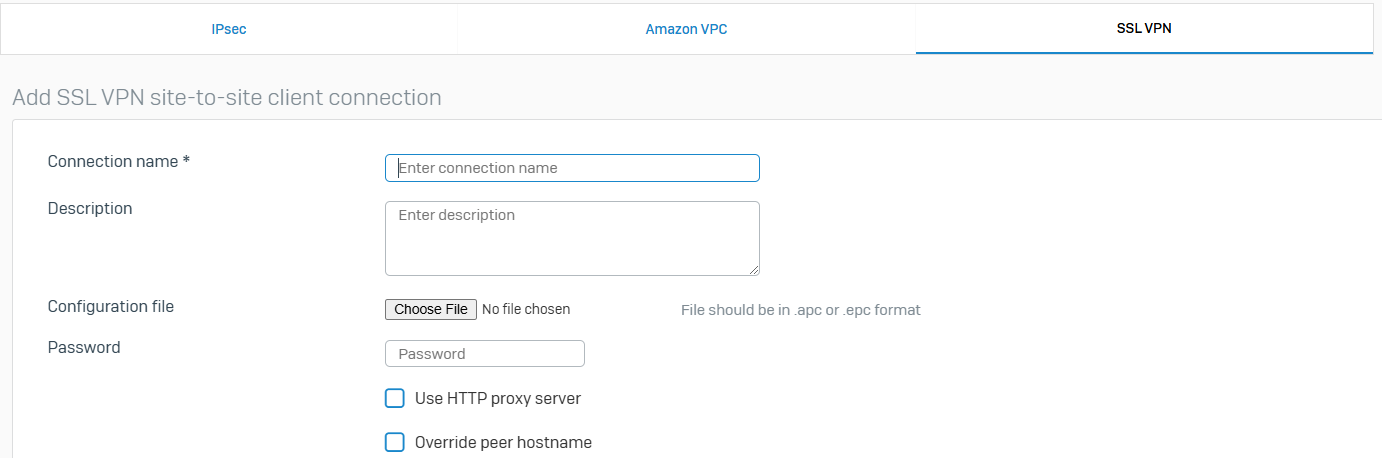
SSL VPN
- Reference - SSL VPN
- With site-to-site SSL VPN, you can provide access between internal networks over the Internet using point-to-point encrypted tunnels
- The tunnel endpoints act as either client or server. The client initiates the connection, and the server responds to client requests. This contrasts with IPsec where both endpoints can initiate a connection. An SSL VPN can connect from locations where IPsec encounters problems due to network address translation (NAT) and firewall rules
Network
Overview
- Network objects enhance security and optimize performance for devices behind the firewall. You can use these settings to configure physical ports, create virtual networks, and support RED devices
- Zones allow you to group interfaces and apply firewall rules to all member devices. Failover and load balancing provide network redundancy and availability
- Other settings allow you to provide secure wireless broadband service to mobile devices and configure advanced support for IPv6 device provisioning and traffic tunneling
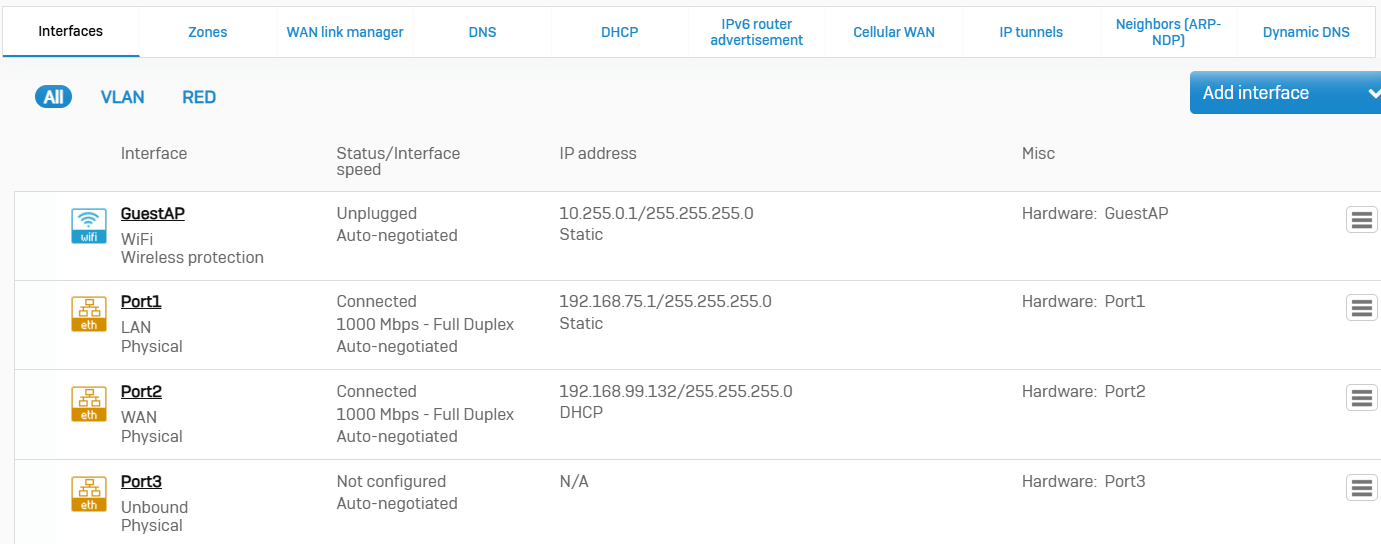
Interfaces
- Reference - Interfaces
- The firewall is shipped with physical and virtual interfaces. A physical interface, for example, Port1, PortA, or eth0. A virtual interface is a logical representation of an interface that lets you extend your network using existing ports. You can bind multiple IP addresses to a single physical interface using an alias
- Sophos Firewall is shipped with a limited number of physical interfaces. The number of interfaces available depends on the specific model of the device
- Sophos Firewall recognizes VLAN IDs, allowing you to apply firewall rules specific to each VLAN, including authentication and other relevant policies. You can also apply firewall rules to secure the network between broadcast domains
- Sophos Firewall supports the following LAG modes
- Active-Backup
- LACP (802.3ad)
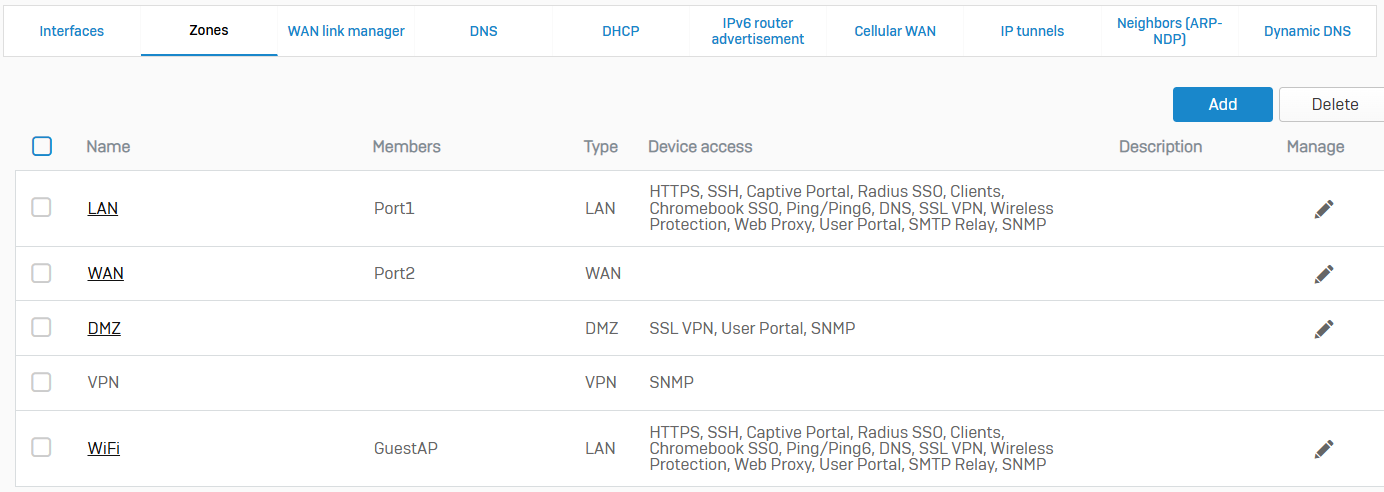
Zones
- Reference - Zones
- A zone is a grouping of interfaces. Zones also specify the services you can use to administer devices and authenticate users. When used with firewall rules, zones provide a convenient method of managing security and traffic for a group of interfaces
- Sophos firewall comes predefined with zones including LAN, WAN, DMZ, VPN, and WiFi
WAN Link Manager
- Reference - WAN Link Manager
- The WAN link manager allows you to configure gateways to support link failover and load balancing
- When you configure a physical WAN interface on 'Network > Interfaces', you can also specify its gateway settings based on your ISP link. If you have more than one ISP link, you can terminate each link on a physical WAN interface. The firewall sends traffic to the ISP link through the gateway configured for the link
- You can configure a gateway as active or backup. These gateways automatically appear on the WAN link manager list. The custom gateways you configure on 'Routing > Gateways' don't appear on this list even if you assign the WAN zone to them
DNS
- Reference - DNS
- You can obtain the address of a DNS server from a DHCP or PPPoE server, or you can specify static DNS servers
- With DNS host entries, you can can resolve requests for specific hosts using a specified IP address. If the host requested by the user matches the DNS host entry, the device resolves the query using the IP address specified. This provides faster resolution and reduces queries to the authoritative DNS server
- DNS request routes allows resolving requests for external domain names through DNS servers on your network. This provides faster resolution, decreases internet traffic over the network, and improves security as less DNS information is exposed on the Internet
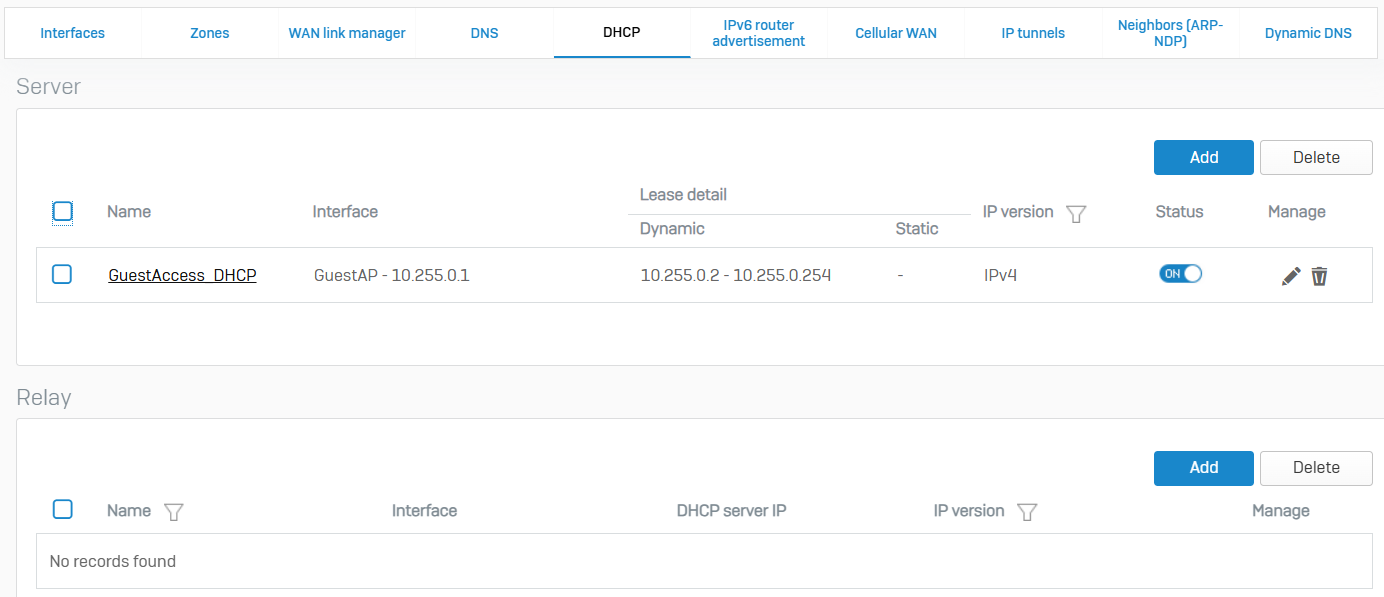
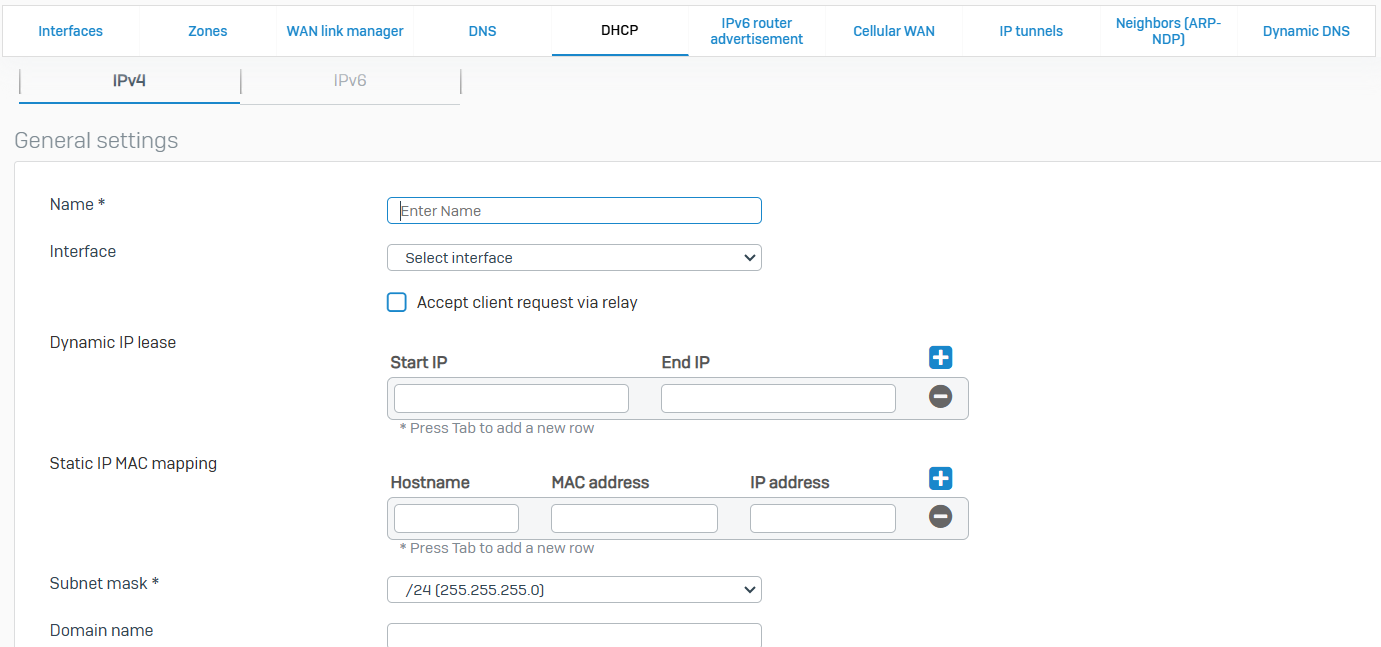
DHCP
- Reference - DHCP
- You can configure Sophos Firewall as a DHCP server and a relay agent to provide IP addresses and network parameters to clients
- Network parameters include the default gateway, subnet mask, domain name, DNS servers, and WINS servers. You can send additional parameters to clients using DHCP options on the CLI
- On the web admin console, you can also view lease records for IP addresses leased to clients
- With DHCP relay, it allows the Sophos Firewall to relay leased IP addresses and network parameters to clients, such as endpoints, servers, and routers, located on a different subnet from the DHCP server
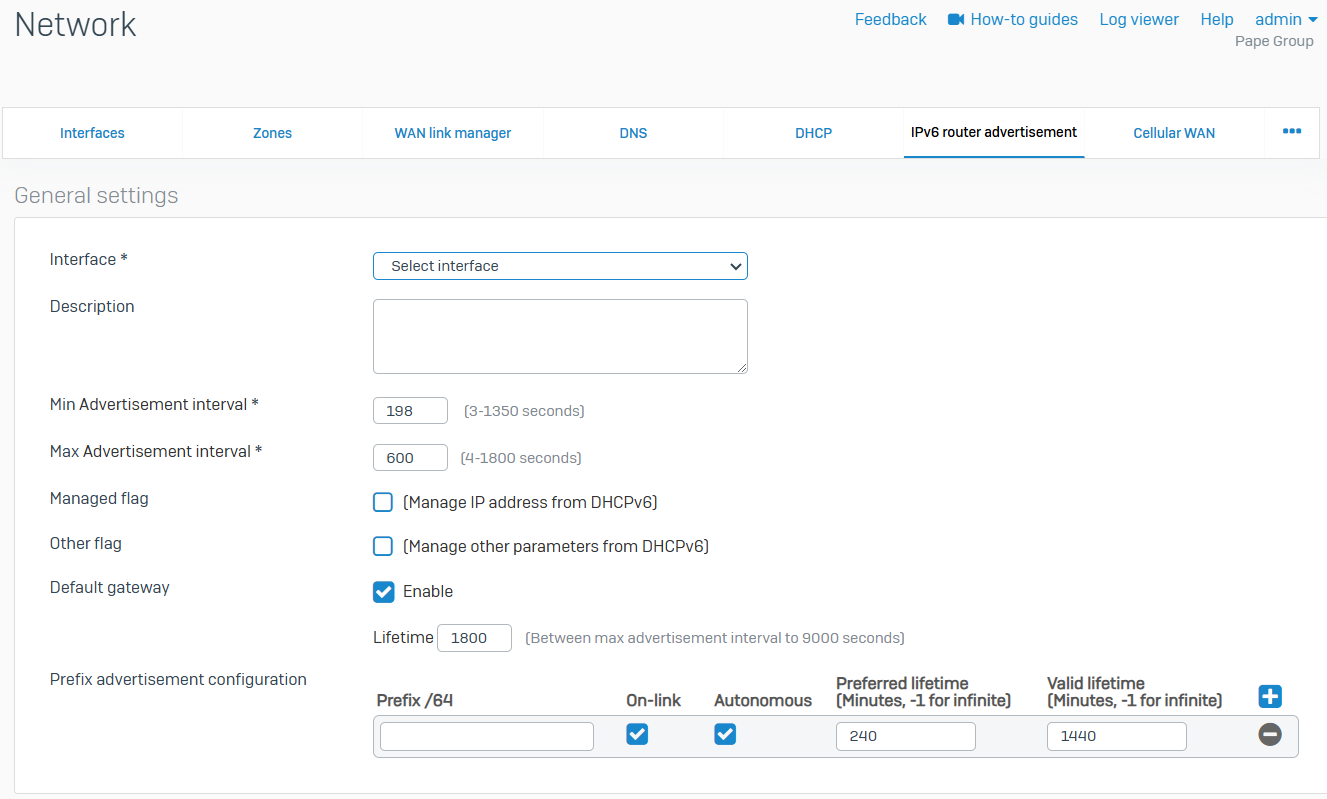
IPv6 Router Advertisement
- Reference - IPv6 Router Advertisement
- The firewall supports stateless address auto-configuration (SLAAC) for IPv6 devices
- Using SLAAC, IPv6 devices automatically create unique link-local addresses for IPv6-enabled interfaces, and clients automatically use router advertisement messages to configure their own IP address
- The firewall can participate in SLAAC. By default, the firewall provides an IPv6 address and a default gateway to the client
- Using SLAAC, the host sends an ICMPv6 Router Solicitation (RS) message that requests a Router Advertisement (RA). On receiving the RS message, the firewall sends an ICMPv6 router advertisement (RA) message announcing the state of its availability
- Router advertisements include information about the method to use for address assignment. For example, prefixes, hop limit value, and flag status. The device advertises information about various interfaces and internet parameters either periodically or in response to the RS message, informing all the nodes on the network about any address modifications
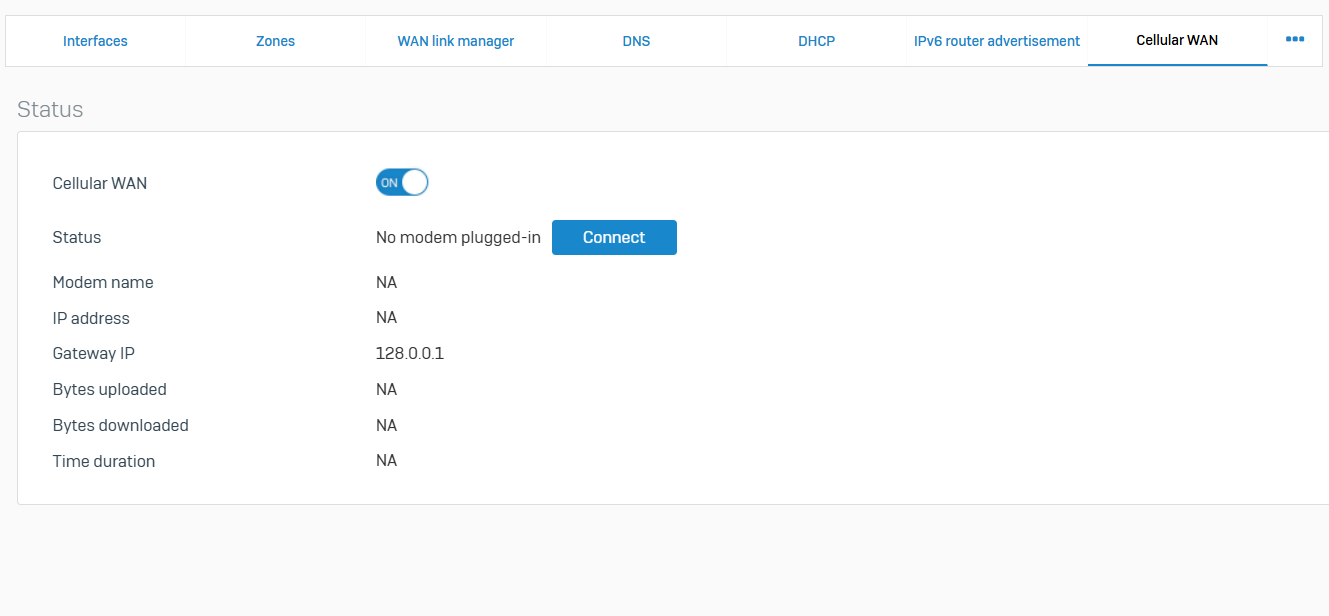
Cellular WAN
- Reference - Cellular WAN
- Cellular WAN networks provide secure wireless broadband service to mobile devices
- When you turn on cellular WAN, the firewall creates the WWAN1 interface. This interface is a member of the WAN zone, and the firewall rules for the WAN zone apply to it. The firewall also creates the ##WWAN1 host. You can protect against malware attacks and unauthorized usage by specifying firewall rules and policies for the host
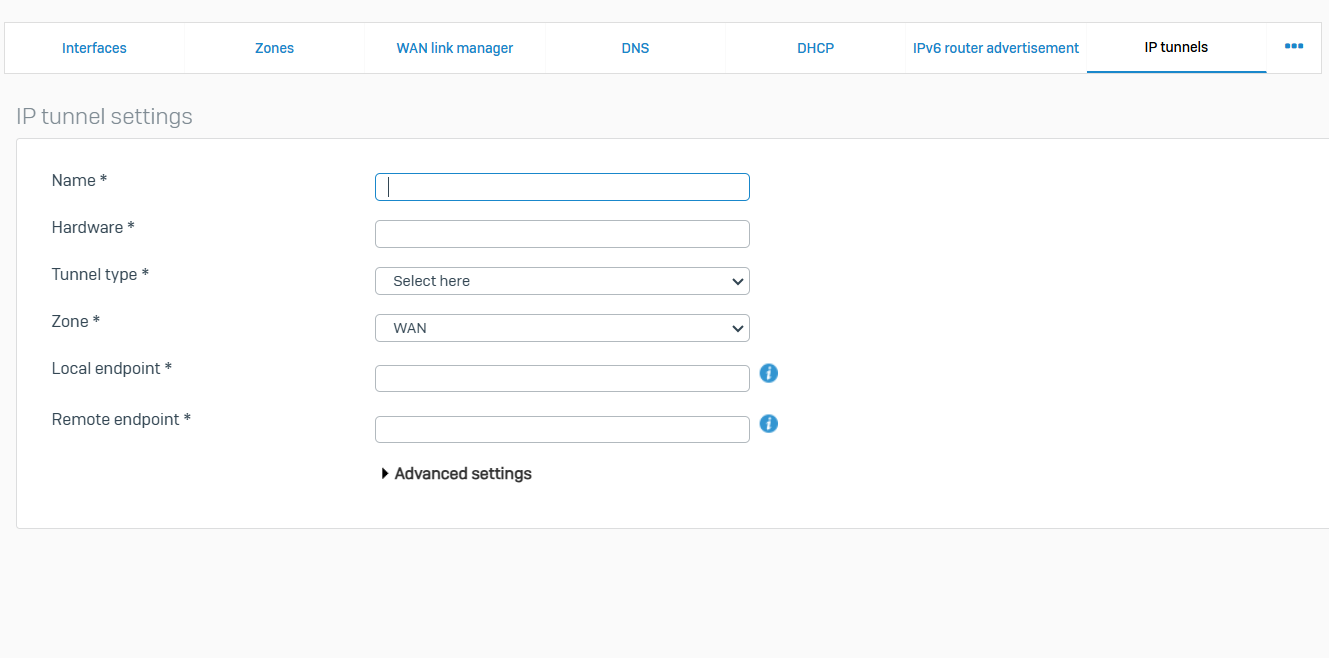
IP Tunnels
- Reference - IP Tunnels
- An IP tunnel is a mechanism that encapsulates one network protocol as a payload for another network protocol
- Using a tunnel, you can encapsulate an IPv6 packet into an IPv4 packet for communication between IPv6-enabled hosts or networks over an IPv4 network, or vice versa
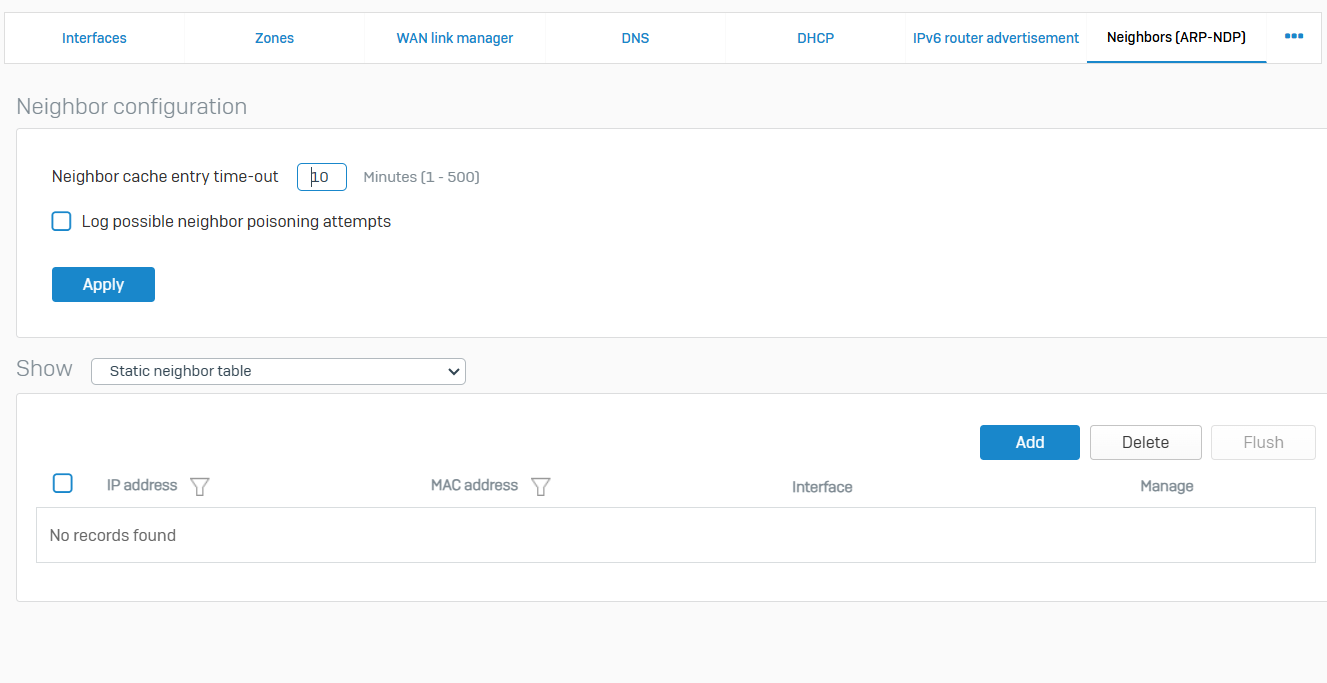
Neighbors (ARP-NDP)
- Reference - Neighbors (ARP-NDP)
- Sophos Firewall uses the ARP and NDP to enable communication between hosts residing on the same subnet. It uses these protocols to create IP/MAC mappings and stores them in neighbor caches. Static mappings are also supported. The firewall uses cached entries to detect neighbor poisoning attempts
- ARP is used for discovering the link layer address (MAC address) associated with an IPv4 address. Hosts find the physical address of other hosts by sending an ARP query packet that includes the IP address of the receiver. When the response is returned, the firewall updates the neighbor cache with the corresponding MAC address. To minimize the broadcast traffic, the firewall reuses previously learned IP/MAC mappings. NDP provides similar functionality for IPv6 addresses
- The default timeout for ARP and NDP requests is 600 seconds (10 minutes)
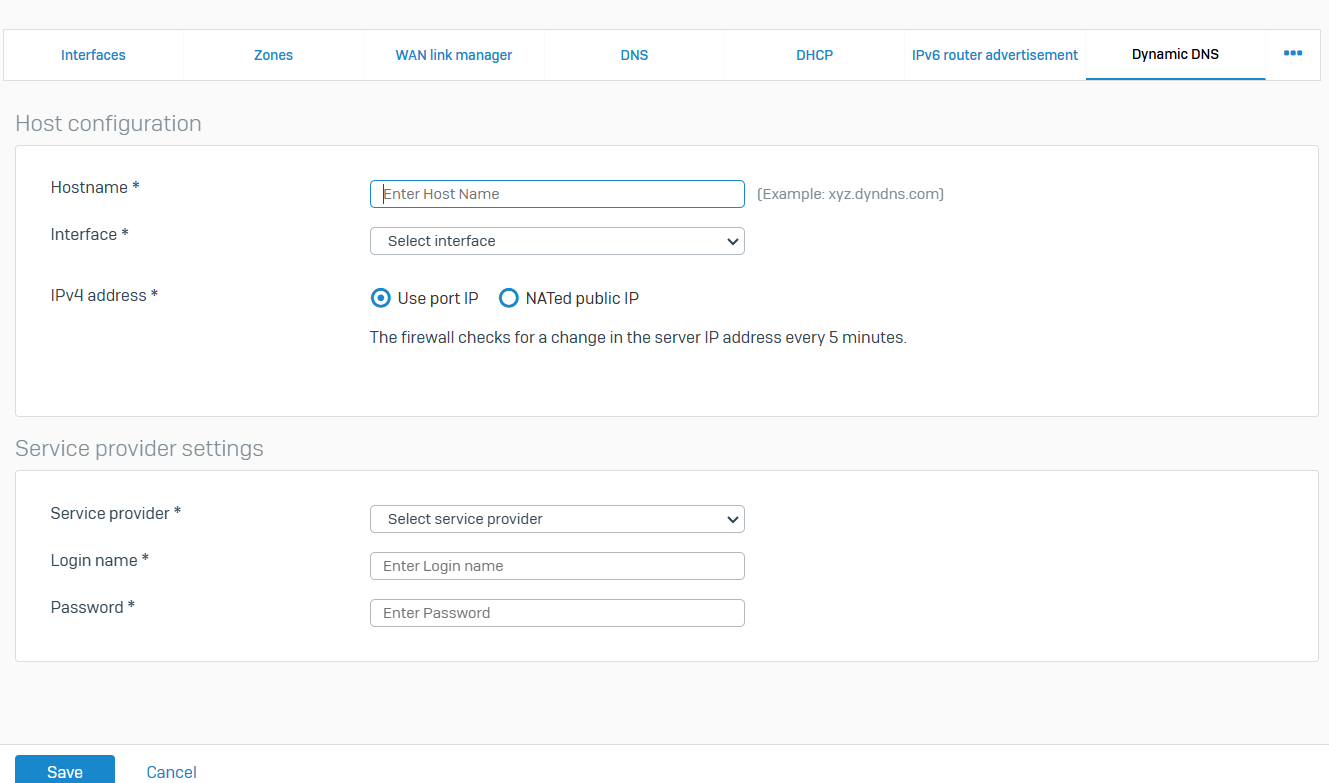
Dynamic DNS
- Reference - Dynamic DNS
- Dynamic DNS (DDNS) enables you to access the firewall when it is provisioned with a dynamic IP address
- When the firewall receives a new IP address, it contacts the dynamic DNS service and updates the public DNS name with the new address. Using DDNS, the public DNS name always points to the correct IP address
- Sophos Firewall supports the following third party DDNS providers
- DynDNS
- DynAccess
- EasyDNS
- ZoneEdit
- Google DDNS
- FreeDNS
Routing
Overview
- Routes enable Sophos Firewall to forward traffic based on the criteria you specify
- You can configure SD-WAN, static, dynamic routes. Sophos Firewall creates VPN routes for IPsec traffic automatically
- With Route Precedence, the default routing order is 'static, SD-WAN, and then VPN routes'
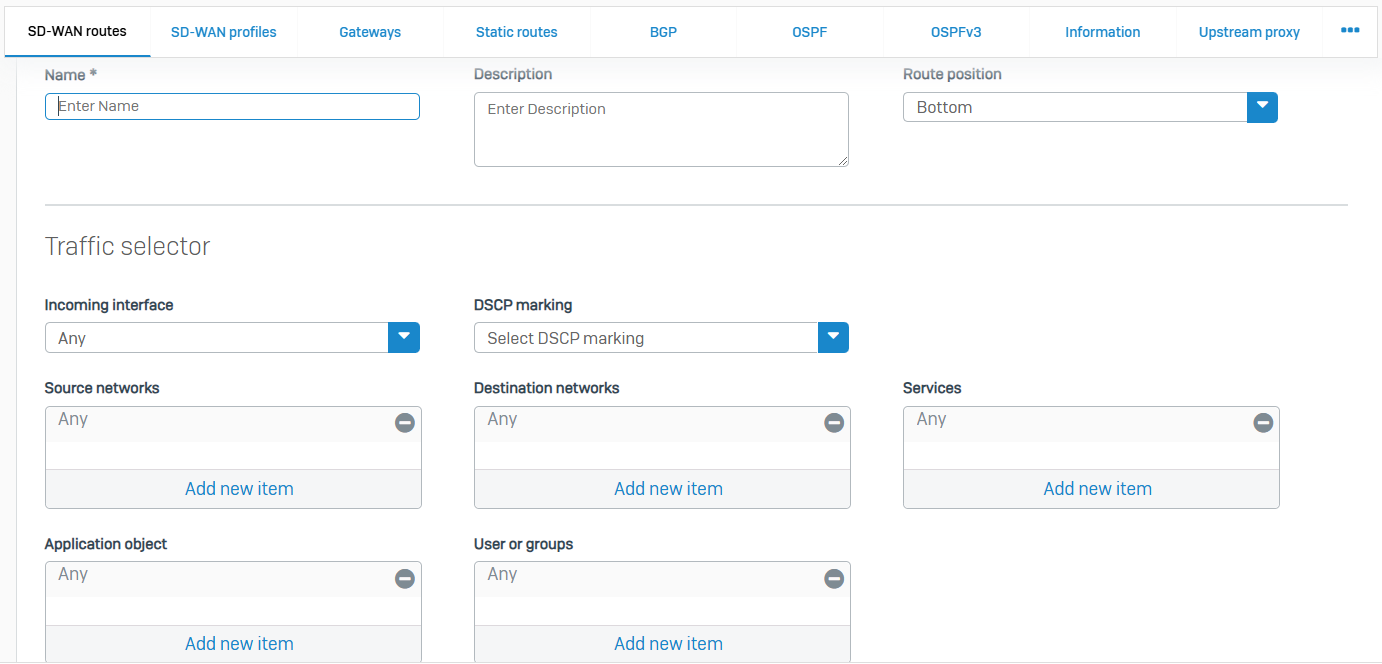
SD-WAN Routes
- Reference - SD-WAN Routes
- Software-defined WAN (SD-WAN) adds a layer of software intelligence to your WAN infrastructure
- SD-WAN routes deliver zero-impact failover with performance SLAs for multiple gateways, enabling you to optimize your WAN infrastructure
- You can route traffic based on applications, users and groups, and network criteria, such as the incoming interface, source and destination networks, and services. You can implement Service Level Agreements (SLA) for gateway performance
SD-WAN Profiles
- Reference - SD-WAN Profiles
- You can use SD-WAN profiles to define an SD-WAN routing strategy across multiple gateways in your SD-WAN network. With two or more gateways configured in your network, you can use an SD-WAN profile to route traffic based on the availability or performance of the gateways. This approach optimizes the performance of your SD-WAN network and helps ensure continuity in the event of an ISP disruption
- When configuring an SD-WAN profile, you add the configured gateways to the SD-WAN profile and list them in the order you want the firewall to evaluate them. If you want to route traffic based on the availability of the gateways, select the 'First available gateway' routing strategy. The firewall performs a health check on all the added gateways in the order you listed and selects the first available gateway
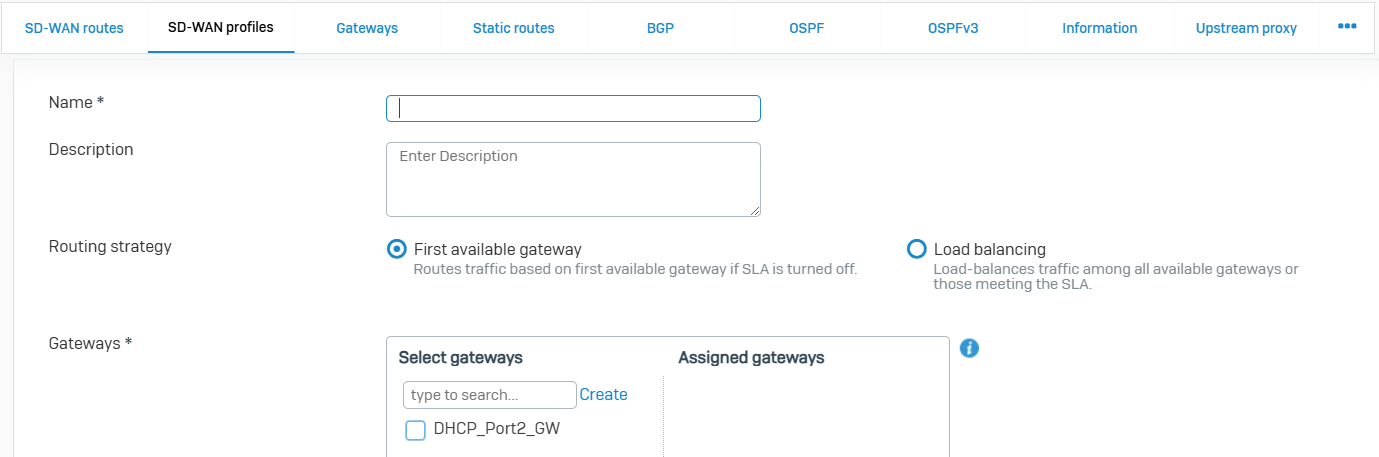
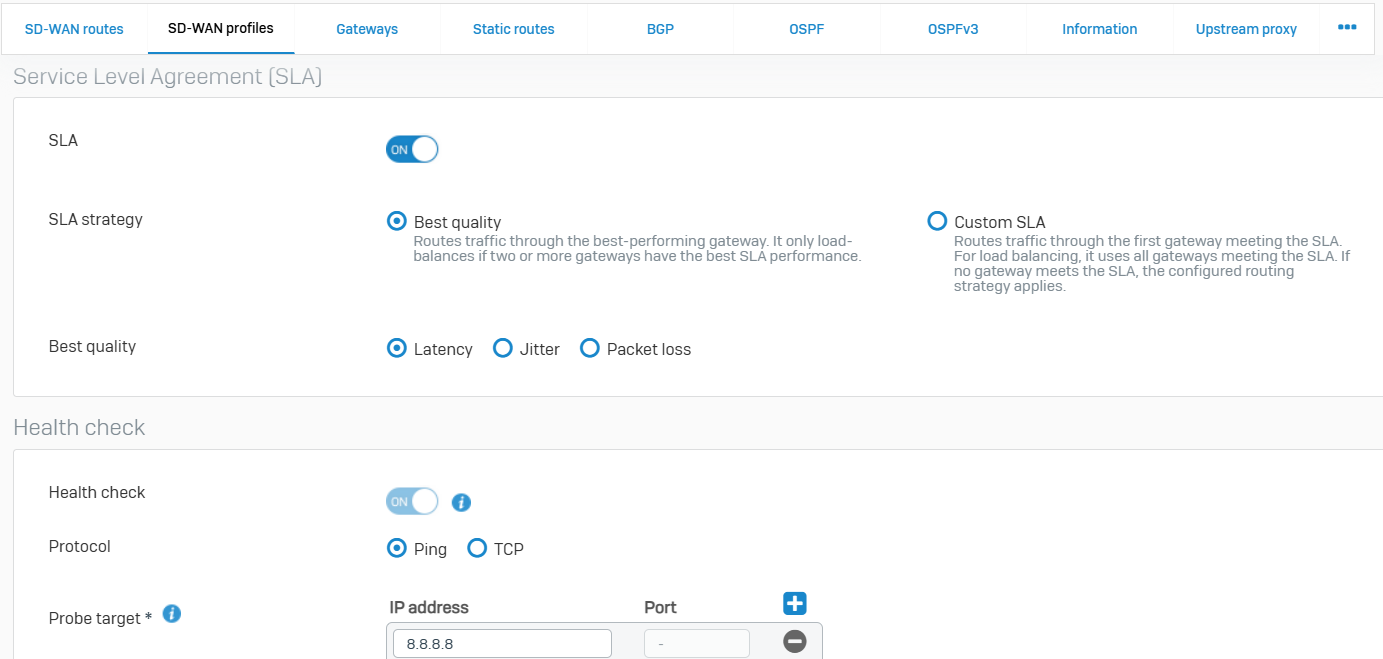
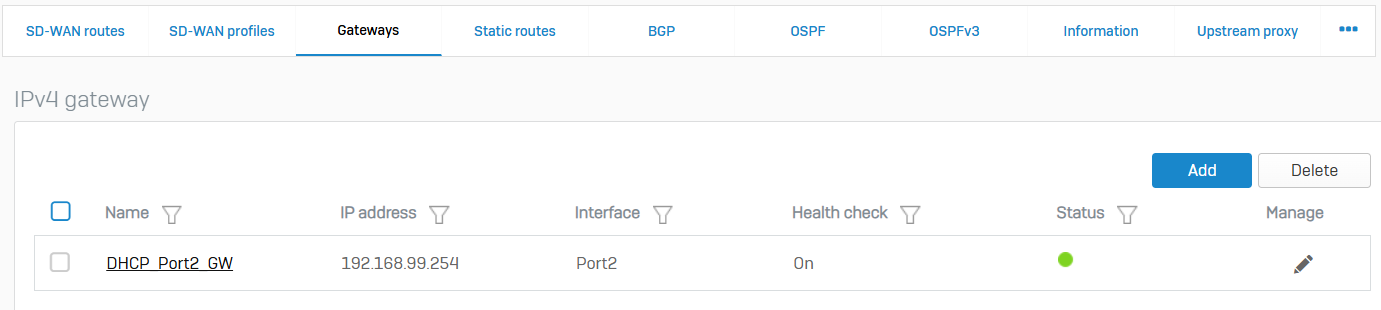
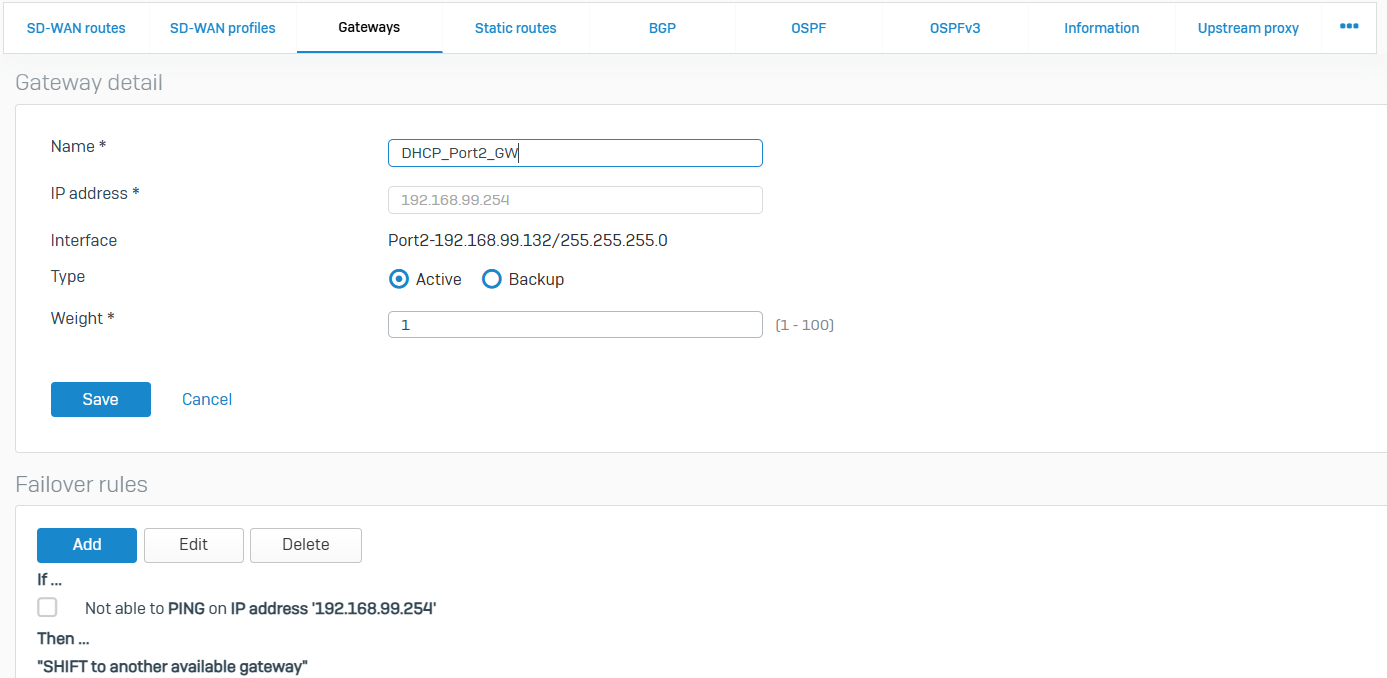
Gateways
- Reference - Gateways
- You can add gateways to forward traffic within the network and to external networks
- You can add IPv4 and IPv6 gateways. You can also edit, clone, and delete custom gateways
- Health check: Sophos Firewall applies the health check conditions you specify to determine if the gateway is active
- Gateway zones: You can assign a zone to custom gateways. Sophos Firewall only applies the zone to traffic when the gateway is assigned to a matching SD-WAN policy route
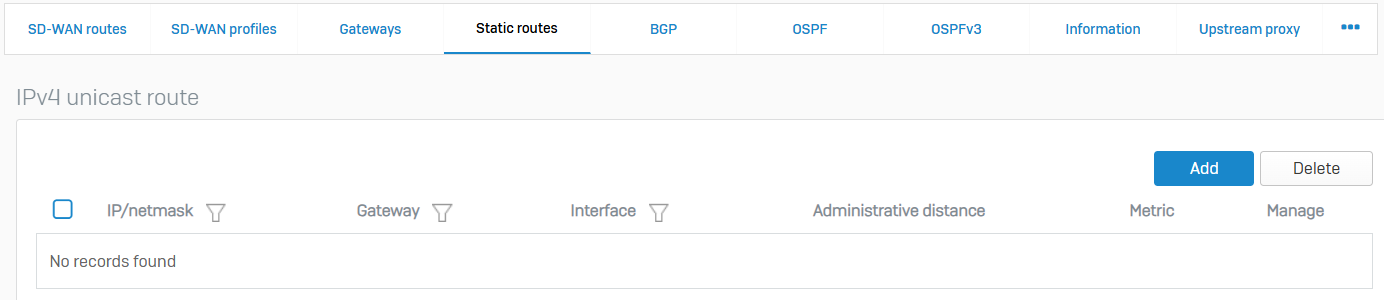
Static Routes
- Reference - Static Routes
- You can create a static route to forward packets to a destination other than the configured default gateway
- When you add a static route, you specify which interface the packet leaves, and to which device the packet is routed
- You can configure unicast and multicast routes on the Sophos Firewall
- Unicast routes send data from a sender to a recipient
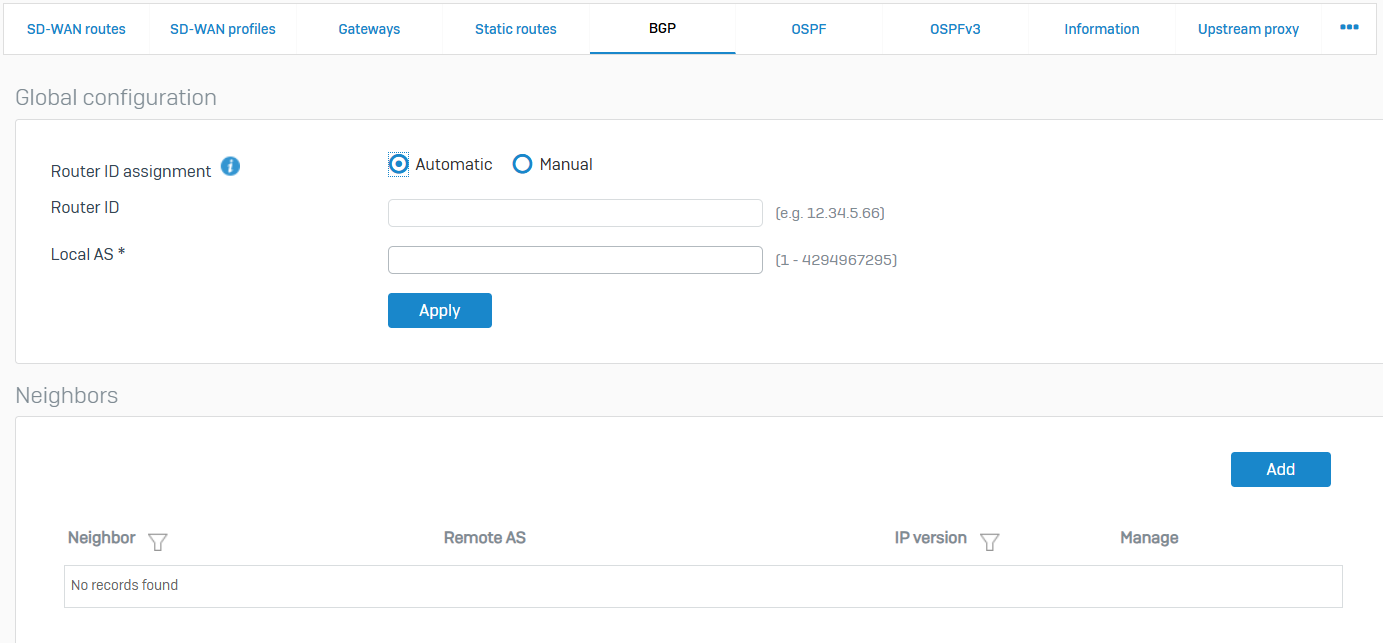
BGP
- Reference - BGP
- You can manage BGP routes
- BGP or Border Gateway Protocol is a path vector protocol that contains path information. It enables the routers to share routing information between autonomous systems (AS) so that loop-free routes can be created. ISPs generally use this protocol
- An AS is a connected group of networks or routers under the control of a single administrative entity. They share common routing policies. A unique AS number is assigned to each AS to identify them uniquely
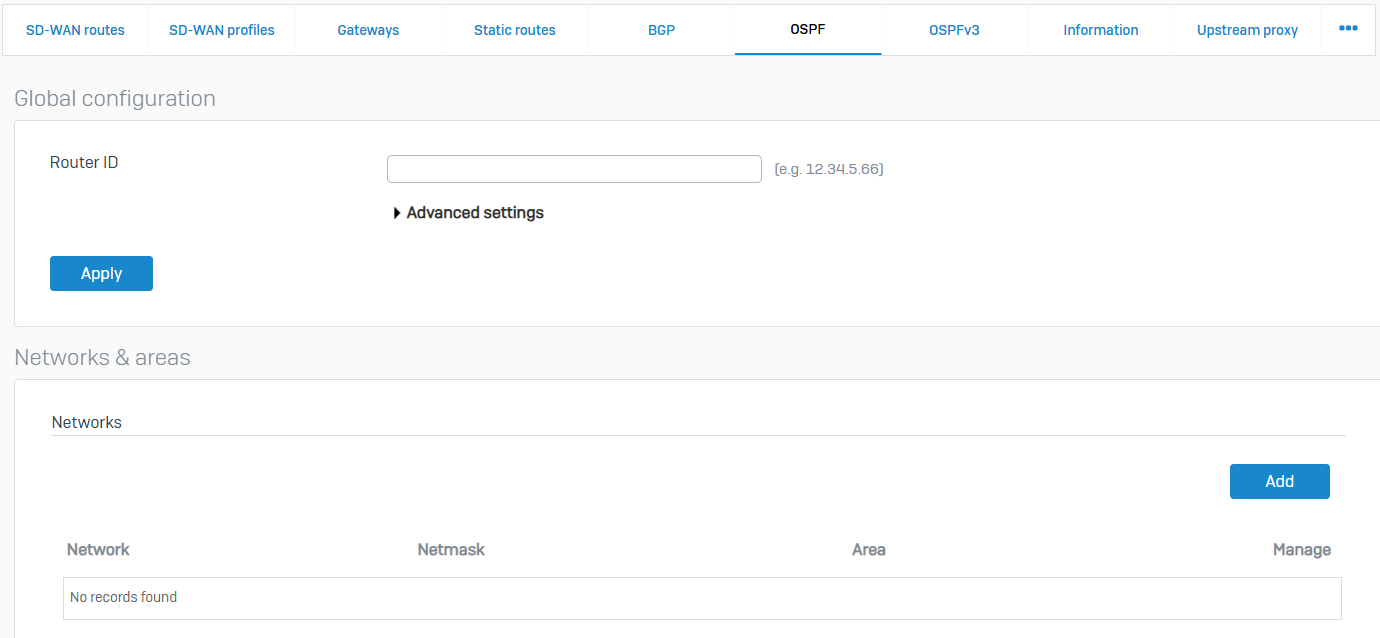
OSPF
- Reference - OSPF
- You can create OSPF routes on a Sophos Firewall
- OSPF or Open Shortest Path First is a link-state routing protocol that multicasts the routing information to all the hosts within a single network. It sends routing information to all the routers in the network by calculating the shortest path to each router based on the structure built up by each router
OSPFv3
- Reference - OSPFv3
- Just like OSPF, OSPFv3 or version 3 can be configured on a Sophos Firewall
- OSPF supports IPv4. OSPFv3 supports IPv4 and IPv6
- OSPFv3 also supports interface configuration
Information
- Reference - Information
- You can view any dynamic routes configured using the RIP, OSPF, BGP, and PIM-SM protocols
- You can use this information for further configuration and debugging
Upstream Proxy
- Reference - Upstream Proxy
- Sophos Firewall can send outgoing web requests from your network to the WAN zone through an upstream parent proxy
- When you configure an upstream proxy with Sophos Firewall, you don't need to configure users' browsers to send traffic to the upstream proxy
- You can add a single upstream proxy to Sophos Firewall. The proxy can be in the LAN, DMZ, or WAN zones. Sophos Firewall forwards all web requests from your network to the upstream proxy. The proxy then sends the requests to the Internet
- The DPI engine doesn't support upstream proxy. Select 'Use web proxy instead of DPI engine' in the firewall rule used for your web traffic
Multicast (PIM-SM)
- Reference - Multicast (PIM-SM)
- Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) is a protocol for routing IP packets efficiently to multicast groups that may span the Internet. PIM provides dynamic multicast support on the device. With dynamic multicast support, a host can join or leave a multicast group dynamically, and you don't need to add or delete multicast routing entries on the device manually
- The device supports PIM version 2 and PIM-SM mode with Rendezvous Point (RP) selection method as BSR (Bootstrap Router)
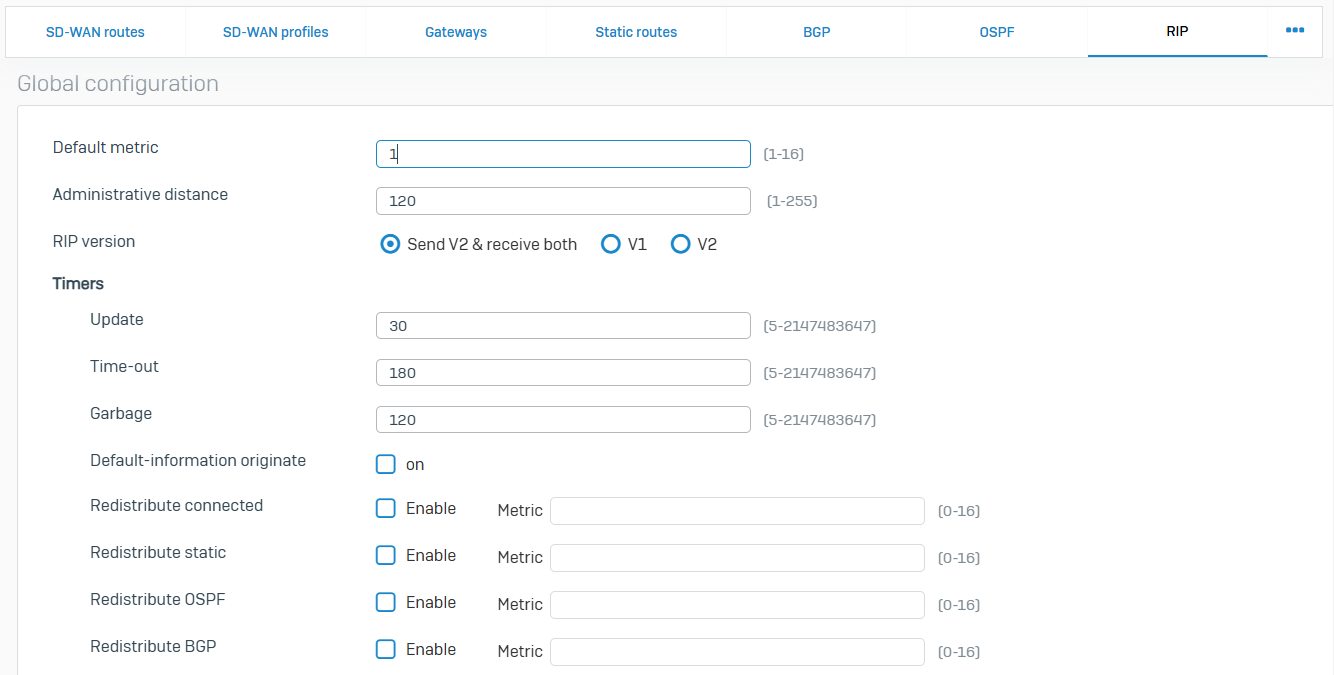
RIP
- Reference - RIP
- You can manage RIP routes and add, update, or delete the network and interface configuration
- Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a routing protocol that uses hop count to determine the best route to a destination
- RIP avoids routing loops from continuing indefinitely by limiting the number of hops permitted between the source and destination. The maximum number of hops supported is 15. So, if the hop count becomes 16, it is known as an infinite distance and is considered unreachable
Authentication
Overview
- You can set up authentication using an internal user database or third-party authentication service. To authenticate themselves, users must have access to an authentication client. However, they can bypass the client if you add them as clientless users
- The firewall also supports two-factor authentication, transparent authentication, and guest user access through a captive portal
Servers
- Reference - Servers
- External servers authenticate users who are attempting to access the firewall and associated services
- The following servers can be added to Sophos Firewall
- LDAP severs
- Active Directory servers
- RADIUS servers
- TACACS servers
- eDirectory servers
Services
- Reference - Services
- Select the authentication servers for the firewall and other services such as VPN. You can configure global authentication settings, as well as settings for Kerberos and NTLM, web client, and RADIUS single sign-on. Web policy actions let you specify where to direct unauthenticated users
- Firewall authentication methods, VPN authentication methods, Administrator authentication methods, SSL VPN authentication methods, Global settings, NTLM settings, Web client settings, SSO using RADIUS accounting request, and Chromebook SSO are all available settings on this page
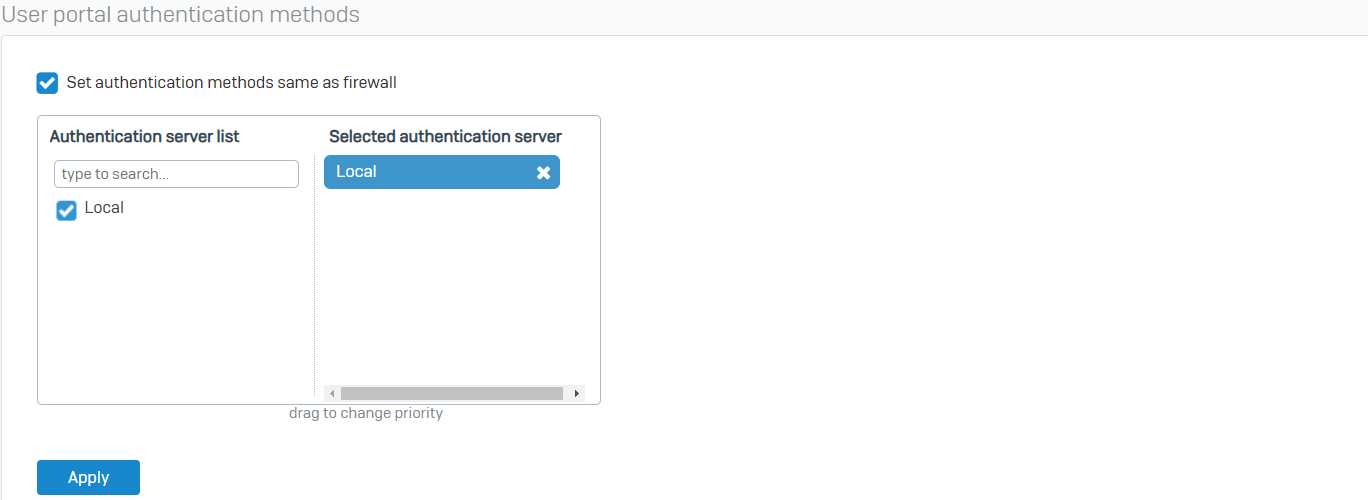
Groups
- Reference - Groups
- Groups contain policies and settings you can manage as a single unit for users. With groups, you can simplify policy management for users
- If you use authentication servers, such as Active Directory, users are automatically created and added to their directory group when they sign in. Directory users who belong to an organizational unit (OU) but not to a directory group are added to the default group when they sign in. You can see the default group on 'Authentication > Services' under 'Firewall authentication methods'
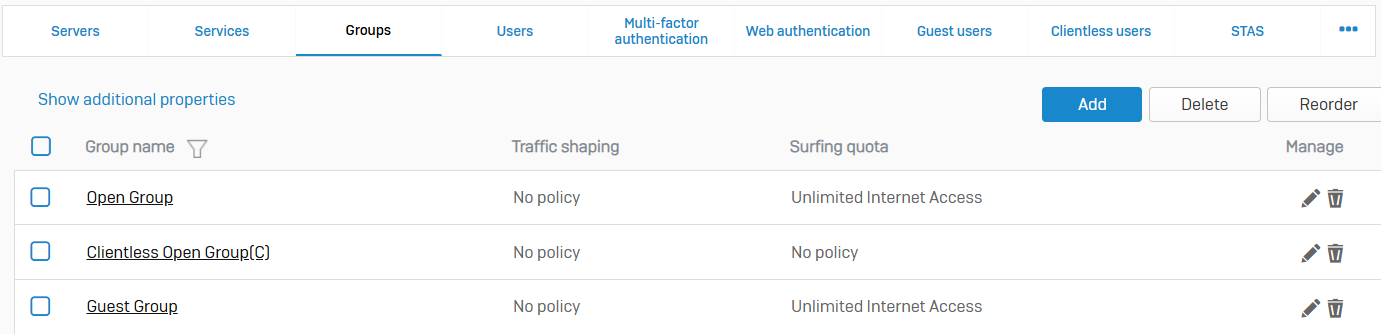
Users
- Reference - Users
- You can create user records locally on the firewall for users and administrators
- The list also shows the users on your external authentication servers. These records are added when users are authenticated for the first time
- A user can belong to more than one group
- The firewall applies the group's settings if you select only the group in rules and policies. It applies the user's settings if you select both the user and their group
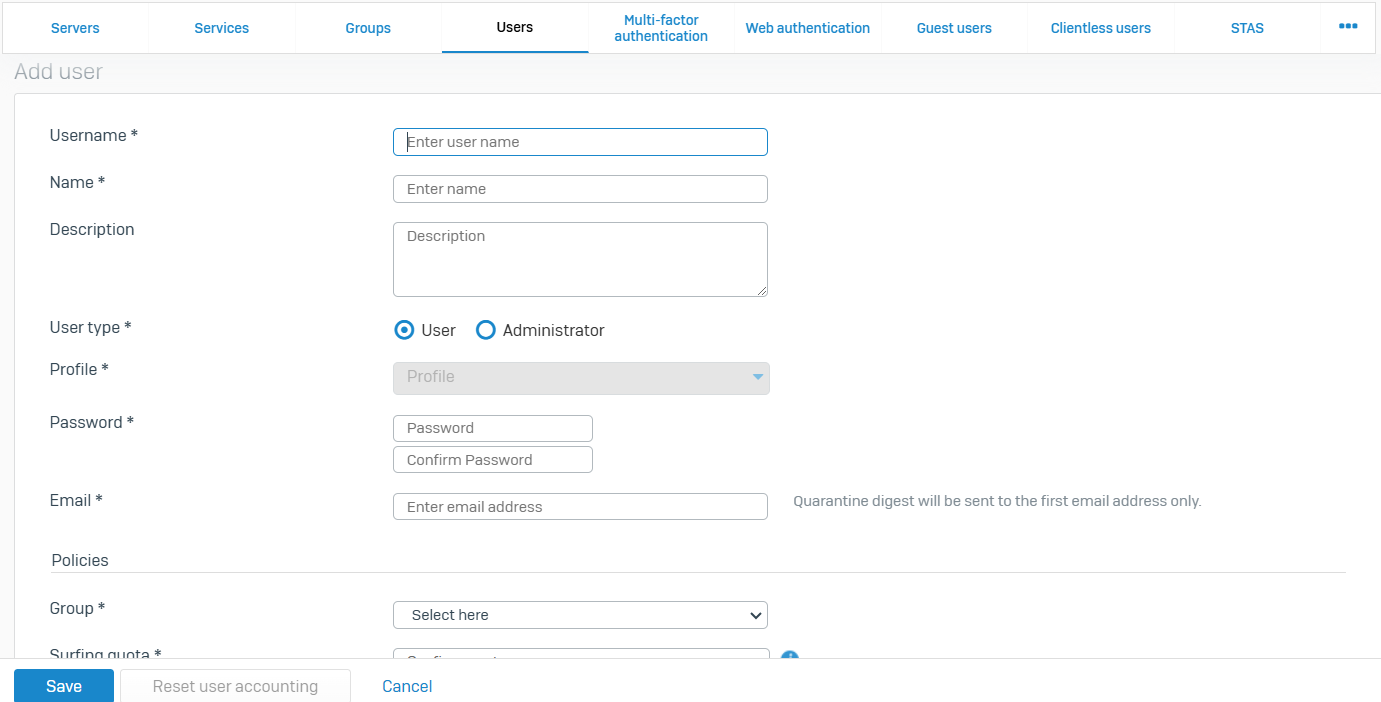
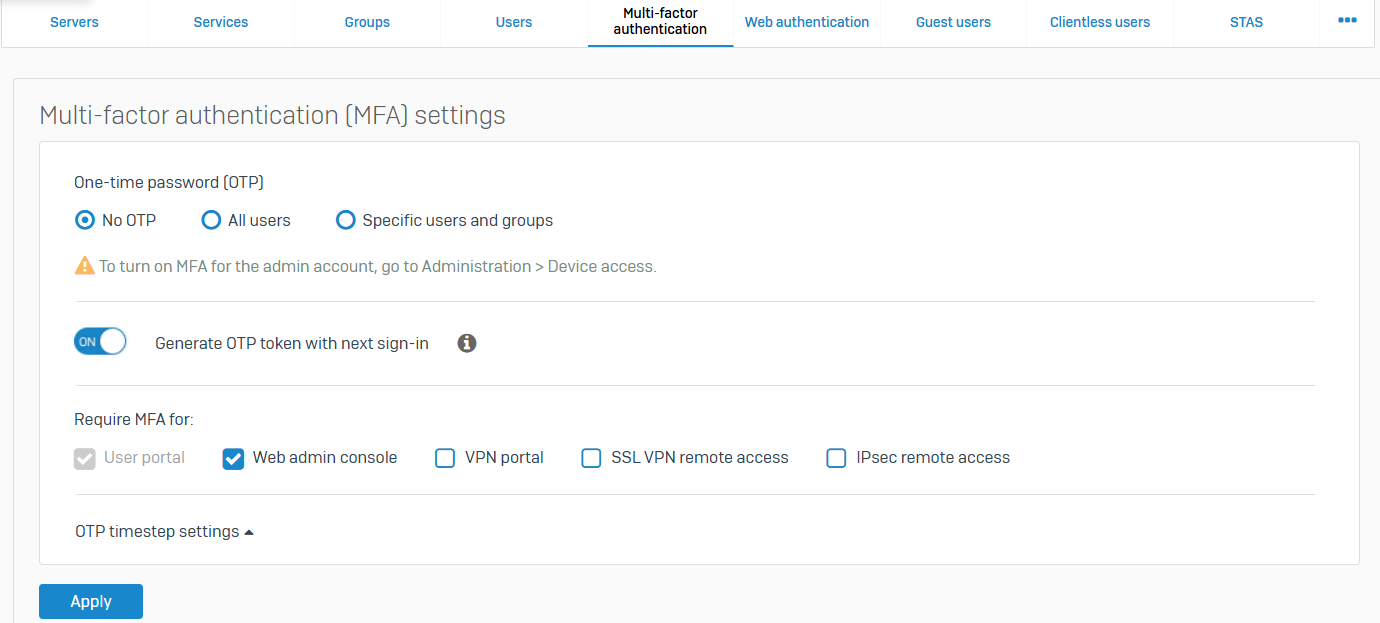
Multi-factor Authentication
- Reference - Multi-factor Authentication
- You can implement multi-factor authentication using hardware or software tokens
- You can configure MFA and apply it to users signing in to certain firewall services, such as the user portal and remote access VPN. The settings determine whether users can use software or hardware tokens
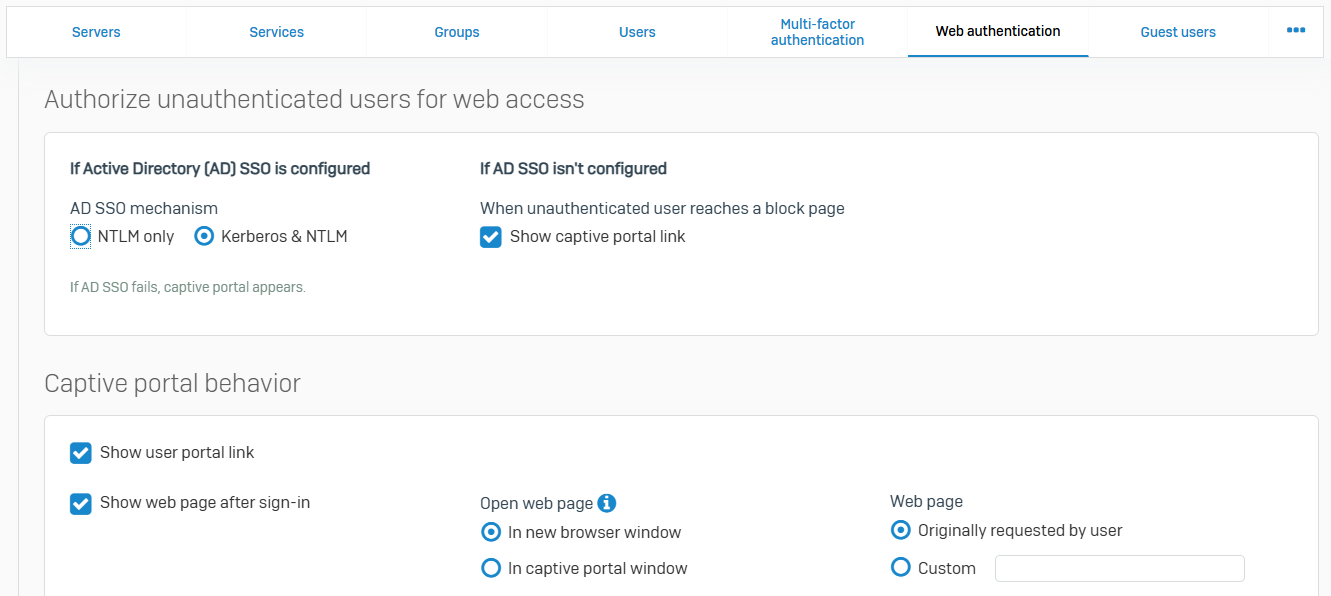
Web Authentication
- Reference - Web Authentication
- You can use Active Directory SSO or the captive portal to authenticate users. Users will then appear in logging and reporting and will be used as matching criteria in firewall rules and web policies
- Active Directory single-sign-on (SSO) attempts to silently authenticate users signed in to endpoint devices with Sophos Firewall without user interaction
- The captive portal is a web page that requires users behind the firewall to authenticate when attempting to access a website. You can also define the behavior and layout of the captive portal
- After authenticating with the captive portal, Sophos Firewall allows users to proceed to their requested destination or redirects them to a URL that you specify
Guest Users
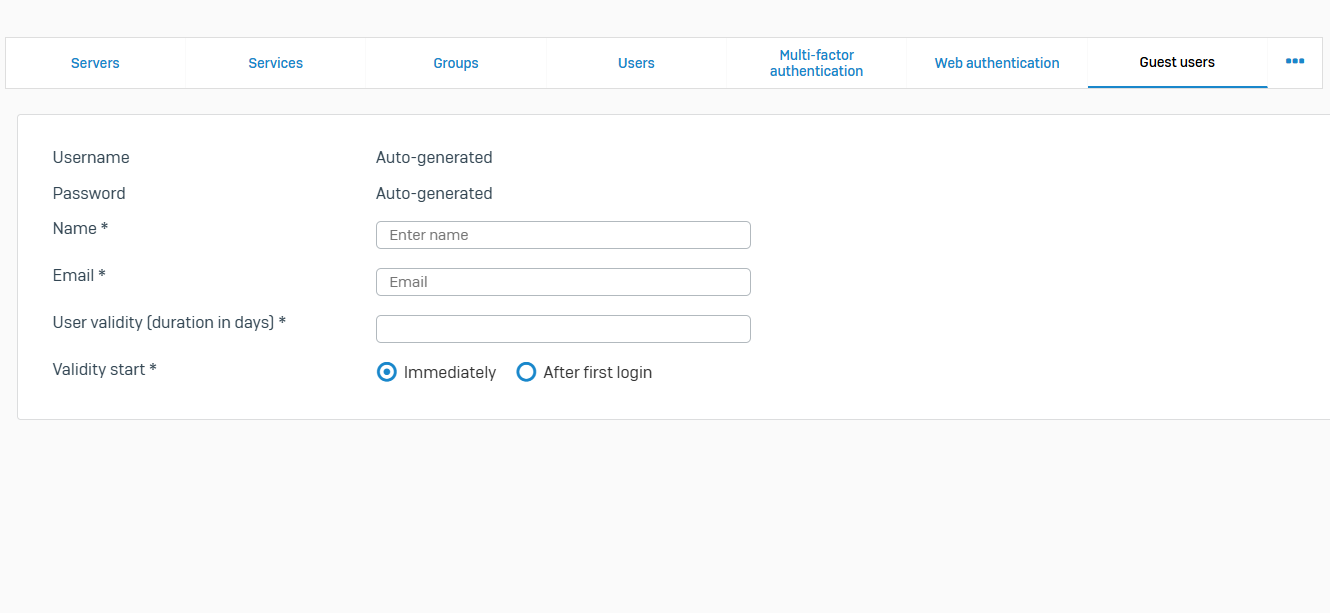
- Reference - Guest Users
- Guest users are users who don't have an account and want to connect to your network to access the internet. You can register guest users or allow them to register through the guest user portal. You can print credentials or send them SMS. After authentication, the guest user is granted access according to the selected policies or is redirected to the captive portal
- Before you add guest users, go to 'Authentication > Guest user settings' and specify settings
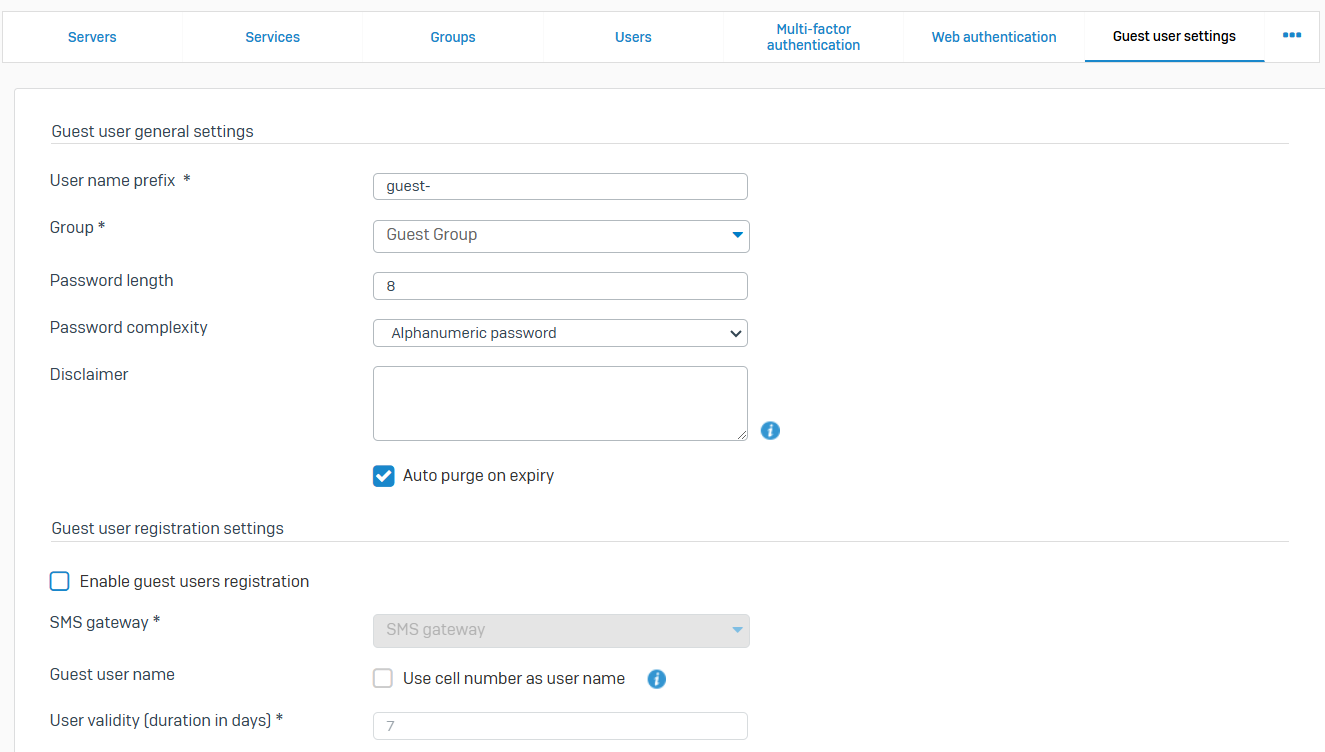
Guest User Settings
- Reference - Guest User Settings
- Use these settings to allow guest users to register through the guest user registration page and to configure guest user authentication settings and default group
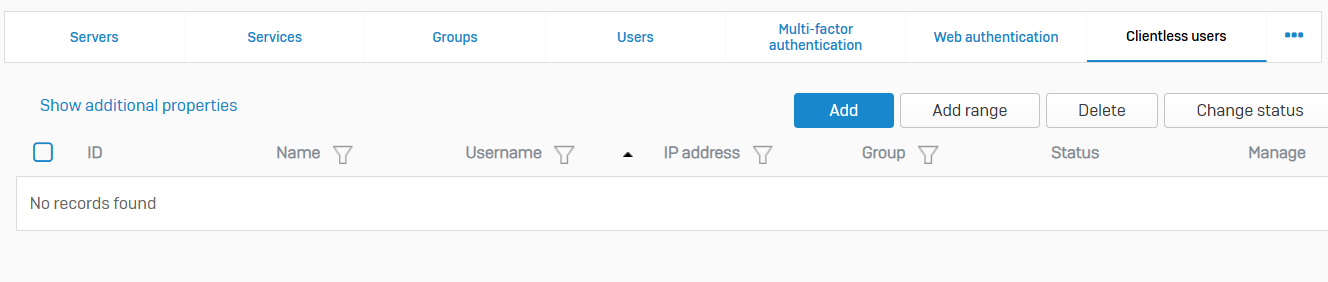
Clientless Users
- Reference - Clientless Users
- You can configure network devices, such as servers and printers, as clientless users
- Clientless users don't require authentication and don't use a client to access the network. Sophos Firewall allows these users to access the network by matching the username to the IP address you specify in the clientless user policy
- Clientless users appear as live users in current activities. If you deactivate these users, they don't appear as live users
- You can also configure people as clientless users. For example, senior executives, for whom you don't want to require a sign-in when they're within the network. If you configure users rather than network devices, Sophos recommends that you map the users with static IP addresses on your DHCP server
STAS
- Reference - STAS
- Sophos Transparent Authentication Suite (STAS) enables users on a Windows domain to sign in to Sophos Firewall automatically when signing in to Windows. This eliminates the need for multiple sign-ins and for SSO clients on each client device
- STAS consists of an agent and a collector. The agent monitors user authentication requests and sends information to the collector for authentication. The collector collects the user authentication requests from the agent, processes the requests, and then sends them to the firewall for authentication
Client Downloads
- Reference - Client Downloads
- Use these settings to download the clients and components that support single sign-on, transparent authentication, and email encryption
- You can use transparent clientless authentication through STAS and SATC or authentication through the clients installed on users' endpoints
System Services
Overview
- Use system services to configure the RED provisioning service, high availability, and global malware protection settings
- Other options let you view bandwidth usage and manage bandwidth to reduce the impact of heavy usage
- Using log settings, you can specify system activity to log and how to store logs
- Data anonymization allows you to encrypt identities in logs and reports
High Availability
- Reference - High Availability
- Sophos Firewall supports high availability. This ensures WAN connectivity, appliance availability, and failover of traffic and services, which minimizes downtime and disruption to your network
- High Availability (HA) allows you to place two firewalls in a group and synchronize their configuration. This prevents a single point of failure on your network. The two firewalls have a heartbeat connection, which ensures failover if one of the firewalls goes down
Traffic Shaping Settings
- Reference - Traffic Shaping Settings
- The firewall applies traffic shaping settings to traffic that doesn't match any traffic shaping policy
RED
- Reference - RED
- A Remote Ethernet Device (RED) provides a secure tunnel between a remote site and Sophos firewall
- REDs connect remote branch offices to your main offices as if the branch office is part of your local network. Using RED interfaces, you can configure and install RED appliances or create site-to-site RED tunnel between two Sophos Firewall devices in a client-server configuration
Malware Protection
- Reference - Malware Protection
- From this page, you can specify malware protection settings
Log Settings
- Reference - Log Settings
- Sophos Firewall provides event logs for traffic, system, and network protection functions. You can use logs to analyze network activity and identify security issues
- You can select the log types to store the logs locally and see them in the Log viewer or send them to Sophos Central or external syslog servers
Notification List
- Reference - Notification List
- You can send alerts to an administrator about system generated events through email notifications and SNMP traps
- You need to configure your email settings before you can send email notifications. To do this, go to 'Administration > Notification settings'
- You need to configure the SNMP agent and the communities or users before you can send SNMP alerts. To do this, go to 'Administration > SNMP'
Data Anonymization
- Reference - Data Anonymization
- Using data anonymization, you can encrypt identities in logs and reports. Identities include user names, IP addresses, MAC addresses and email addresses. When you enable data anonymization, you specify one or more administrators who are authorized to de-anonymize the data
- You can also override anonymization using exceptions
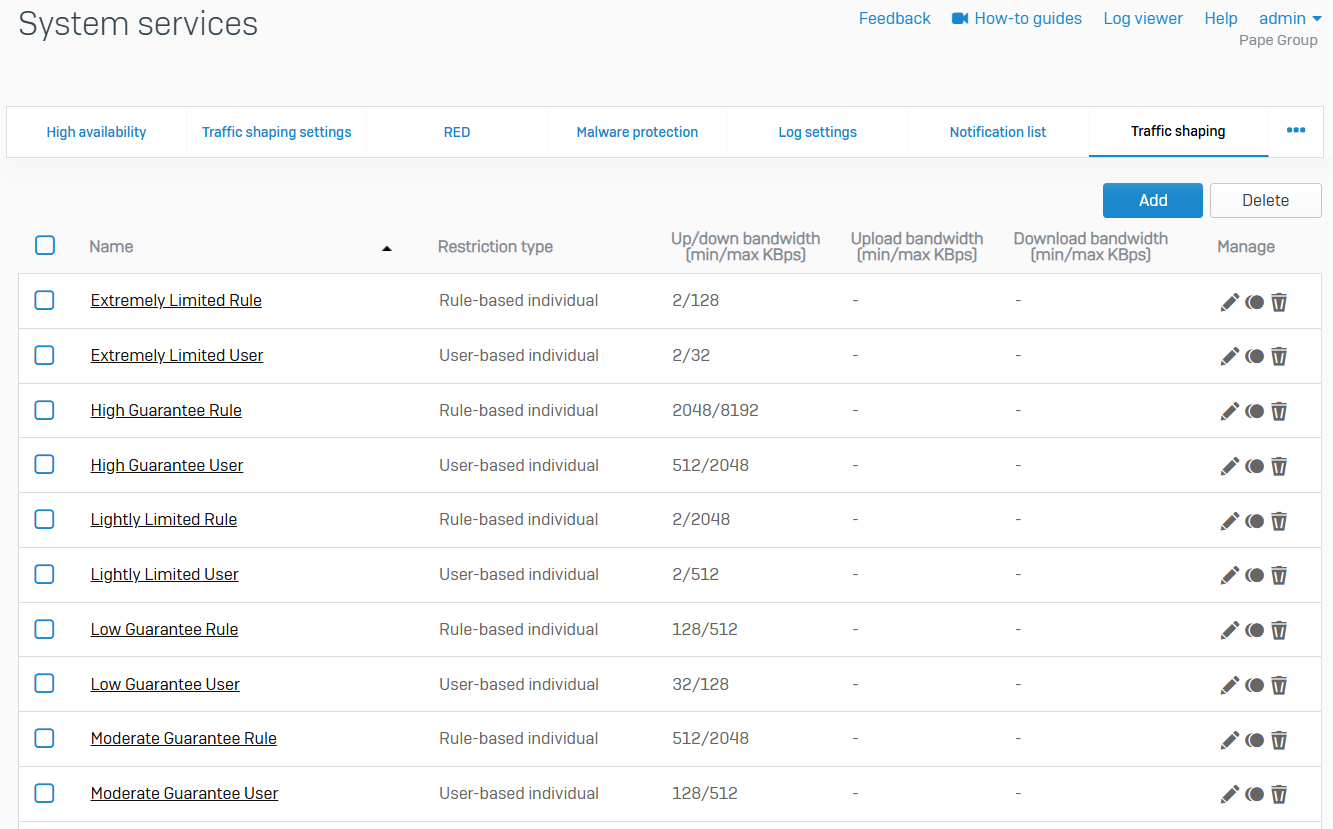
Traffic Shaping
- Reference - Traffic Shaping
- Traffic shaping policies determine the Quality of Service (QoS) for traffic
- You can create policies to guarantee and limit bandwidth. Policies can assign bandwidth to individual objects or be shared among the objects to which you apply them. You can also specify a time for the policy. You can't edit a policy after creating it
- You can apply traffic shaping policies to firewall rules and WAF rules, users and groups, applications and application categories, and web categories. To apply a policy to these objects, you associate it with the object through the policy association type. Only the policies created for the object appear on the object page for selection
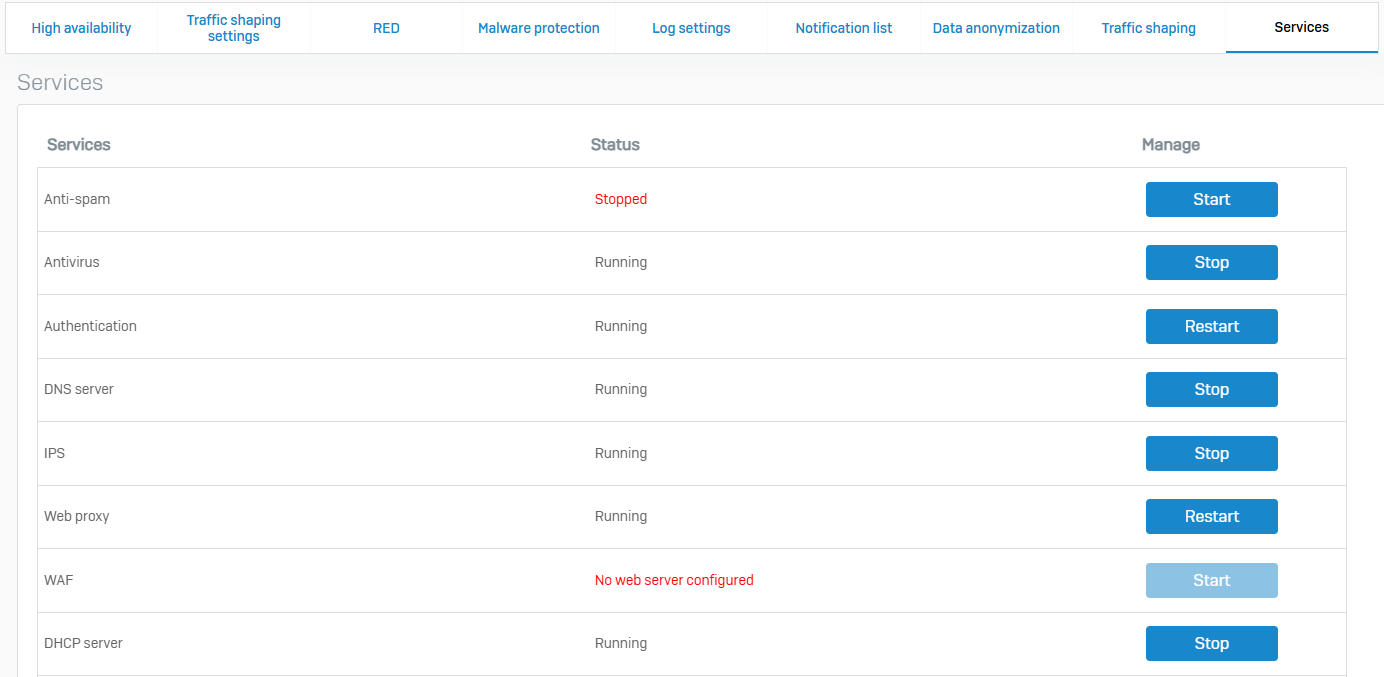
Services
- Reference - Services
- On this page, you can view system service status and manage services
Protect Section
Overview
- The Protect section in the Sophos Firewall control center refers to the settings and features that are designed to safeguard the network, users, and devices from various security threats
- It is one of the primary sections of the Sophos Firewall and its functionality is focused on providing security related protections
Rules & Policies
Overview
- Rules and policies enable traffic to flow between zones and networks while enforcing security controls, IP address translation, and decryption and scanning
- You can create firewall, web server protection, NAT, and SSL/TLS inspection rules
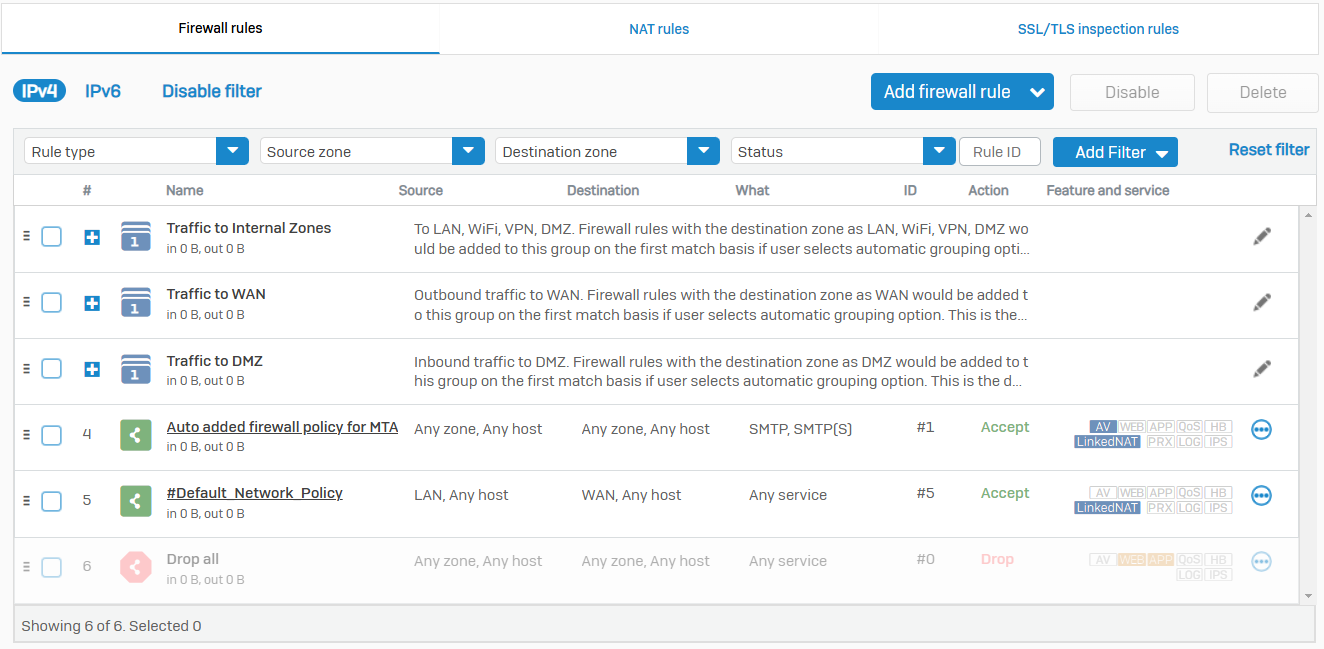
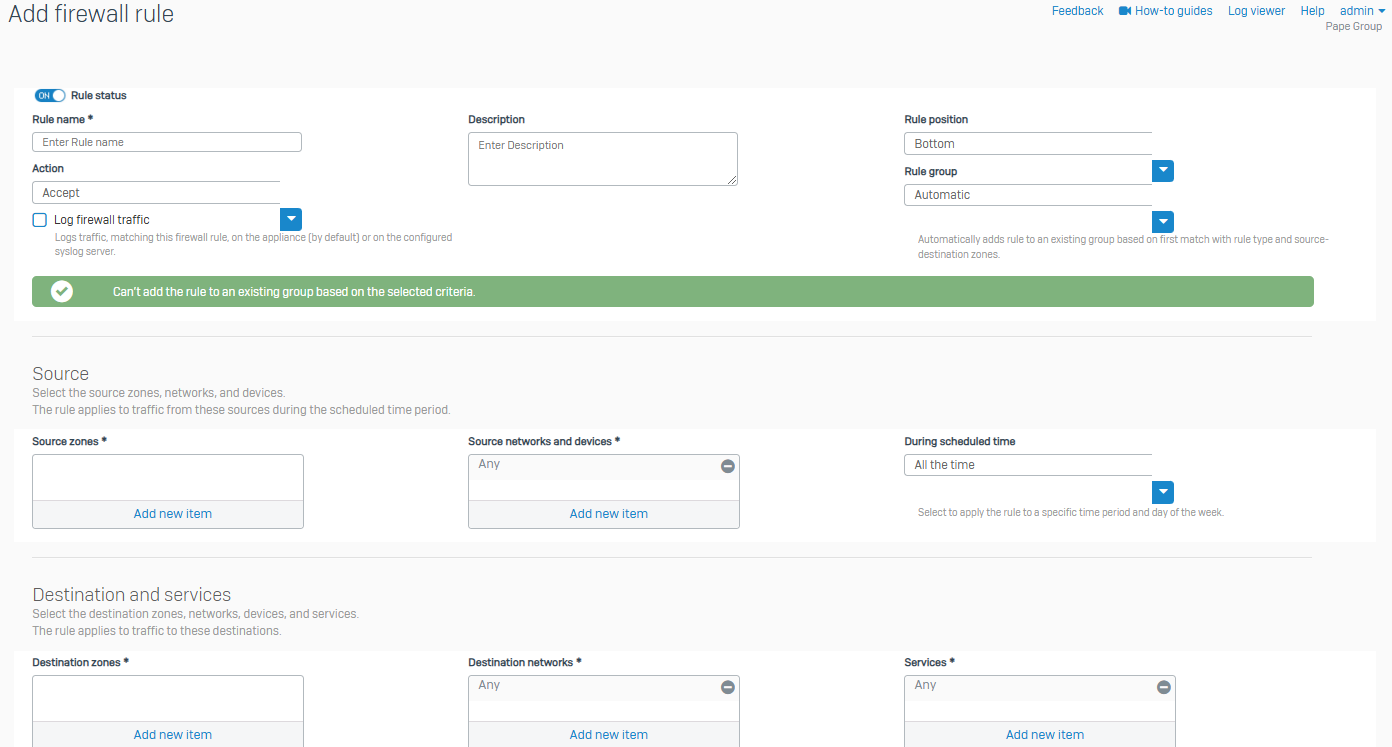
Firewall Rules
- Reference - Firewall Rules
- With firewall rules, you can allow or disallow traffic flow between zones and networks. You can implement policies and actions to enforce security controls and traffic prioritization
- From this page you can create DNAT rules to translate incoming traffic to servers, such as web, mail, SSH, or other servers, and access remote desktops. The assistant also creates a reflexive SNAT rule (for outbound traffic from the servers), a loopback rule (for internal users accessing the servers), and a firewall rule (to allow inbound traffic to the servers) automatically
- You can create firewall rules and add them to rule groups. Sophos Firewall evaluates firewall rules, not rule groups, to match criteria with traffic. It uses the matching criteria of rule groups only to group firewall rules
- The WAF rules portion protects applications and websites hosted on physical or cloud based web servers from exploits and attacks. The firewall acts as a reverse proxy, protecting your internal and external web servers. You can create WAF rules for IPv4 traffic
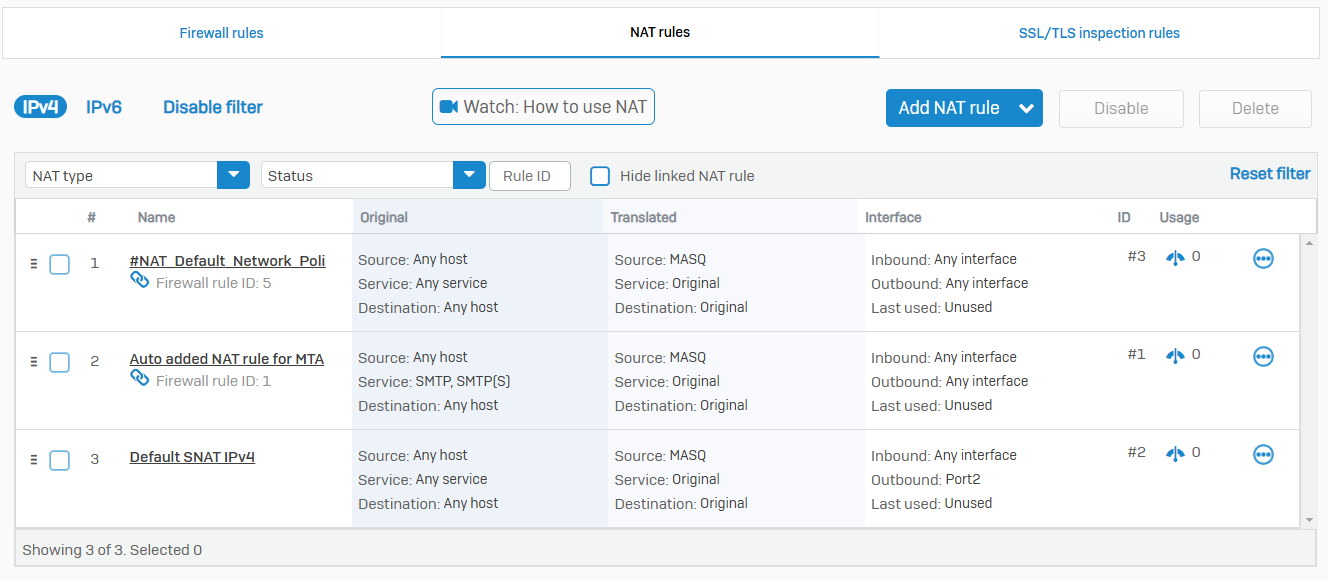
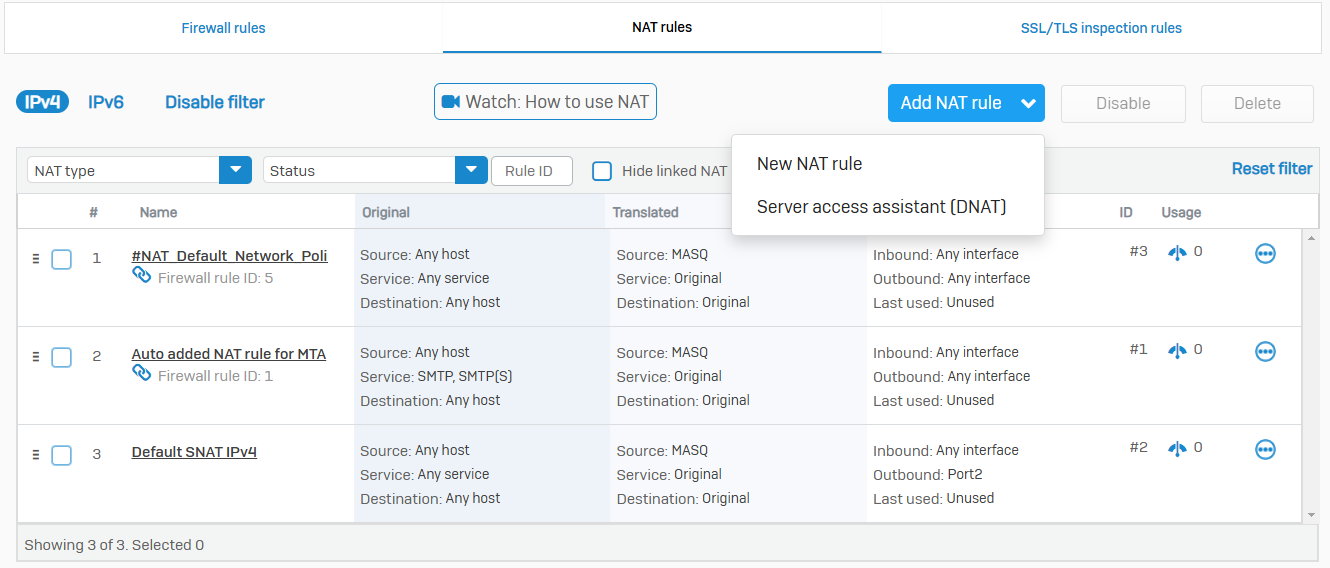
NAT Rules
- Reference - NAT Rules
- Network Address Translation (NAT) allows you to translate IP addresses and ports for traffic flowing between networks
- It translates private IP addresses into public IP addresses, allowing private IP networks to connect to the internet and hiding the internal network behind the public IP address
- You can create source NAT (SNAT) and destination NAT (DNAT) rules to enable traffic flow between private and public networks by translating non-routable, private IP addresses to routable, public IP addresses. You can create NAT rules for IPv4 and IPv6 networks
- You can specify loopback and reflexive rules for a destination NAT rule. These rules remain independent of the original rule from which they've been created. Changing or deleting the original NAT rule doesn't affect them
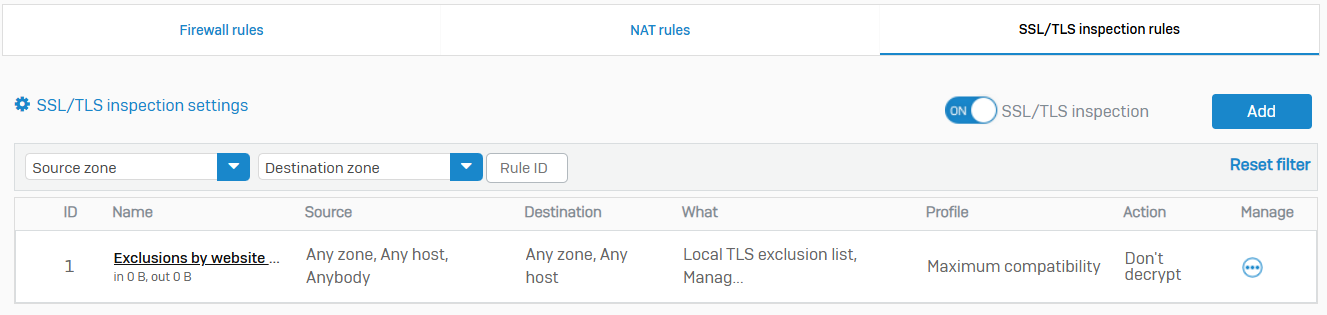
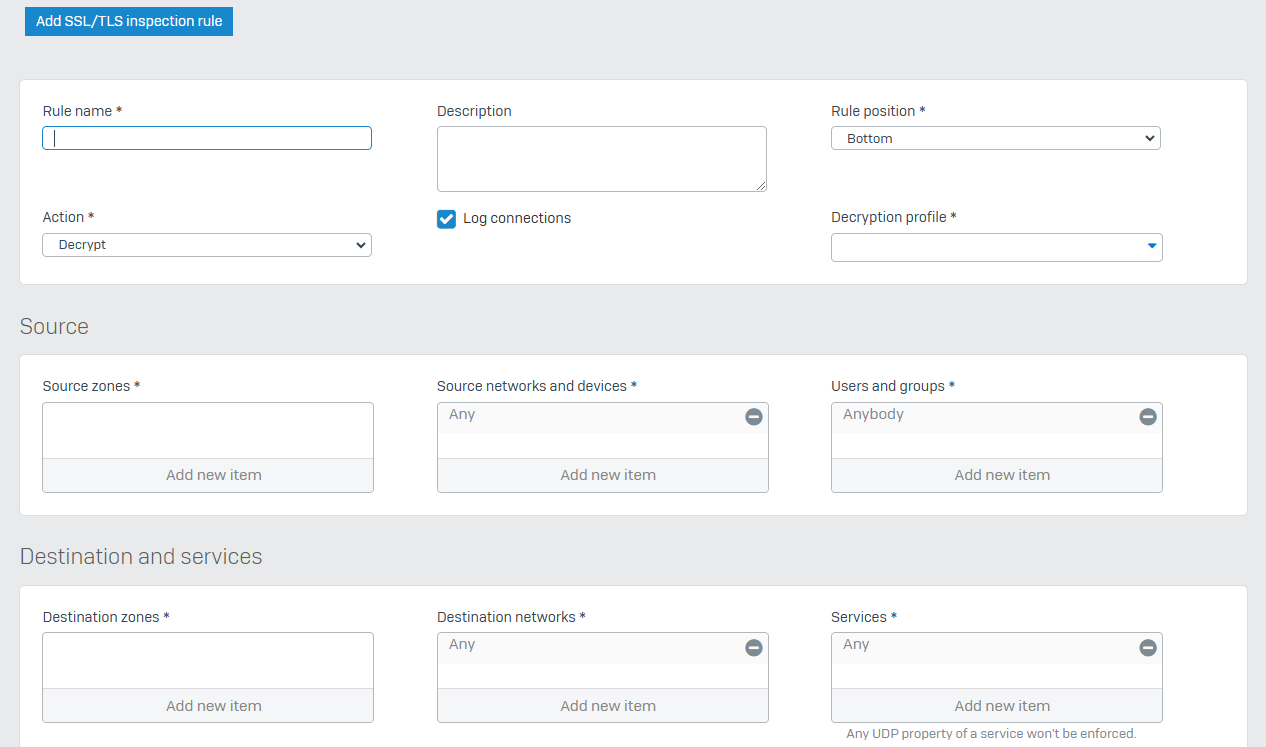
SSL/TLS Inspection Rules
- Reference - SSL/TLS Inspection Rules
- With SSL/TLS inspection rules, you can intercept and decrypt SSL and TLS connections over TCP, allowing Sophos Firewall to enforce secure connections between clients and web servers
- SSL/TLS inspection rules enables the prevention of malware transmitted through encrypted connections
- You can enforce policy-driven connections and decryption for SSL/TLS traffic based on the traffic and risk level
- SSL/TLS inspection rules don't affect the decryption of traffic handled by the web proxy. You specify the method of web filtering (web proxy or DPI engine) in firewall rules. By default, Sophos Firewall uses the DPI engine, applying SSL/TLS inspection rules to traffic matching the firewall rule criteria
Intrusion Prevention
Overview
- With intrusion prevention, you can examine network traffic for anomalies to prevent DoS and other spoofing attacks. Using policies, you can define rules that specify an action to take when traffic matches signature criteria. You can specify protection on a zone-specific basis and limit traffic to trusted MAC addresses or IP-MAC pairs. You can also create rules to bypass DoS inspection
- You must turn on IPS protection to enforce the protection. To turn it on, go to 'Intrusion prevention > IPS policies'
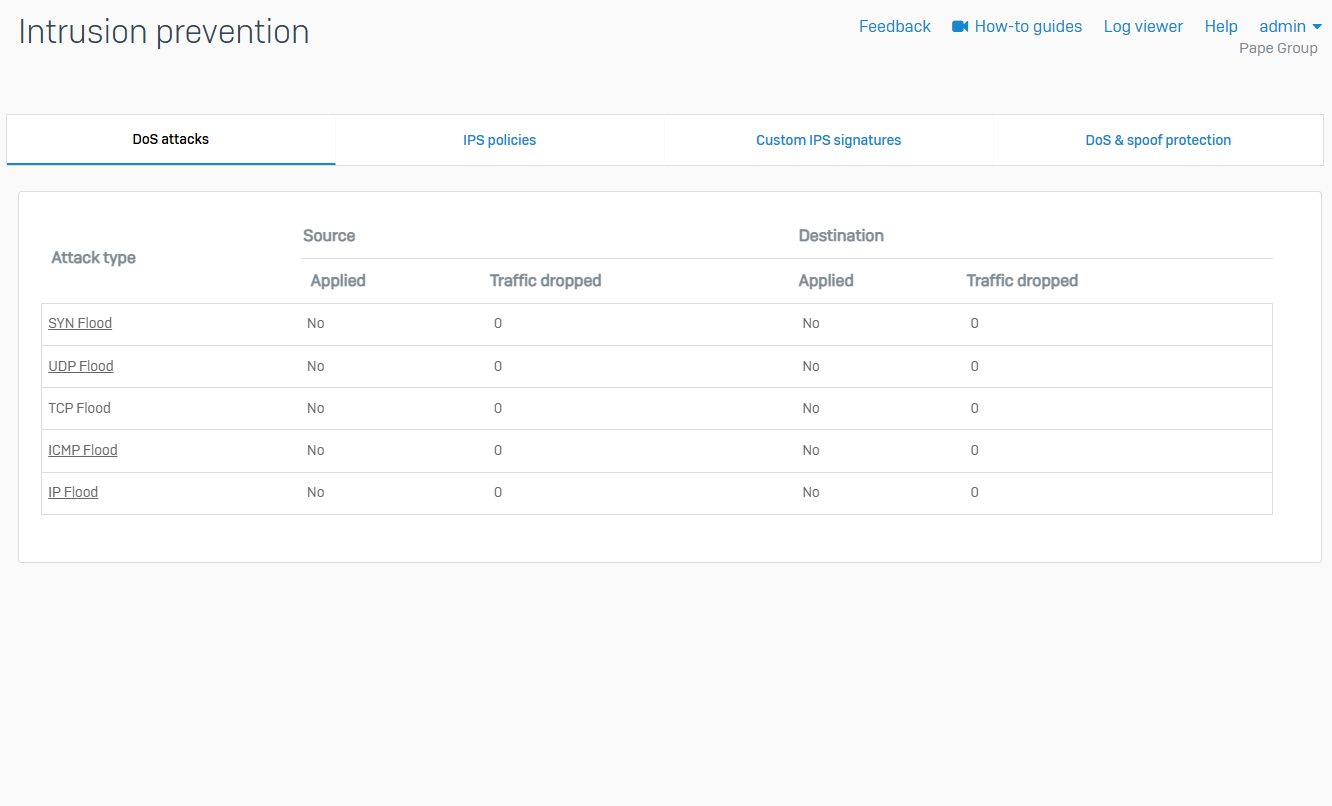
DoS Attacks
- Reference - DoS Attacks
- DoS attack status allows you to see if traffic limits have been applied and the amount of data dropped after the limit has been exceeded. The firewall applies the traffic limits specified in DoS settings and logs the corresponding events. Data is available for the source and destination in real time. Once the attack stops, the firewall removes the data after 30 seconds
- When the firewall detects a DoS attack, it applies traffic limits to the source or destination for 10 seconds. After this time, if the DoS attack stops, the firewall removes the traffic limits. If the DoS attack continues, the counter is reset every 10 seconds on a rolling basis, and the firewall keeps the traffic limits
- If there's a new DoS attack from the same source or to the same destination, the firewall resets the counter and applies the traffic limits again
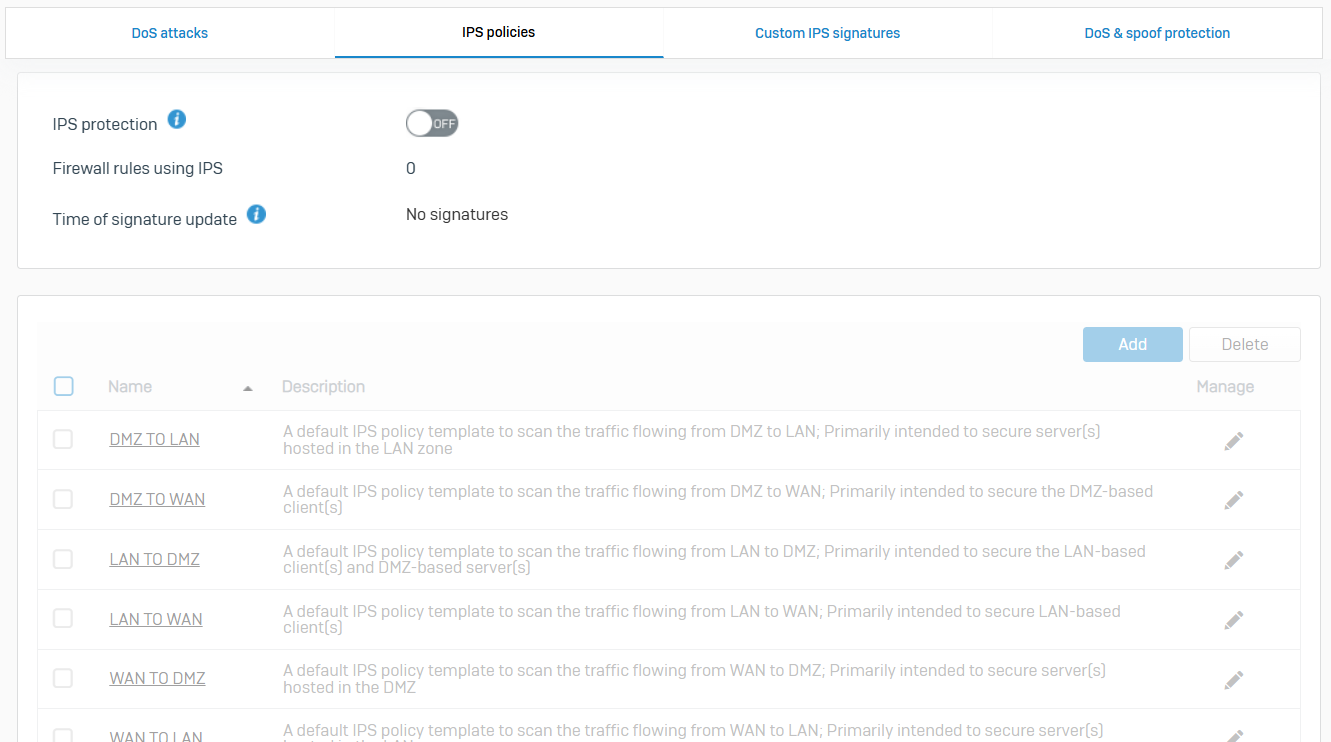
IPS Policies
- Reference - IPS Policies
- With IPS policies, you can prevent network attacks using rules
- The firewall enforces the actions specified in the rules and logs the corresponding events. The set of default policies prevents network attacks for several common types of traffic. You can create custom policies with rules that meet your traffic requirements
- IPS protection is turned off by default. To download IPS signatures to Sophos Firewall, configure IPS policies, and enforce IPS protection, you must turn it on
- Go to 'Intrusion prevention > IPS policies' to turn on IPS protection
- To be able to turn on, you must have either a Network Protection subscription or trial license
Custom IPS Signatures
- Reference - Custom IPS Signatures
- With custom signatures, you can protect your network from vulnerabilities related to network objects such as servers, protocols, and applications. You can create custom signatures and later add them to IPS policy rules
- You can't configure custom IPS signatures if your trial license has expired or if you turn off IPS protection on 'Intrusion prevention > IPS policies'
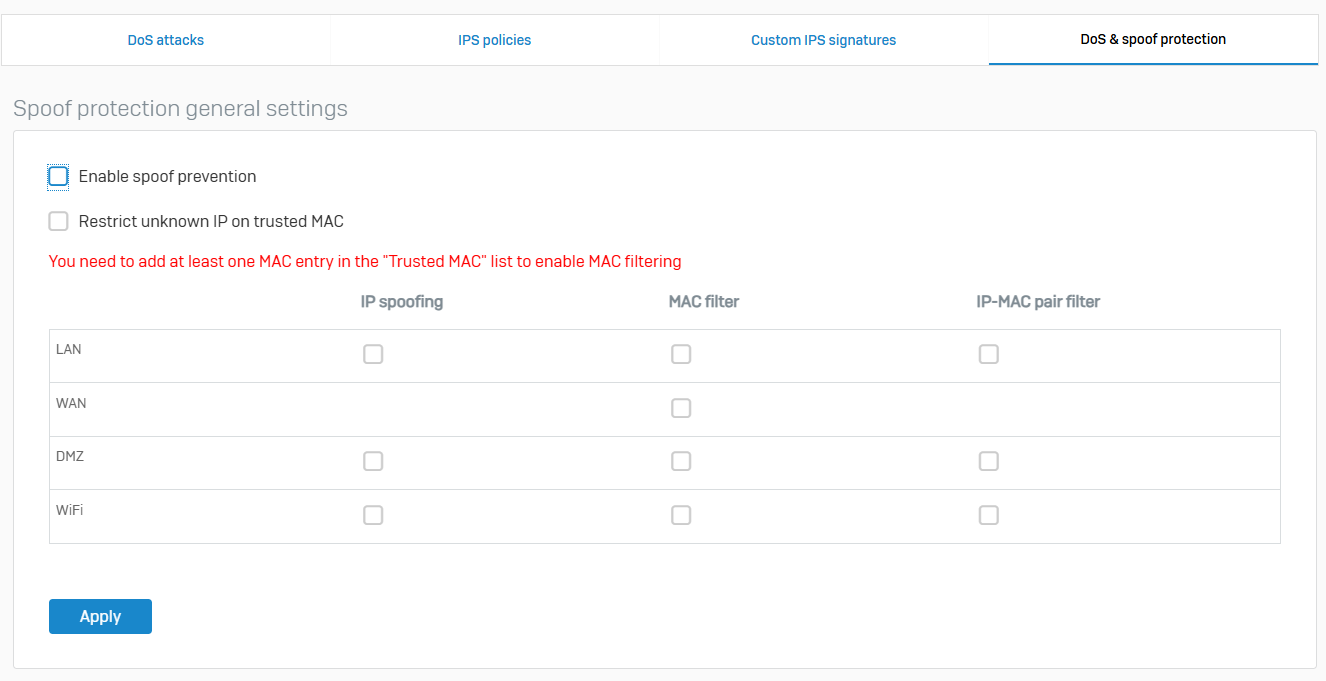
DoS & Spoof Protection
- Reference - DoS & Spoof Protection
- To prevent spoofing attacks, you can restrict traffic to only recognized IP addresses, trusted MAC addresses, and IP-MAC pairs. You can also set traffic limits and flags to prevent DoS attacks and create rules to bypass DoS inspection. The firewall logs dropped traffic
Web
Overview
- Web protection keeps your organization safe from attacks that result from web browsing and helps you increase productivity. You can define browsing restrictions with categories, URL groups, and file types. By adding these restrictions to policies, you can block websites or show a warning message to users
- For example, you can block access to social networking sites and executable files. General settings let you specify scanning engines and other types of protection. Exceptions let you override protection as required for your business needs
Policies
- Reference - Policies
- With web policies, you can create rules to control end users' web browsing activities
- Policies take effect when you add them to firewall rules. The default set of policies specifies some common restrictions. You can change one of the default policies to fit your requirements or create new policies
- The firewall evaluates rules from highest to lowest. For example, if a rule that allows all traffic precedes a rule that blocks a specific type of traffic, the rule that allows all traffic is the effective rule
Policy Quota Status
- Reference - Policy Quota Status
- You can see the time quota remaining for individual users in specific web policies within a 24-hour period
- The time quota applies to web categories with a quota action in a web policy
User Activities
- Reference - User Activities
- User activities combine web categories, file types, and URL groups in one container. You can include user activities in policies to control access to websites or files that match any of the criteria specified
Categories
- Reference - Categories
- With web categories, you can organize and classify domains and keywords in a container. You can use categories within policies to control access to websites. The firewall evaluates them in the order shown on the category list
- Within a category, you can create a list of domains and keywords specific to your organization or import a database. These include country-specific blocklists and open-source categorization lists. The firewall checks for updates every 48 hours, and this can't be changed
URL Groups
- Reference - URL Groups
- URL groups contain one or more domains that you can use in web policies to control access to websites
- You can have a maximum of 128 URLs in a URL group
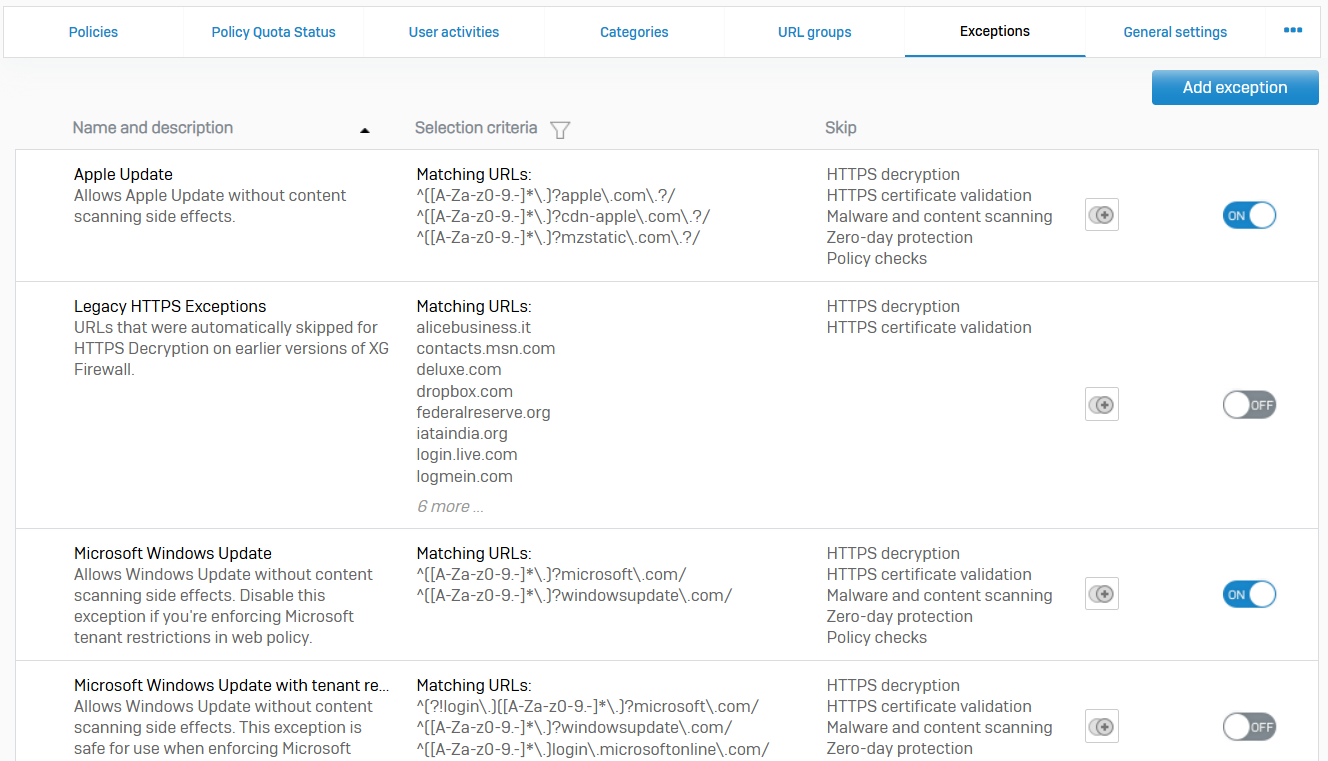
Exceptions
- Reference - Exceptions
- With exceptions, you can override protection settings for all web traffic that matches the specified criteria, regardless of any policies or rules in effect
- For example, you can create an exception to skip HTTPS decryption for sites that contain confidential data. The default set of exceptions allows software updates and other important functions for well-known websites without being affected by web filtering
- The behaviors that you can override include checking by Zero-day protection. Exceptions (including those created in previous releases) that skip malware scanning also skip Zero-day protection analysis
General Settings
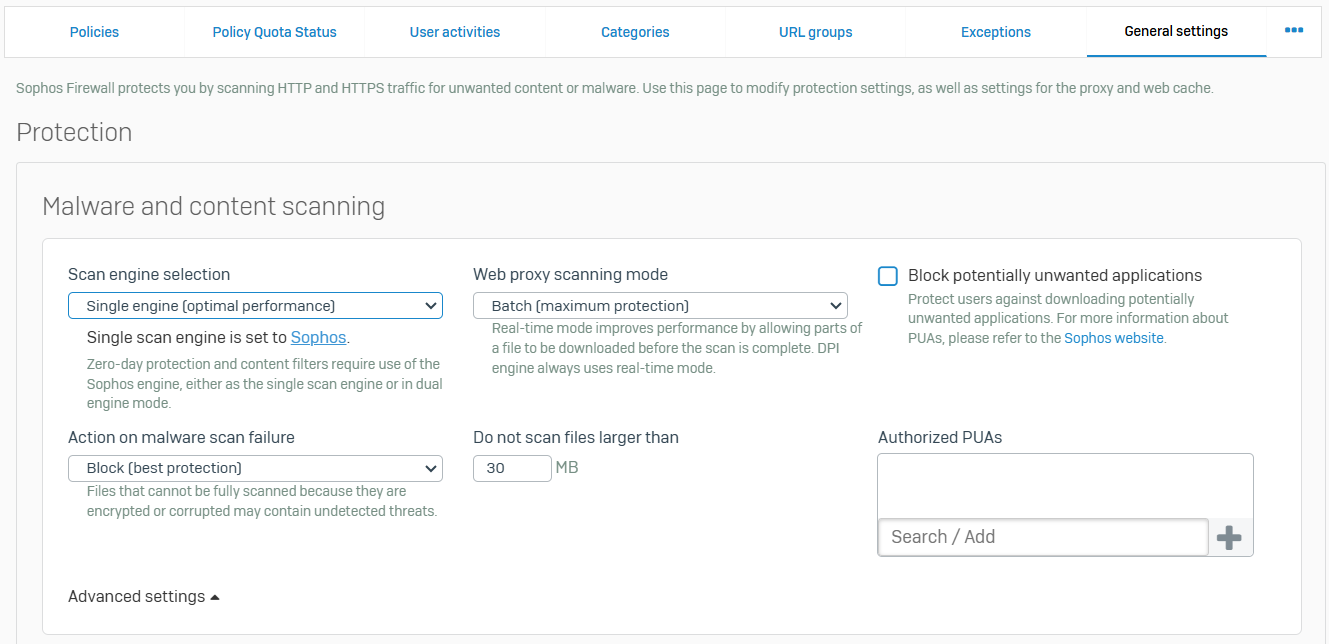
- Reference - General Settings
- The firewall scans HTTP(S) and FTP traffic for threats as specified by your firewall rules and for inappropriate web usage when a policy is selected for a rule. These settings apply only to traffic that matches firewall rules with these options set. You can specify the type of scanning, maximum file size to be scanned, and additional checking. You can also create policy overrides to allow end users to access otherwise blocked websites
File Types
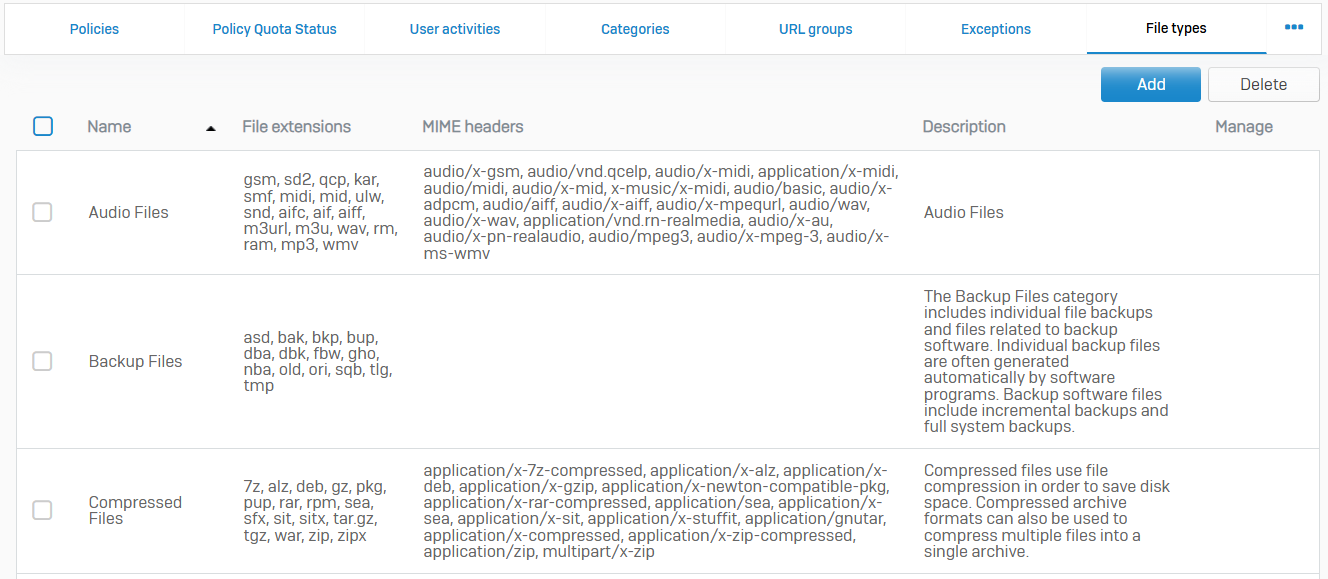
- Reference - File Types
- A file type is a classification determined by the file extension or MIME type
- You can include file types in web and email policies to control access to files. The default file types contain some common criteria. You can create additional file types
Surfing Quotas
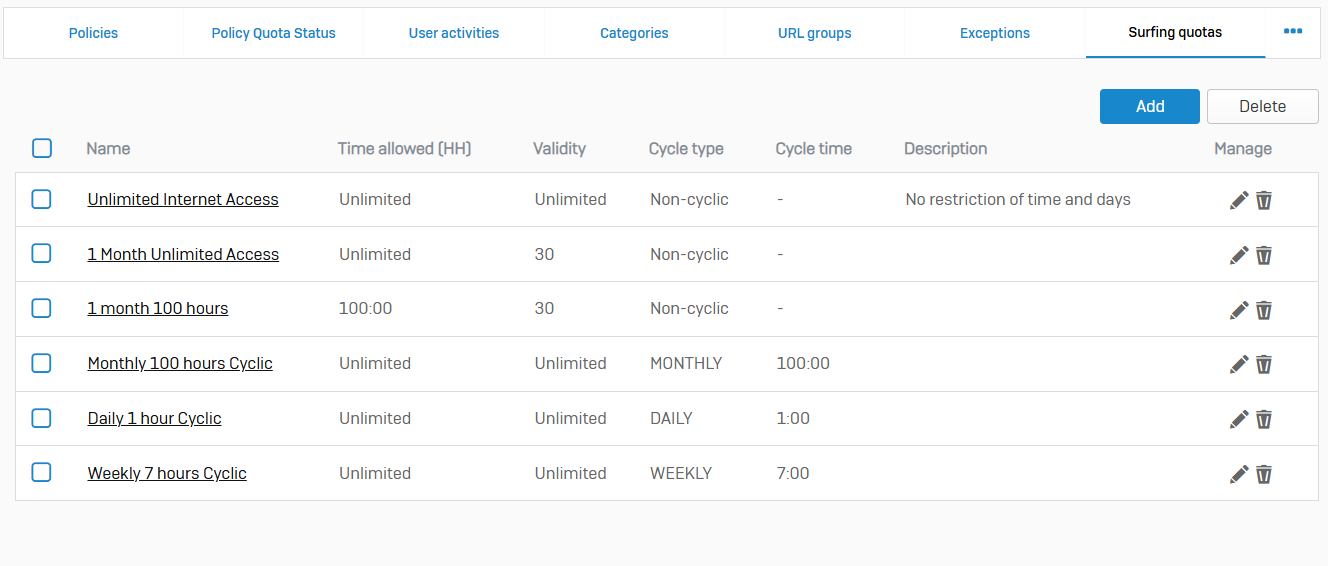
- Reference - Surfing Quotas
- Surfing quotas allow you to allocate internet access time to your users
- Quotas allow access on a cyclical (repeat) or non-cyclical (one-time) basis. You can add quotas and specify the access time allowed, or use the default quotas
- When more than one quota applies to a user, the firewall restricts access according to the first policy that reaches its limit
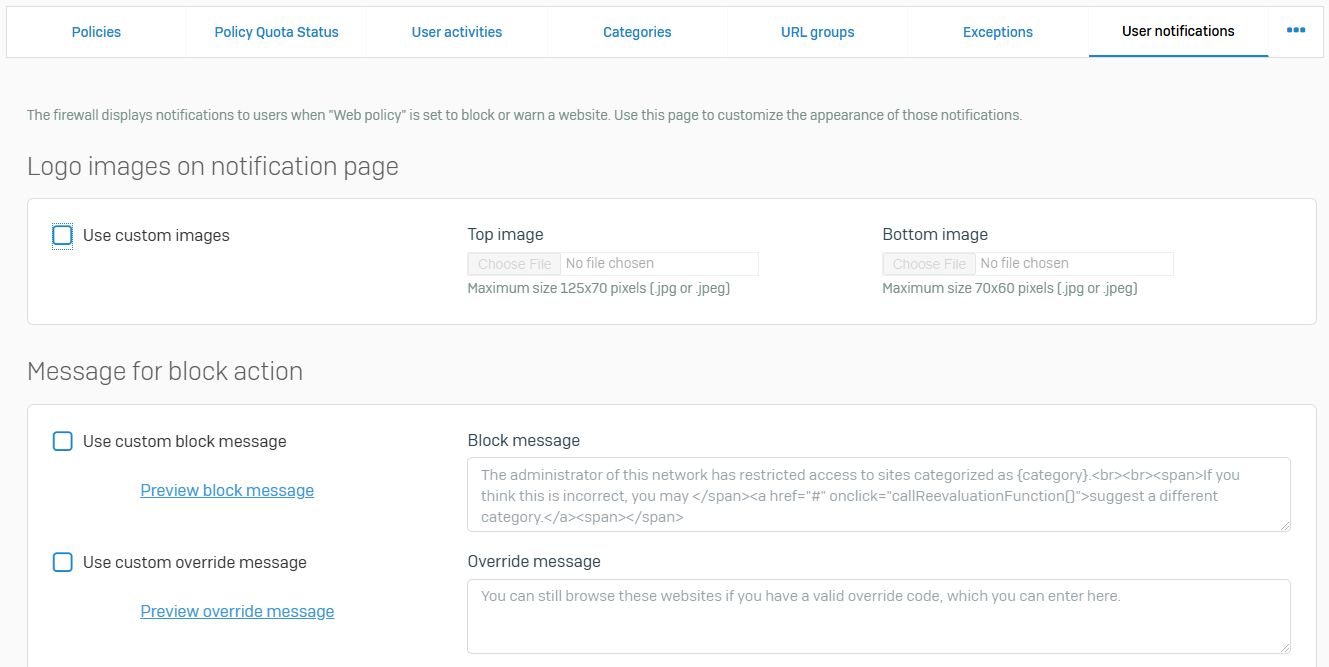
User Notifications
- Reference - User Notifications
- The firewall displays a notification to users when a web policy is set to block access or warn before connecting
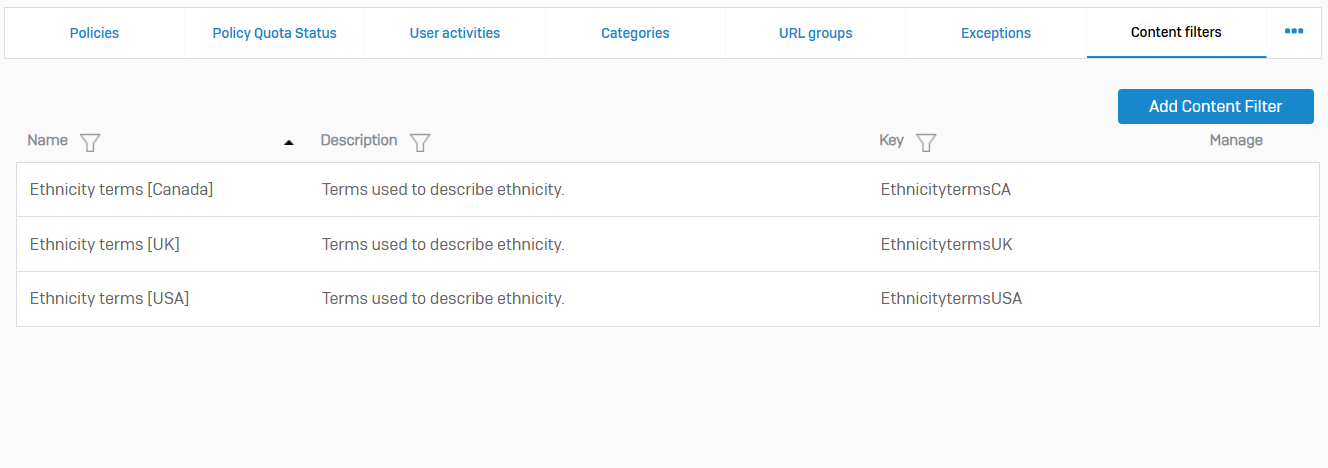
Content Filters
- Reference - Content Filters
- A content filter is a named list of terms. You can use content filters in policies to restrict access to websites that contain any of the terms listed. The default set of filters includes terms that are blocked by many organizations
Applications
Overview
- Application protection helps keep your organization safe from attacks and malware that result from application traffic exploits
- You can also apply bandwidth restrictions and restrict traffic from applications that lower productivity
- Application filters allow you to control traffic by category or on an individual basis
- With synchronized application control, you can restrict traffic on endpoints that are managed with Sophos Central
- Managing cloud application traffic is also supported
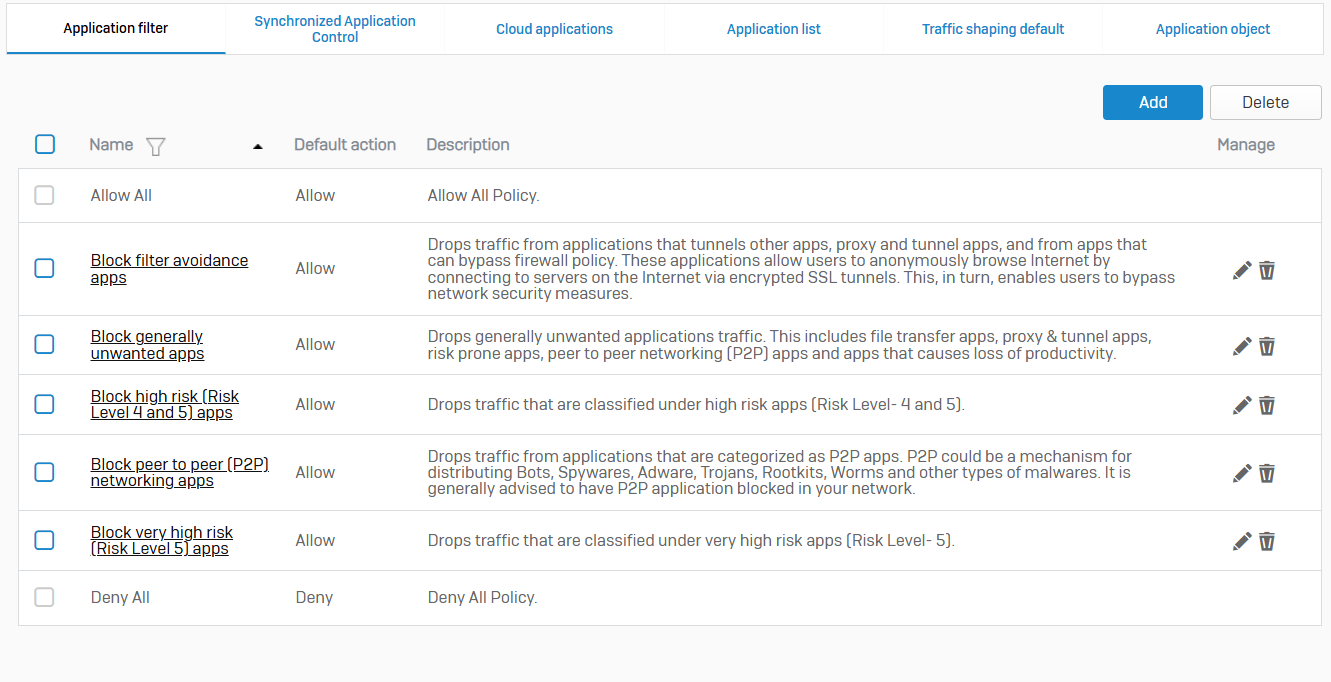
Application Filter
- Reference - Application Filter
- With application filter policies, you can control access to applications by users behind the firewall
- Policies specify access to application categories or individual applications using rules. The default set of policies includes some commonly used restrictions. You can also create custom policies according to the requirements of your organization
- In application filter policies, the web proxy detects applications that use HTTPS
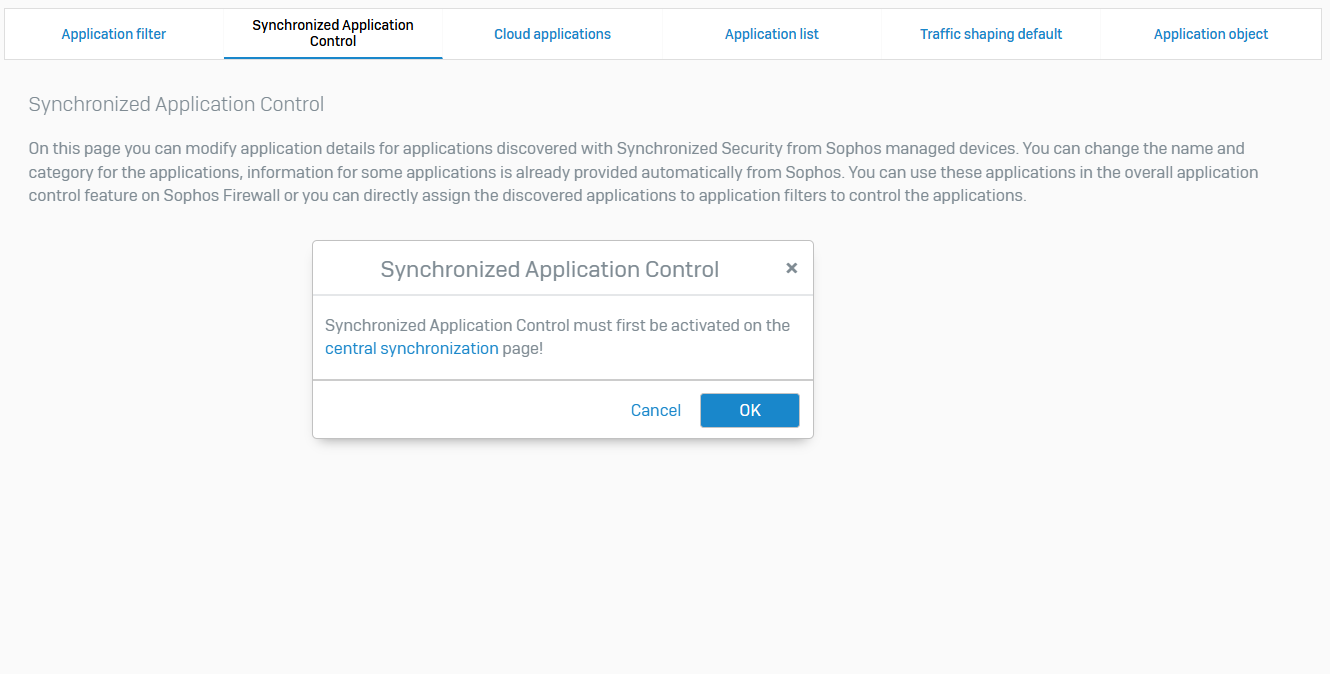
Synchronized Application Control
- Reference - Synchronized Application Control
- Synchronized Application Control monitors all applications on endpoints connected through Security Heartbeat
- You can see newly detected applications, hide known applications, sort applications into categories, and control their traffic through application filters. Synchronized Application Control supports up to 15,000 applications
- If you're using Synchronized Application Control for the first time, you must turn it on from Sophos Central
Cloud Applications
- Reference - Cloud Applications
- By analyzing cloud application traffic, you can mitigate the risks posed by cloud application usage. Options allow you to classify traffic and apply a traffic shaping policy
- Use the filters to refine the search results by date, classification, category, and bytes transferred. For example, you can filter traffic to show only unsanctioned social networking traffic for a specified period
Application List
- Reference - Application List
- The Application list contains many commonly used applications
- New applications are automatically added to application filter policies and firewall rules when the application signature database is updated
- For example, if a new signature is added for a high-risk application, and a firewall rule has an application filter policy that blocks high-risk applications, the application is blocked based on the new signature
Traffic Shaping Default
- Reference - Traffic Shaping Default
- You can implement bandwidth restrictions using traffic shaping policies. You can apply default traffic shaping policies to categories or individual applications
- If a traffic shaping policy is added to a firewall rule, it will override the default traffic shaping policy
Application Object
- Reference - Application Object
- An application object is used together with an SD-WAN route enabling easy control of how application traffic is routed through the network
- An application object is made up of one or more applications for which traffic needs to be routed together. For example, you may use more than one VoIP application but want all traffic for those applications routed together
- The applications available are updated dynamically via IPS updates when added by Sophos or via SSC discovery when added manually
Wireless
Overview
- Wireless protection lets you define wireless networks and control access to them
- The firewall supports the latest security and encryption, including rogue access point scanning and WPA2
- WPA2 is an AES-based security standard for wireless networks
- Wireless protection allows you to configure and manage access points, wireless networks, and clients
- You can also add and manage mesh networks and hotspots
Wireless Client List
- Reference - Wireless Client List
- The wireless client list displays all clients that are currently connected to a wireless network through an access point. You can view clients by access point or SSID. Connection characteristics such as signal strength and frequency are also displayed
Wireless Networks
- Reference - Wireless Networks
- A wireless network provides common connection settings for wireless clients. These settings include SSID, security mode, and the method for handling client traffic
- Sophos Firewall's WiFi interface shows the unplugged status until you connect and add a wireless network to an access point
Access Points
- Reference - Access Points
- Sophos access points, built-in Wi-Fi devices, and Wi-Fi RED appliances allow users to connect to your Wi-Fi network
- You can also use the Wi-Fi expansion module with some Sophos Firewall and SD-RED models
Access Point Groups
- Reference - Access Point Groups
- With access point groups, you can assign wireless networks and specify VLAN tagging to a group of access points. Groups provide a convenient method of managing wireless networks for several access points, rather than individually
- If you turn off a group, all included access points will stop broadcasting the wireless networks
Mesh Networks
- Reference - Mesh Networks
- A mesh network is a network topology in which each node relays data for the network, extending over a large area. In a mesh network, access points can act as root or as mesh nodes. You can set up a mesh network as a wireless repeater or as a wireless bridge
Hotspots
- Reference - Hotspots
- A hotspot is a network node that provides Internet connectivity using a Wi-Fi device, such as a wireless access point. Hotspots can provide guest access in public areas. When you add an interface to a hotspot, the associated access points act as hotspots. Hotspots support a full suite protection features and authentication methods
- When you add a hotspot, the firewall creates a corresponding firewall rule. This rule allows you to enforce policies and scan traffic
Hotspot Voucher Definitions
- Reference - Hotspot Voucher Definitions
- Hotspot voucher definitions specify network access. You can use voucher definitions to limit the validity period, time quota, and data volume for users accessing voucher-type hotspots
Wireless Settings
- Reference - Wireless Settings
- Use these settings to turn on wireless protection, set notification time-out, and configure a RADIUS server for enterprise authentication
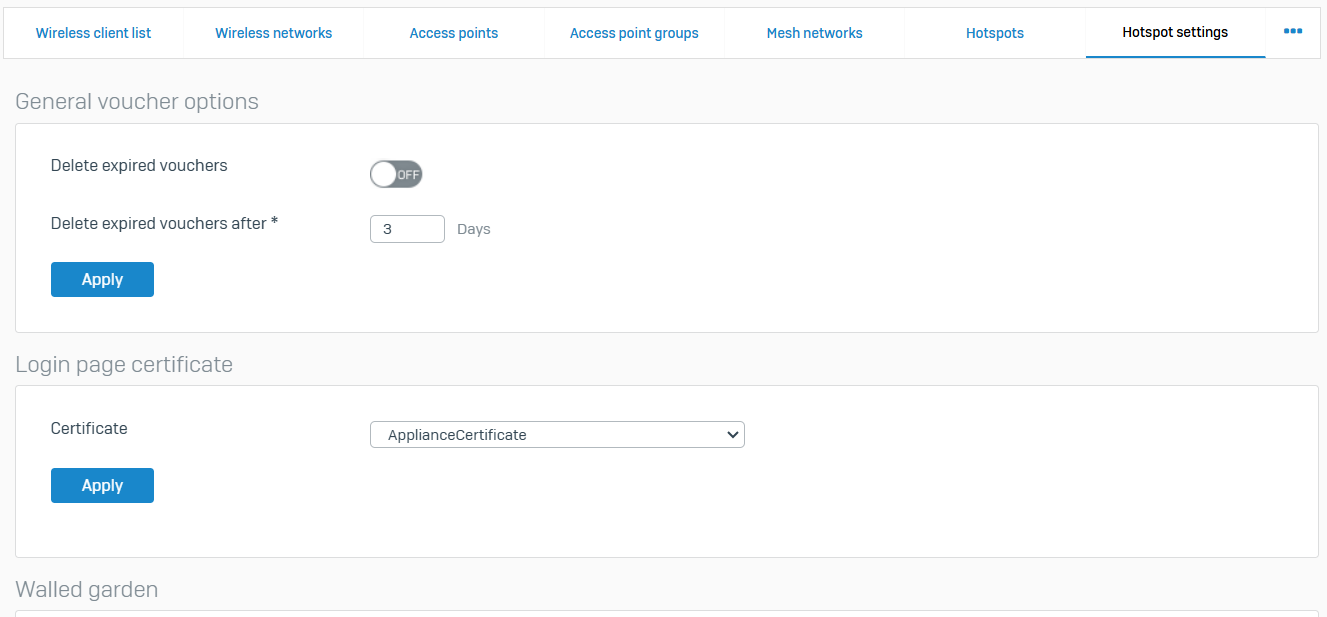
Hotspot Settings
- Reference - Hotspot Settings
- Use these settings to configure various hotspot settings, such as deletion options and certificates for HTTPS authentication
Overview
- Manage email routing and protect domains and mail servers
- You can configure SMTP/S, POP/S, and IMAP/S policies with spam and malware checks, data protection, and email encryption
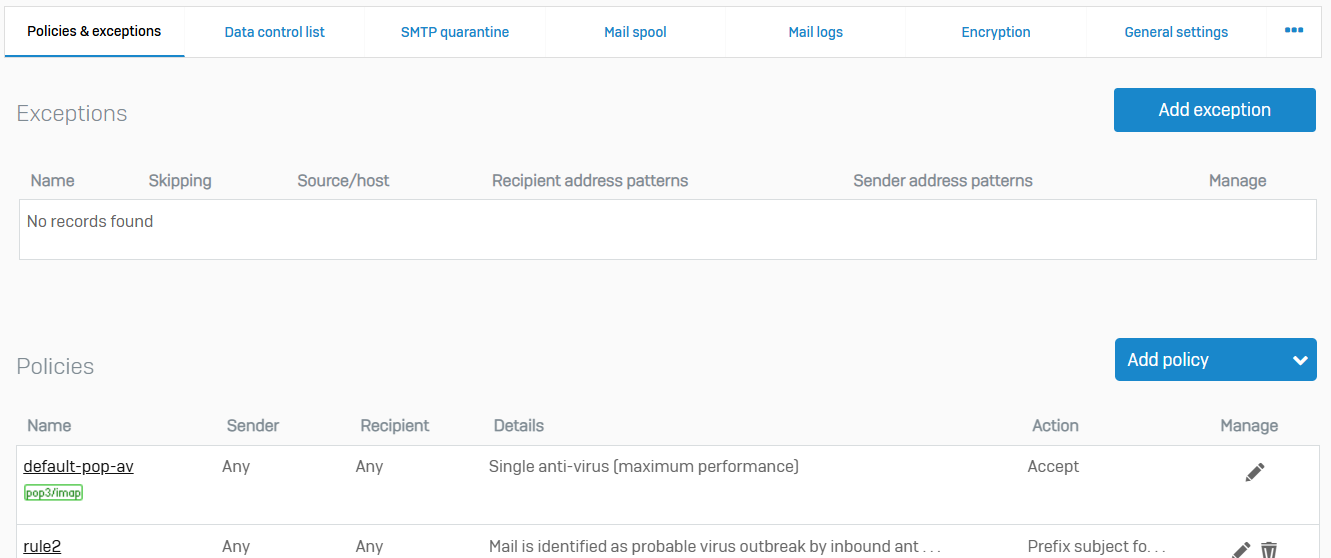
Policies & Exceptions
- Reference - Policies & Exceptions
- In MTA mode, you can specify routing, protection, and encryption settings for emails related to protected domains. You can create exceptions from checks for specific senders and recipients
- With policies in Legacy mode, you can apply spam and malware checks as well as file and data protection for inbound and outbound emails. You can specify quarantine, encryption, and notification settings
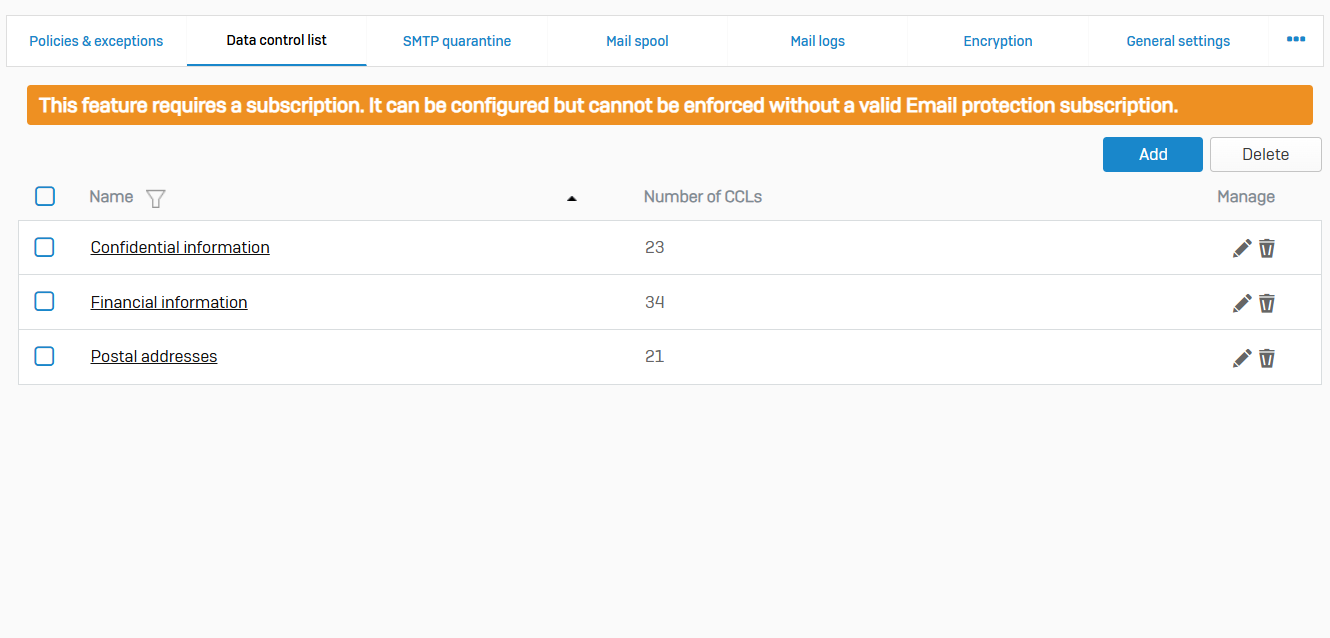
Data Control List
- Reference - Data Control List
- With data control lists, you can specify sets of sensitive information
- You can create data control lists from the content control list (CCL). CCLs are based on common financial and personally identifiable data types, such as credit card or social security numbers, postal, or email addresses
- You can specify data control lists in email policies to protect sensitive information. When Sophos Firewall finds a match for the specified information, it applies the action specified in the policy
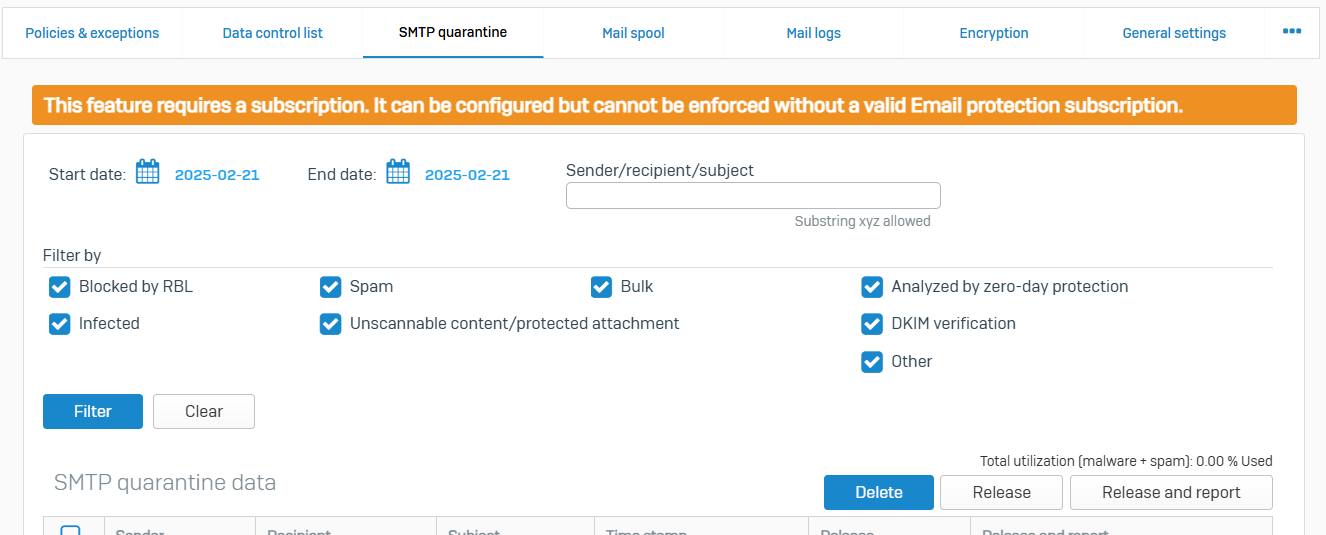
SMTP Quarantine
- Reference - SMTP Quarantine
- With SMTP Quarantine, you can filter quarantined emails. You can delete or release emails from the quarantine area
Mail Spool
- Reference - Mail Spool
- The mail spool shows emails waiting to be delivered or have returned an error message. You can apply filters and take action on these emails
Mail Logs
- Reference - Mail Logs
- Mail logs show the list of all emails. You can filter these by the action taken and scanning outcome
Encryption
- Reference - Encryption
- Secure PDF Exchange (SPX) is clientless email encryption that converts email and attachments to a PDF file and encrypts it with a password
- Sophos firewall encrypts outbound emails based on the domain and content you specify in the SMTP policies. Recipients can decrypt emails and then read them, using a PDF reader on their devices. To reply, recipients must click the reply button in SPX-encrypted emails and go to the SPX reply portal
General Settings
- Reference - General Settings
- With general settings, you can turn Sophos Firewall into a mail transfer agent (MTA) or a transparent mail proxy
- In MTA mode, Sophos firewall routes and protects emails of protected domains on more than one mail server. You can specify inbound and outbound mail relay, and configure encryption and quarantine settings. You can also view the cause of delay in email delivery and view mail logs
- In Legacy mode (transparent mail proxy), you can specify policies to protect emails from spam, malware, and data leakage. You can also specify encryption settings
Quarantine Settings
- Reference - Quarantine Settings
- The quarantine digest is emailed to users. It contains a list of the spam emails Sophos Firewall quarantines
- The list includes all spam to the recipient's individual and alias addresses and is emailed at the configured frequency. The digest contains the date and time of email receipt, sender and recipient email addresses, and the email subject
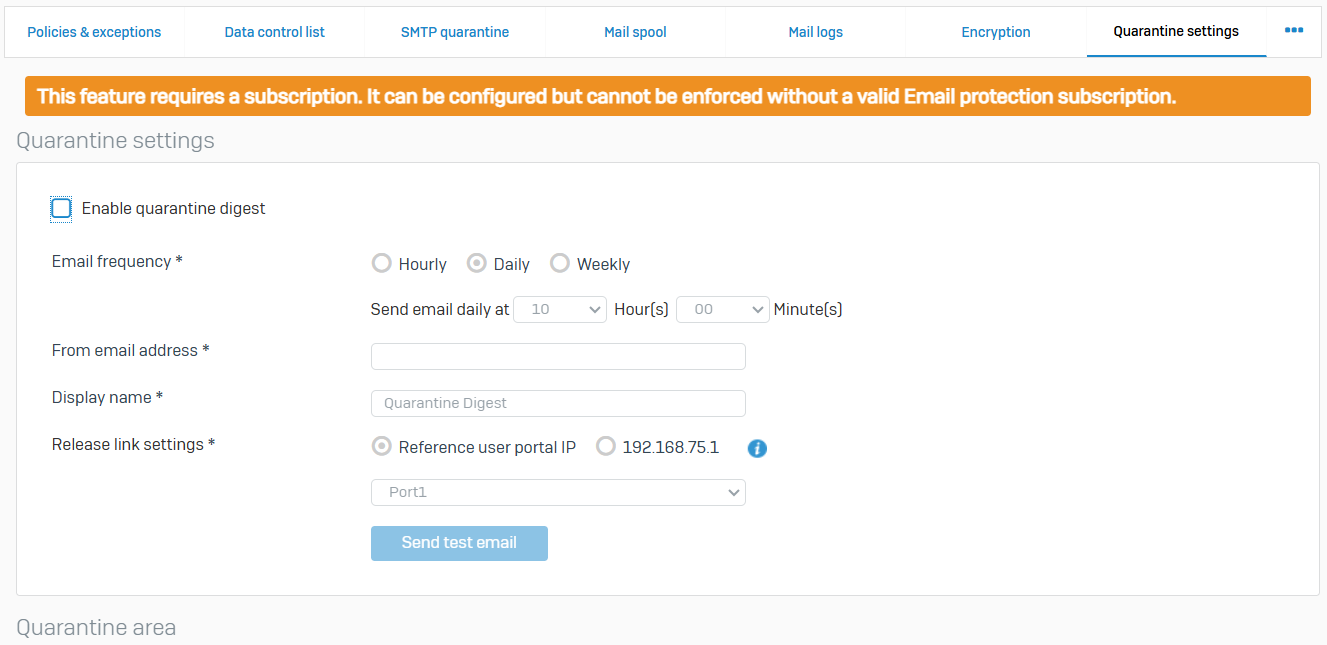
Address Groups
- Reference - Address Groups
- You can create address groups with email addresses, domains, IP addresses, or RBLs (real time blackhole lists)
- You can add email addresses to more than one group. You can then apply email policies to address groups
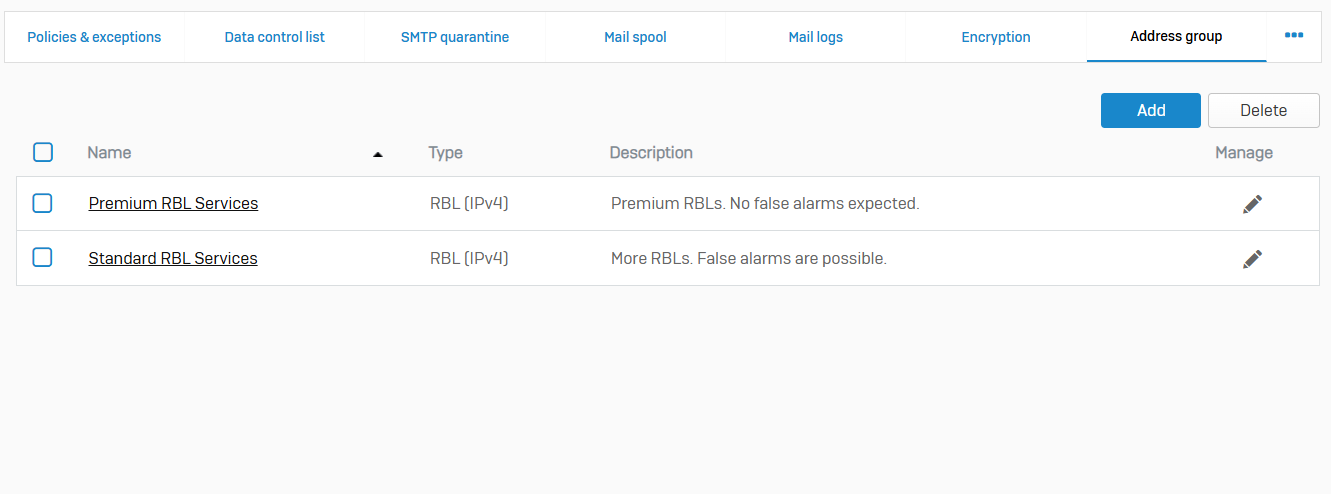
Relay Settings
- Reference - Relay Settings
- In MTA mode, you can allow Sophos Firewall to act as an outbound mail relay for hosts in the network and an inbound relay for emails from upstream hosts. You can enforce user authentication to use the relay
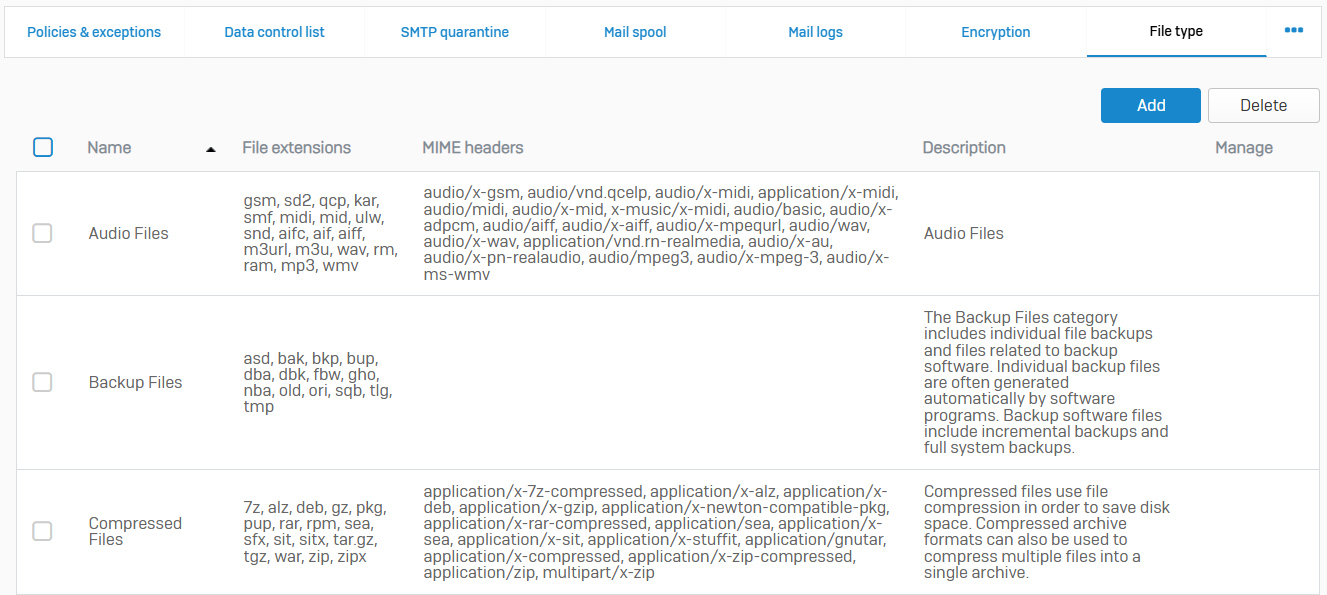
File Type
- Reference - File Type
- A file type is a classification determined by the file extension or MIME type
- You can include file types in web and email policies to control access to files. The default file types contain some common criteria. You can create additional file types
Web Server
Overview
- You can protect web servers against Layer 7 (application) vulnerability exploits, such as cookie, URL, and form manipulation
- You can configure the web servers you want to protect and the protection and authentication policies
- To protect the web servers, you add them and the policies to Web Application Firewall (WAF) rules. General settings apply to all the protected web servers
- To manage the WAF service, go to 'System services > Services'
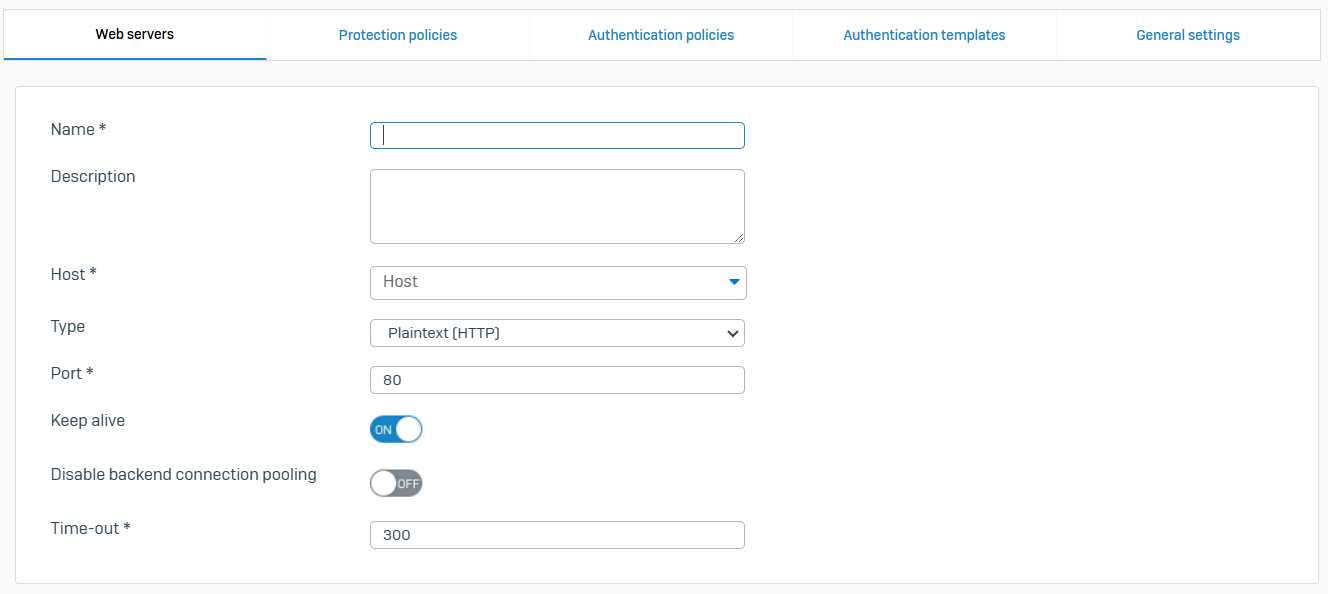
Web Servers
- Reference - Web Servers
- Define the servers to be protected. Web servers specify a host, a type, and other connection settings
- You can protect plain text (HTTP) and encrypted (HTTPS) servers
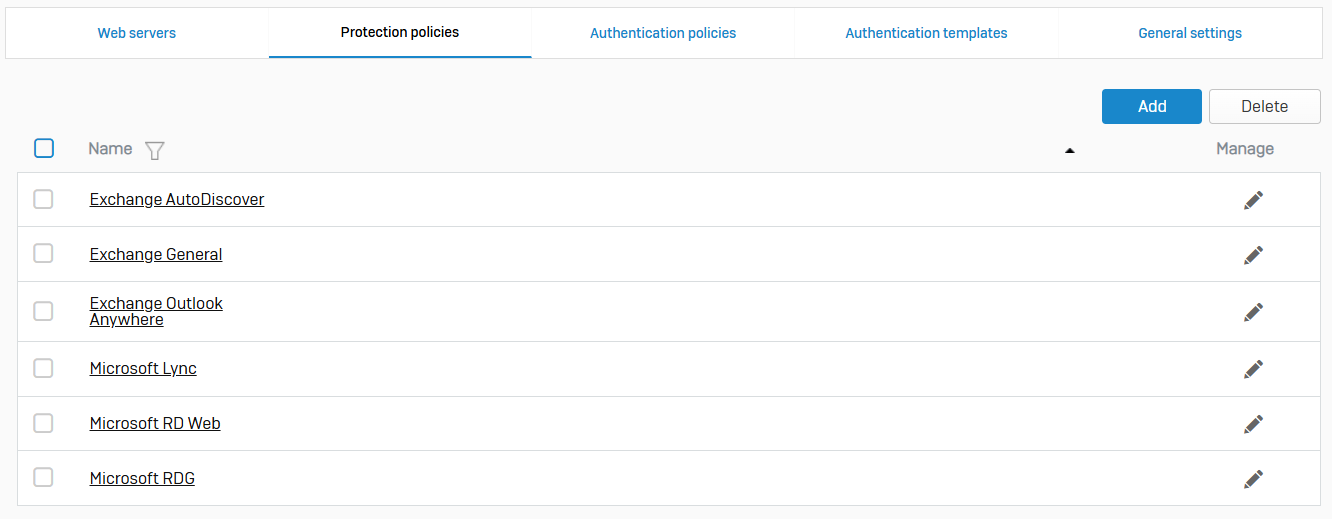
Protection Policies
- Reference - Protection Policies
- Using policies, you can define protection from vulnerability exploits, such as cookie, URL, and form manipulation
- Policies also mitigate common threats, such as application and cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks
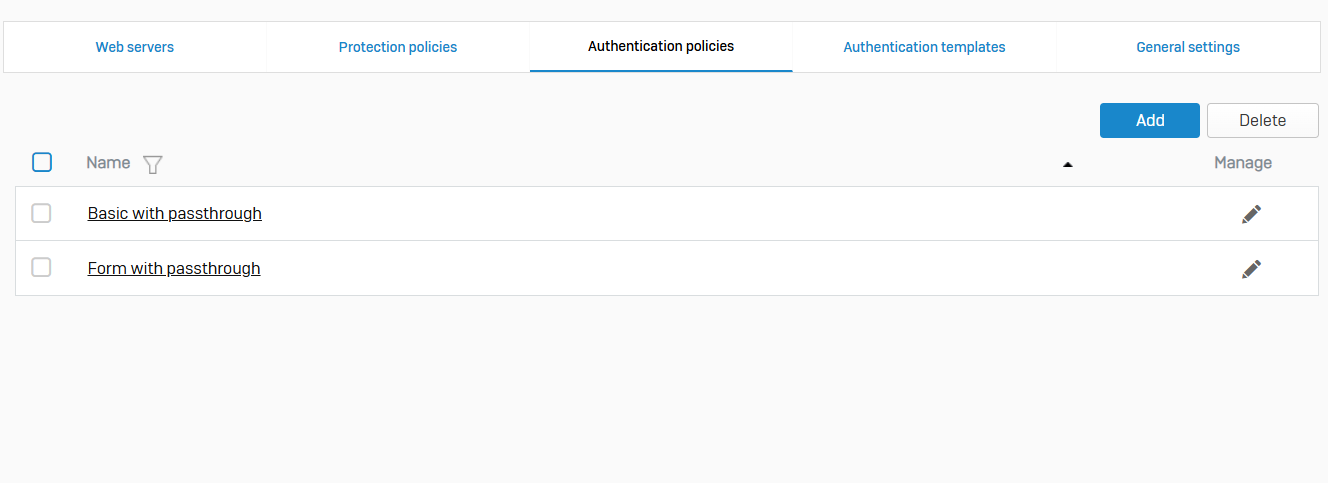
Authentication Policies
- Reference - Authentication Policies
- Using authentication policies, you can provide basic or form-based reverse-proxy authentication for your web servers. You can also use them to control access to the paths specified in firewall rules. The firewall supports basic HTTP authentication as described in RFC 7617
- Authentication policies specify an authentication method and users
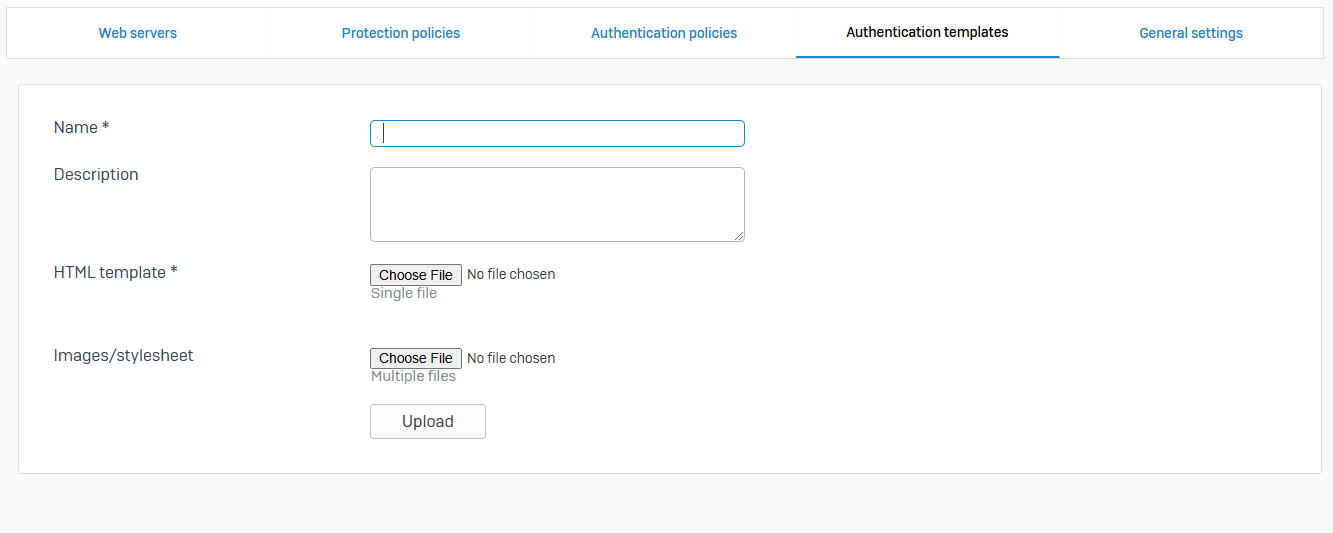
Authentication Templates
- Reference - Authentication Templates
- Authentication templates define HTML forms for use in form-based authentication policies
- Sophos Firewall provides customizable HTML and CSS templates. To ensure that the authentication templates work well, learn more about the variables
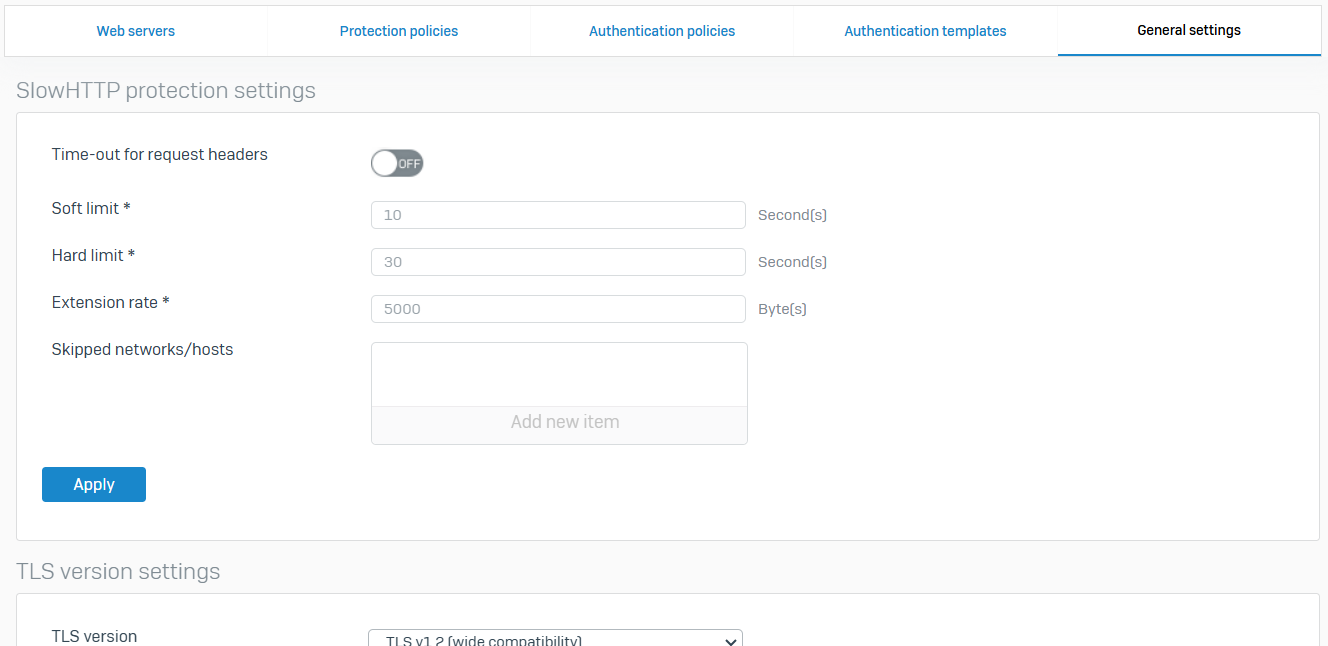
General Settings
- Reference - General Settings
- You can configure slow HTTP protection and set the TLS revision
- Slow HTTP attacks are DoS attacks in which the attacker sends HTTP requests in pieces slowly, one at a time, to a web server. If an HTTP request isn't complete or the transfer rate is very low, the server keeps its resources busy waiting for the rest of the data. When the server's concurrent connection pool reaches its maximum, this creates a DoS
- Slow HTTP protection helps to protect against slow HTTP attacks by setting a time-out for request headers
Active Threat Response
Overview
- Active threat response provides instant and automated response to active adversaries equipped with sophisticated software and networking skills. These adversaries try to gain entry into your network and systems and continuously adapt their techniques using hands-on keyboard and AI-assisted methods
- Active threat response offers multiple modules of threat intelligence feeds, enabling the firewall to coordinate defenses immediately without manual intervention
- Threat feeds are a list of IP addresses, domains, and URLs involved in threat activity, such as phishing and malware. These objects are called Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) or indicators of attack
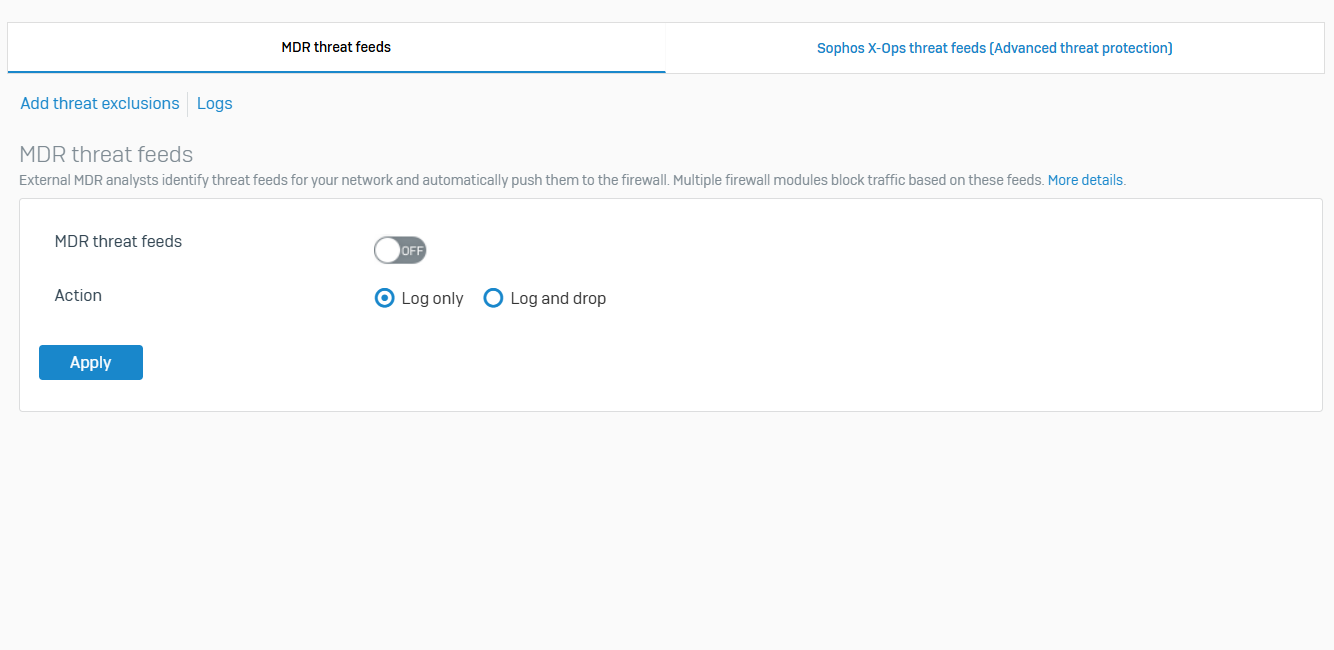
MDR Threat Feeds
- Reference - MDR Threat Feeds
- MDR threat feeds is the Sophos Managed Detection and Response (MDR) service that's integrated with the firewall
- Sophos MDR analysts can push threat intelligence to the firewall directly from Sophos Central, allowing the firewall to coordinate defenses immediately. The feed is based on your network's traffic related to malicious servers
- The firewall automatically blocks traffic based on the IPv4 addresses, domains, and URLs in the MDR threat feeds
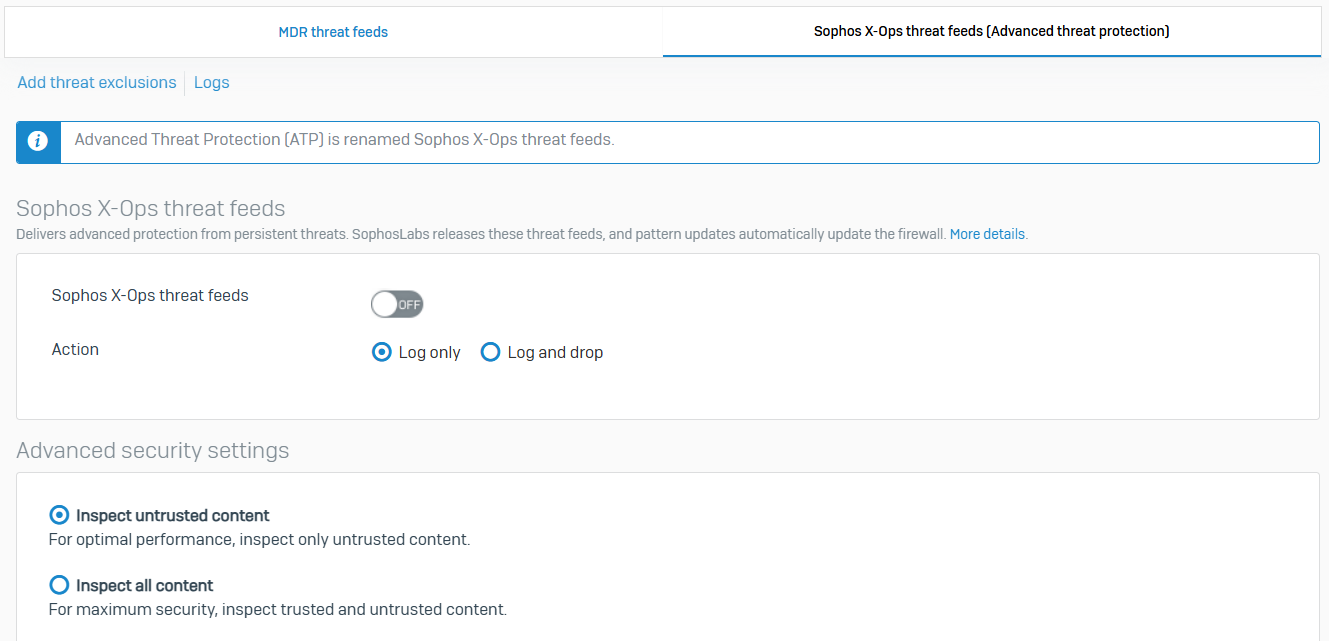
Sophos X-Ops Threat Feeds (Advanced Threat Protection)
- Reference - Sophos X-Ops Threat Feeds
- Sophos X-Ops threat feeds is a SophosLabs-managed global threat database that's regularly updated and pushed to the firewall. The firewall blocks all requests and traffic matching this database of malicious IP addresses, domains, or URLs
- Sophos X-Ops threat feeds are turned off by default
Monitor & Analyze Section
Overview
- The Monitor & Analyze section in the Sophos Firewall control center is where administrators can access detailed information about the firewall's activity, performance, and security events
- This section provides tools to monitor the system in real-time and analyze logs, traffic patterns, and threat data

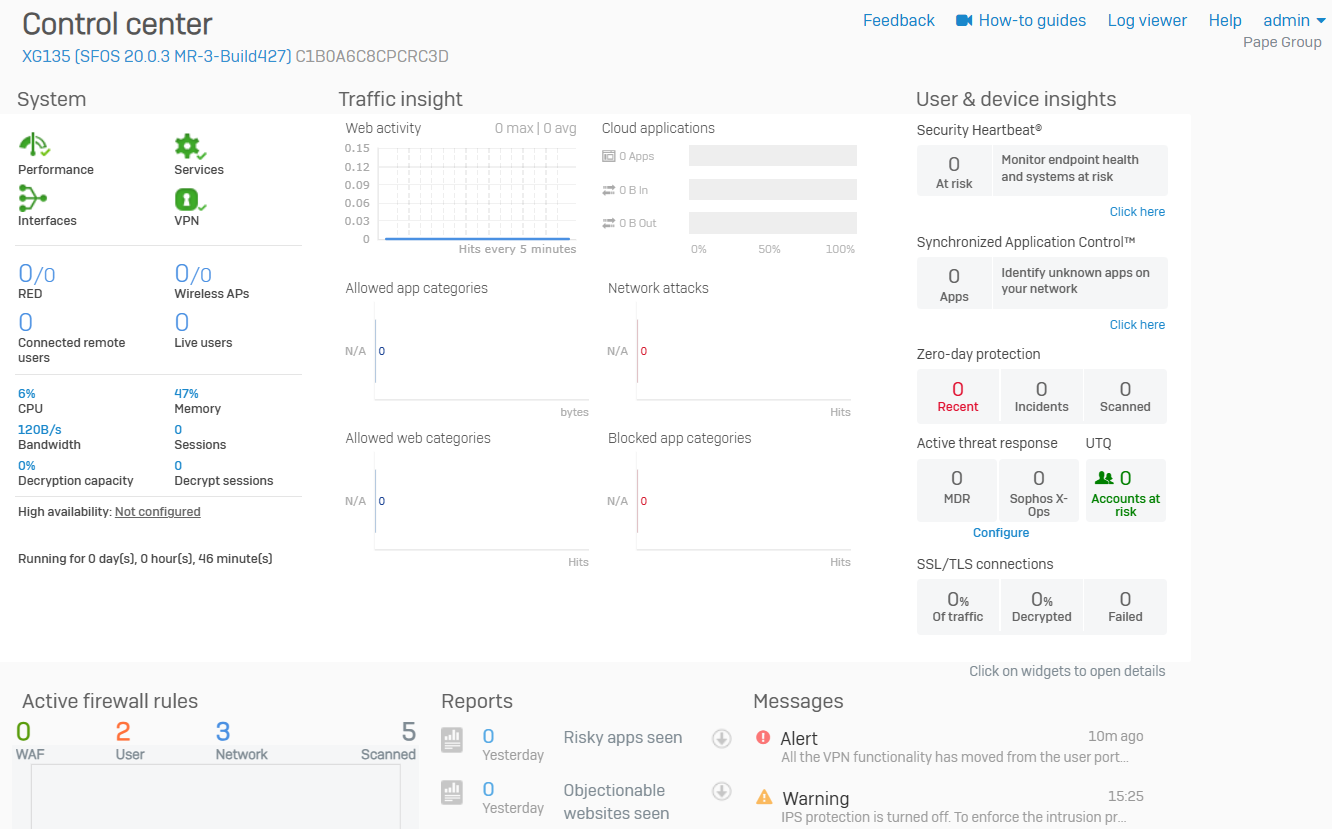
Control Center
Overview
- The control center shows the firewall's appliance model, firmware version, build, and serial number
- It also provides a snapshot of the security system's status and health
- The control center appears as soon as you sign in
Control Center
Current Activities
Overview
- This page keeps track of currently signed-in local and remote users, current IPv4, IPv6, IPsec, SSL, and wireless connections
Live Users
- Reference - Live Users
- Live users are users who are currently signed in to the firewall
- To disconnect users, select them, and click Disconnect. You can change the notification text. Click Disconnect again
Live Connections
- Reference - Live Connections
- You can see the connection details of IPv4 and IPv6 traffic for applications, usernames, and source IP addresses
- You can see the data transfer, bandwidth consumed, number of connections, and other traffic details
- The live connection details shown are from the time a connection was established. For example, upload transfer is for total data uploaded from the time the connection was established
IPsec Connections
- Reference - IPsec Connections
- You can see a list of the established IPsec connections. You can filter the list based on connection name, server name, local subnet, username, remote server/host, or remote subnet
Remote Users
- Reference - Remote Users
- To see the signed-in remote users, go to 'Current activities > Remote users'
- You can filter the connections based on the connection date, username, source IP address, and leased IP address
Reports
Overview
- Reports help you analyze traffic and threats and in regulatory compliance
- For example, you can view a report that includes all web server protection activities taken by the firewall, such as blocked web server requests and identified viruses
- Use reports to identify threats, manage usage, and increase security
Dashboards
- Reference - Dashboards
- View information about network traffic passing through the firewall and security threats
- Traffic Dashboard
- Categories of network traffic, for example, applications, web categories, and users
- Security Dashboard
- Denied network activities and traffic. Also provides information about malware, spam, and top source and destination countries
- Executive Report
- Frequently viewed information about the firewall, for example, network traffic and threats
- User Threat Quotient
- Ranking of users by threat score
Application & Web
- Reference - Application & Web
- View information about application and internet usage on your network
- The firewall calculates scores based on the risk level and number of hits of individual applications. The application risk meter is based on the average score of all application traffic
- When the meter is closer to the red mark, the network traffic includes more high-risk applications, indicating a high risk of compromise. When the meter is closer to the green mark, the network traffic includes more low-risk applications, indicating a low risk of compromise
Network & Threats
- Reference - Network & Threats
- View information about network usage and associated threats
- Intrusion Attacks
- Attack attempts
- Active Threat Response
- Threat events and compromised network hosts based on MDR threat feeds and Sophos X-Ops threat feeds
- Wireless
- Access point usage and configured SSIDs
- Security Heartbeat
- Health of endpoints in your network based on communications between an endpoint and the firewall
- Zero-day Protection
- Enhanced protection against advanced and targeted attacks
VPN
- Reference - VPN
- View information about remote users connecting to your network using IPsec VPN, SSL VPN, and clientless access
- VPN
- Traffic generated by remote users connecting through IPsec, L2TP, or PPTP connections
- SSL VPN
- Traffic generated by remote users connecting through an SSL VPN client
- Clientless Access
- Traffic generated by remote users connecting through a web browser
- Reference - Email
- View information about email traffic on your network
- Email Usage
- Email traffic on your network
- Email Protection
- Virus and spam infected email traffic on your network
Compliance
- Reference - Compliance
- View information about regulatory compliance
- Compliance Standards
- HIPAA
- GLBA
- SOX
- FISMA
- PCI
- NERC CIP v3
- CIPA
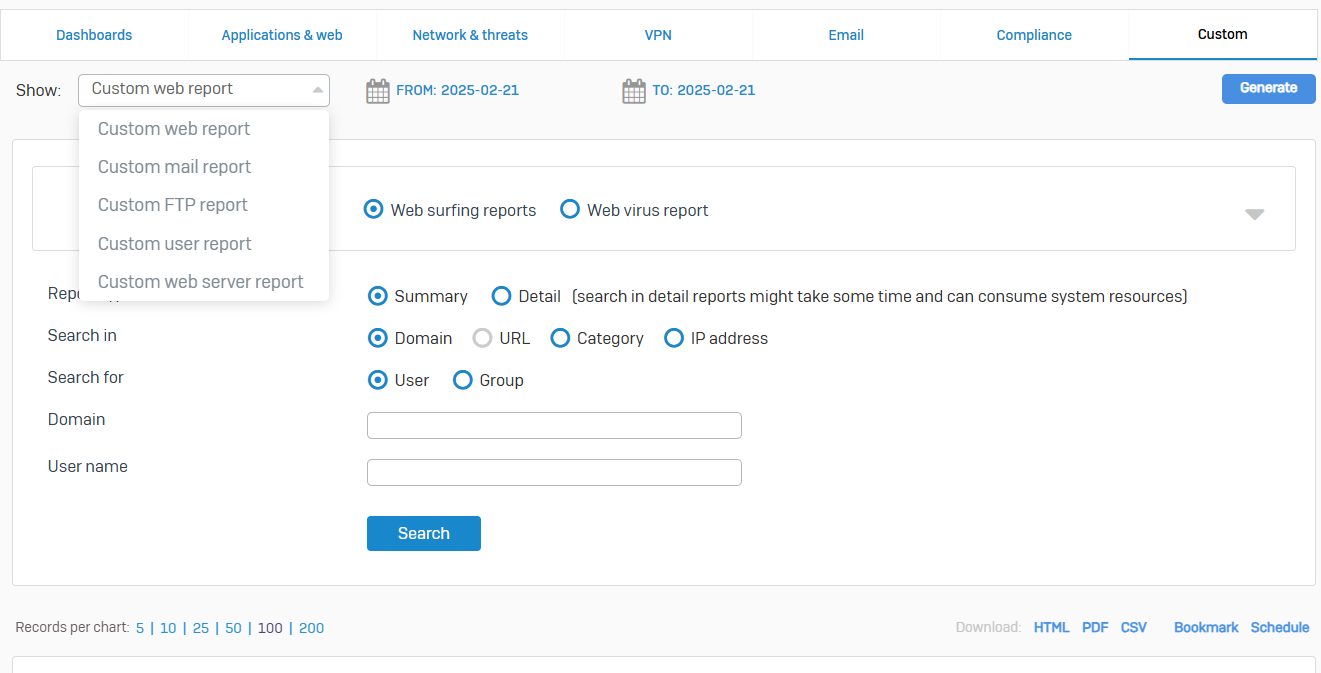
Custom
- Reference - Custom
- Create reports that include only the criteria that you specify
- You can create the following custom reports
- Web report
- Mail report
- FTP report
- User report
- Web server report
Zero-Day Protection
Overview
- Zero-day protection is powered by SophosLabs Intelix, a cloud service that combines machine learning, sandboxing, and research to detect known and unknown threats by analyzing suspicious downloads and email attachments
- Sophos Firewall sends new files to SophosLabs Intelix for zero-day protection analysis when they enter your network
- Intelix uses layers of analytics to determine the level of risk posed to your network by each file
- In addition to blocking risky files, zero-day protection also provides detailed reports of the analysis performed to help you understand the risk
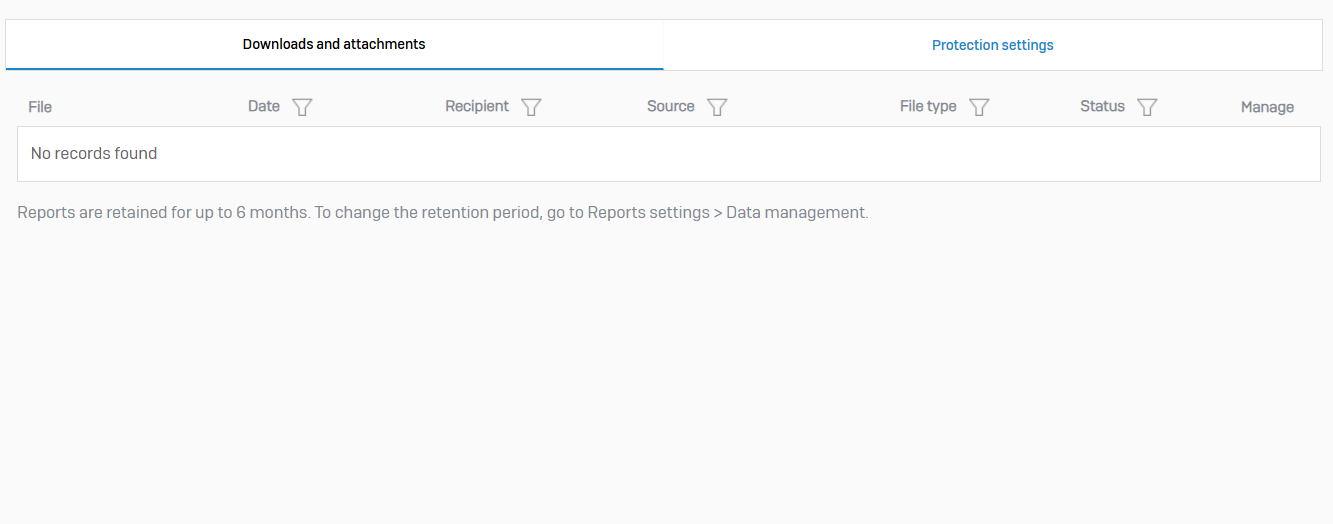
Downloads & Attachments
- Reference - Downloads & Attachments
- The activity records provide basic information such as the date and time on which files or emails containing suspicious attachments were sent to Zero-day protection
- You can also view the analysis, release status, report details, and release files or emails
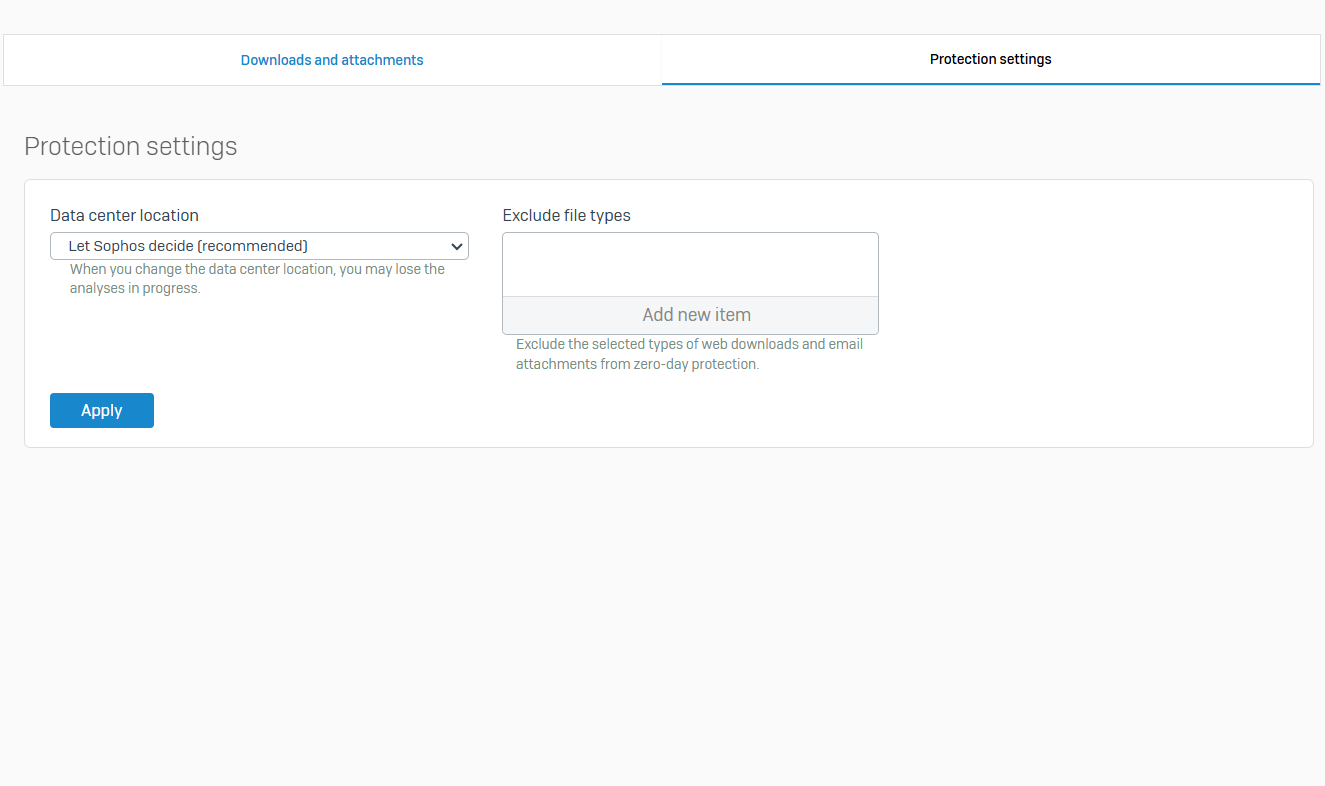
Protection Settings
- Reference - Protection Settings
- Use these settings to specify a datacenter and to exclude files from the zero-day protection analysis
- Zero-day Protection Datacenter Location
- Files to be analyzed are sent to a Zero-day protection datacenter in the cloud over a secure SSL connection. By default, Sophos firewall selects the closest datacenter. However, you can select a datacenter of your choice
- Exclude File Types
- Exclude the selected types of email attachments and web downloads from Zero-day protection analysis. The file type is determined by the file extension and MIME header
Diagnostics
Overview
- You can check the health of your Sophos Firewall
- You can use this information to troubleshoot and diagnose issues
Tools
- Reference - Tools
- You can diagnose connectivity, packet loss, and network issues, and test network communication
- With the Policy tester, you can test firewall rules, SSL/TLS inspection rules, and web policies to see the action that Sophos Firewall would take for traffic matching these criteria
- The Log viewer shows the event logs. It is automatically updated with new events
- You can run ping and traceroute checks from the web admin console. You can also run name and route lookups
- From this page, you can download individual log files or generate a Consolidated troubleshooting report (CTR)
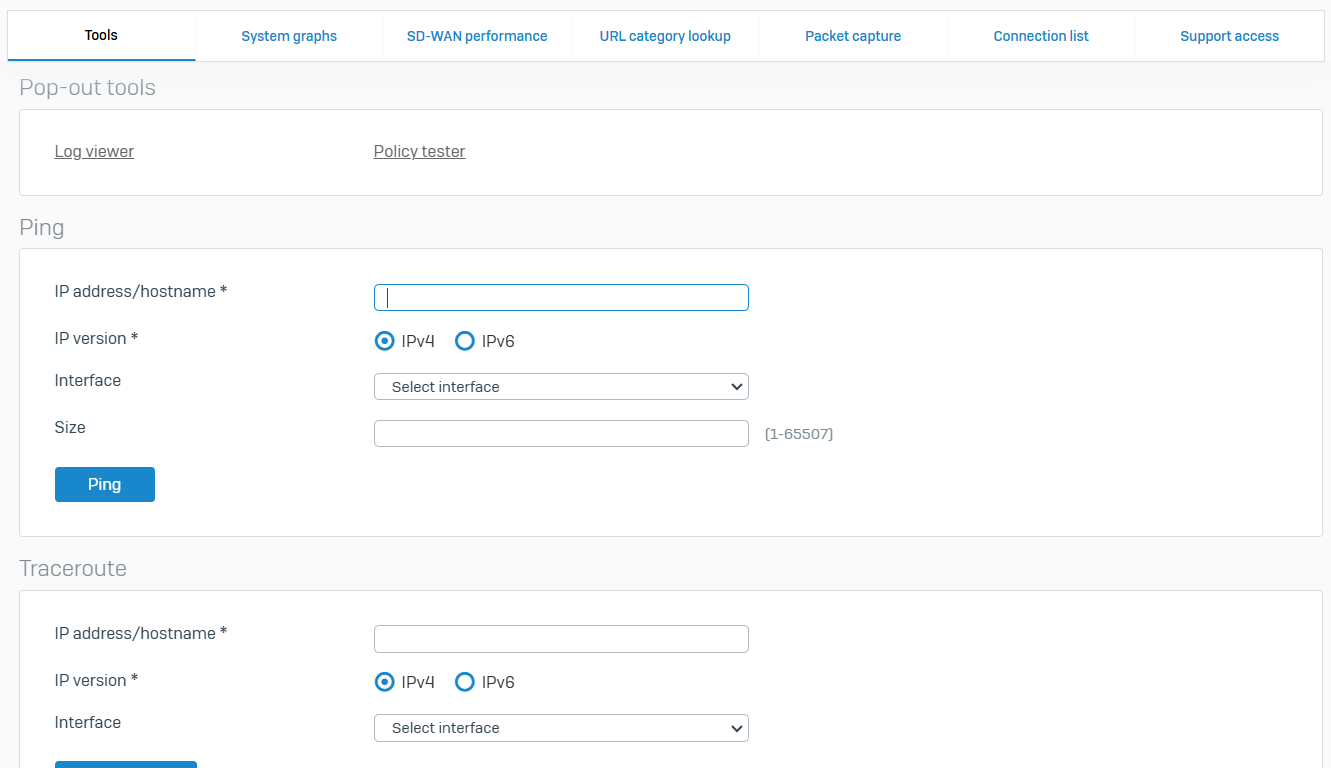
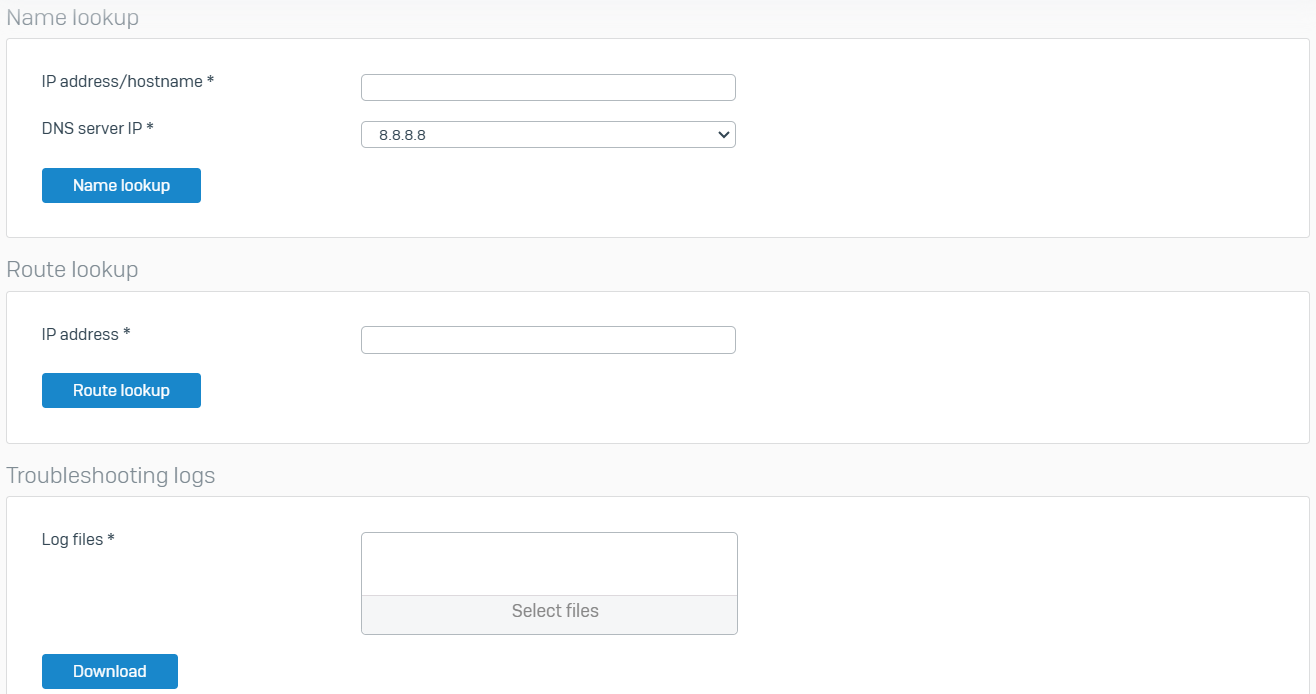
System Graphs
- Reference - System Graphs
- You can see graphs showing user-related activities for different time periods
- You can filter the graphs you want to see by time period and graph type
- Graph Types
- CPU usage graphs
- Memory usage graphs
- Load average graphs
- Disk usage graphs
- Live users graphs
- Data transfer speed through WAN zone graphs
- Interface graphs
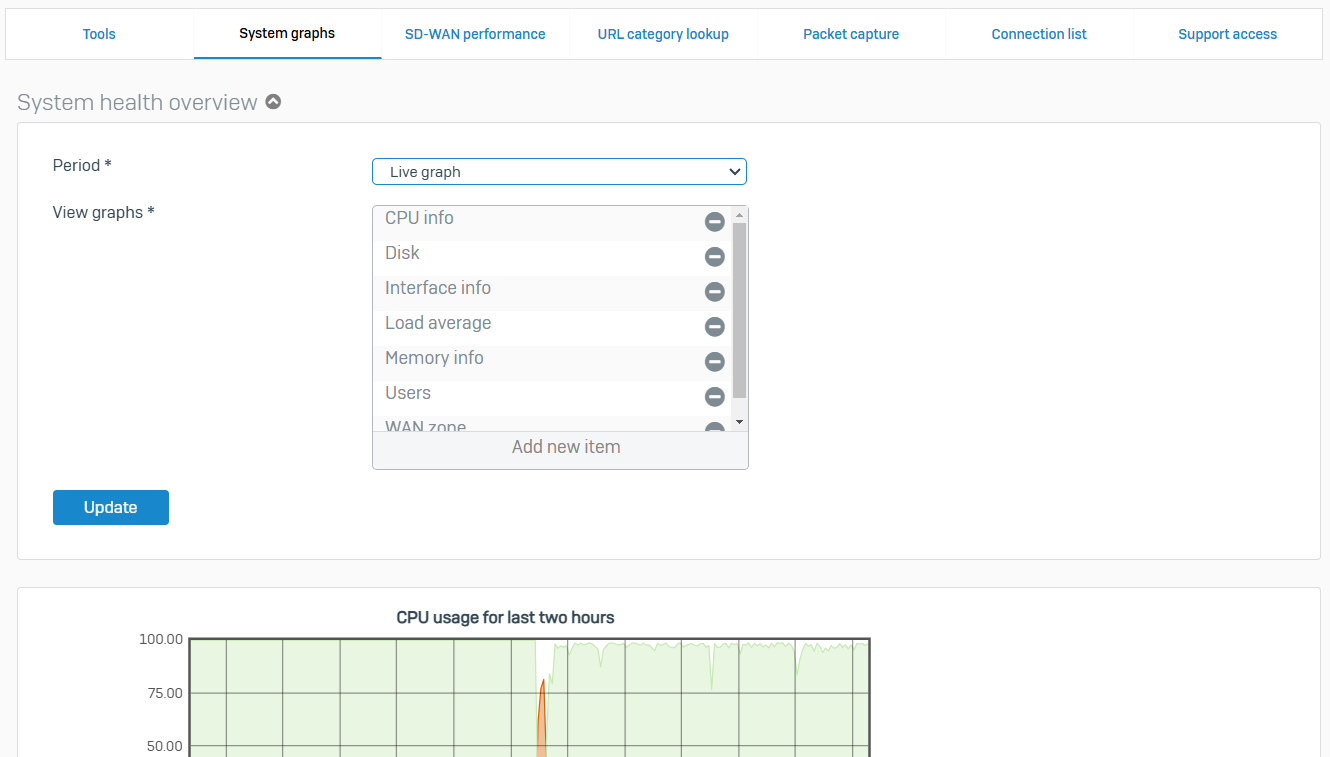
SD-WAN Performance
- Reference - SD-WAN Performance
- You can see graphs showing the real-time performance of the gateways in your SD-WAN network
- You can see graphs showing each gateway's total connections and the amount of data transferred
- You can see graphs for latency, jitter, and packet loss for each gateway in the SD-WAN profile. You can filter the graphs by time (Live, 24h, 48h, Week, or Month)
URL Category Lookup
- Reference - URL Category Lookup
- Use URL category lookup to search whether the URL is categorized
- It searches the specified URL and show the category name and description
- To use this feature, you need a Web Protection subscription
- If the URL is categorized under both a custom category and a default category, the name of the custom category is shown in the search result
Packet Capture
- Reference - Packet Capture
- Packet capture shows the details of the packets that pass through an interface. You can see the connection details and details of the packets processed by each module, such as firewall and IPS
- Packet capture also shows the firewall rule number, user, web, and application filter policy number. This information can help you troubleshoot instances where firewall rules fail
- You can perform the following:
- Configure filter settings for capturing the packets
- View the packet information
- Specify the filter conditions for the packets
- Start and stop packet capturing
- Refresh the details of the captured packets
- Clear the details of the captured packets
Connection List
- Reference - Connection List
- The connection list provides a current or live connection snapshot of your device. It shows the connection information. You can filter the connection list
- You can set the refresh interval to automatically refresh the list at the configured time interval. To manually refresh the list, click 'Refresh'. To filter the connection list, click 'Display filter' and specify the parameters
Support Access
- Reference - Support Access
- You can allow Sophos Support to temporarily access your firewall for troubleshooting purposes
- Support access enables Sophos Support to connect to the web admin console of your firewall without requiring admin credentials
- When you turn Support access on, Sophos Support can access the web admin console and shell of your firewall. The firewall initiates all connections with Sophos Support over TCP port 22 for both HTTPS and SSH. It closes idle SSH sessions after 15 minutes
- You can turn off Support access at any time